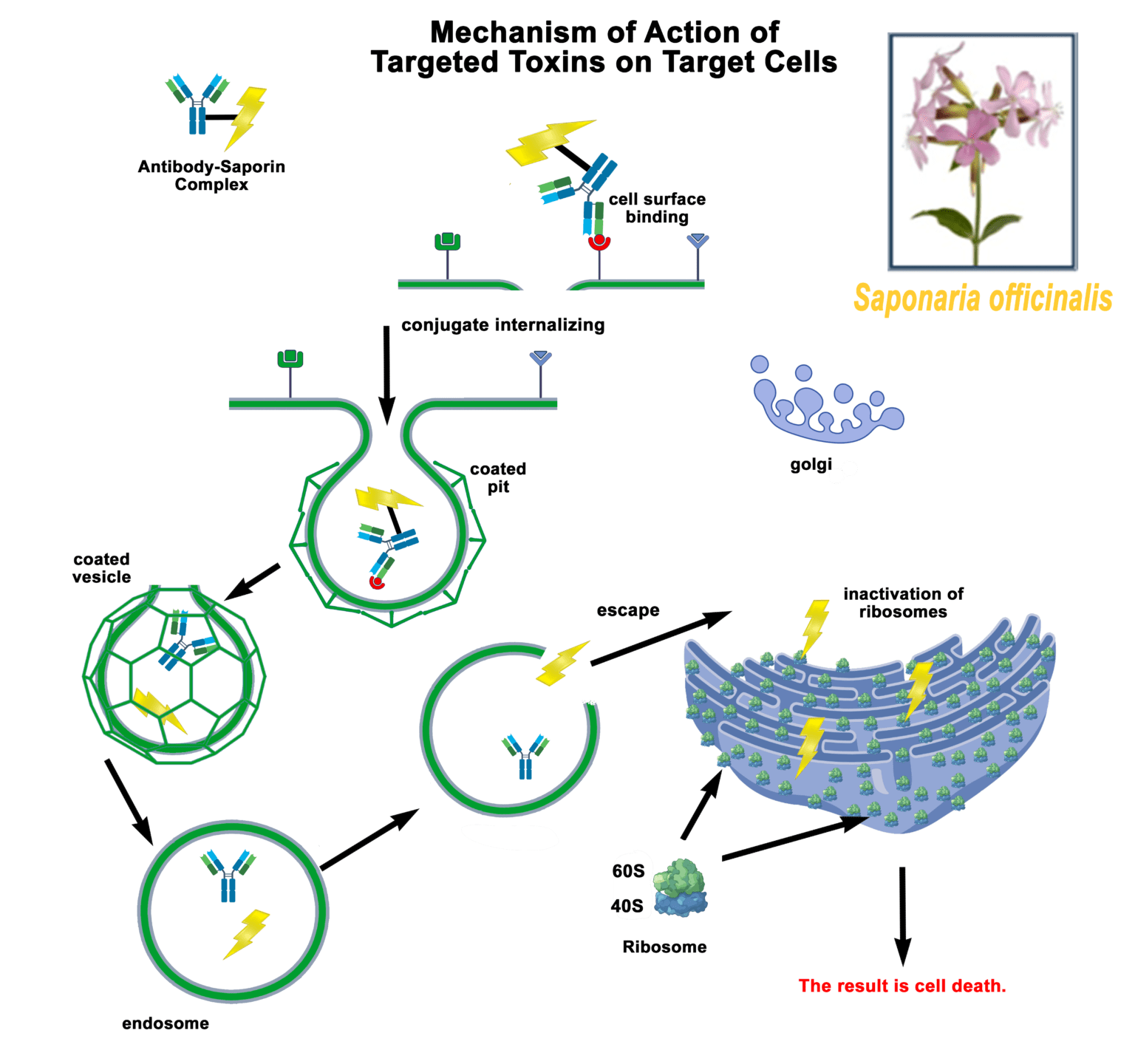
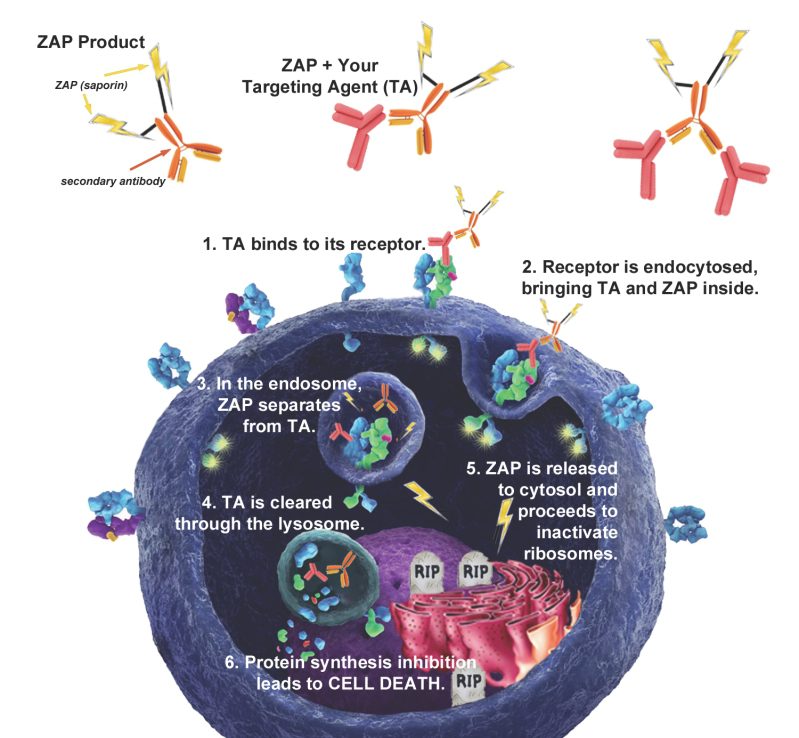
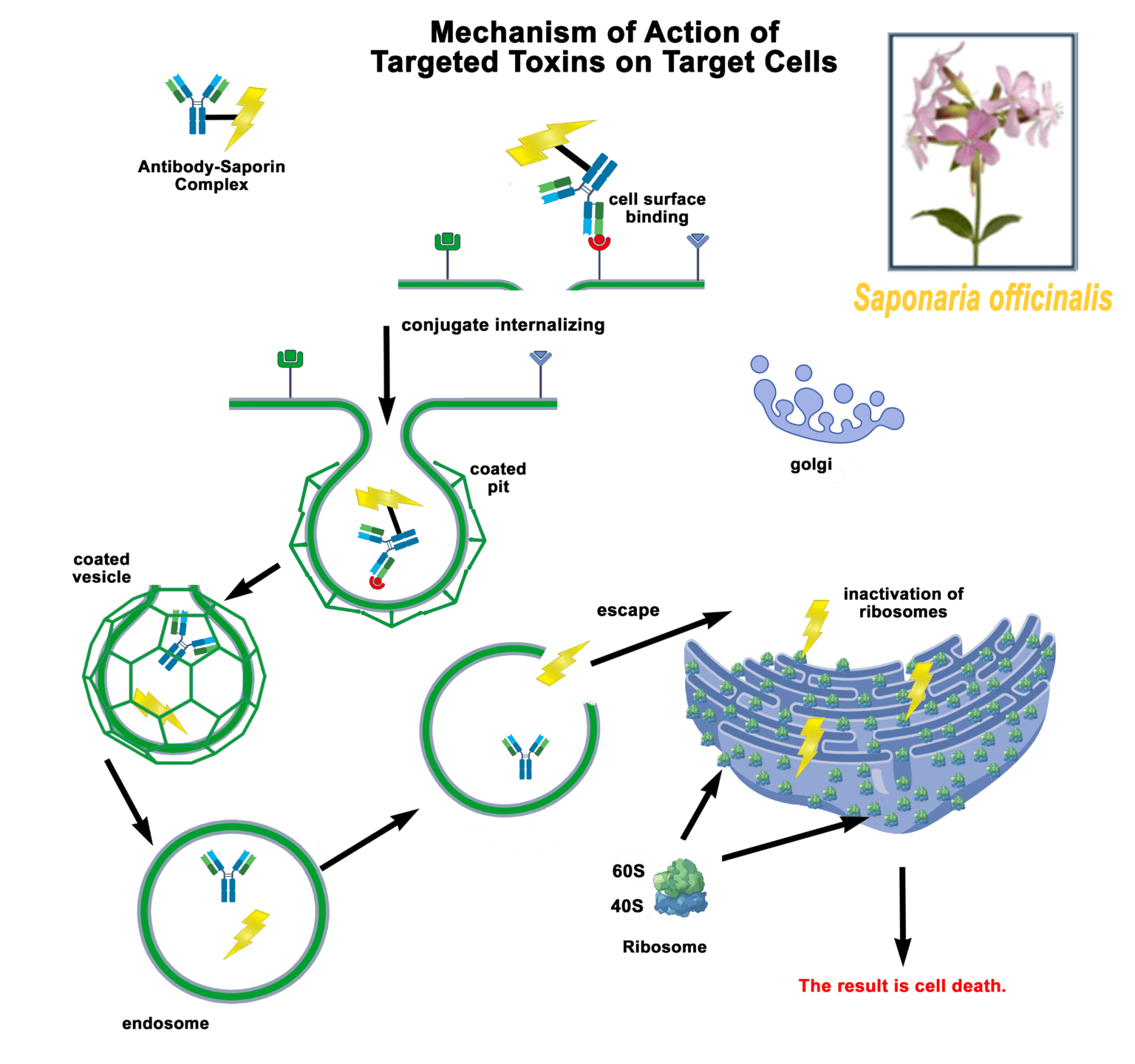
Streptavidin-pHast [PH-03]
100 mcg, 250 mcg, 1000 mcg
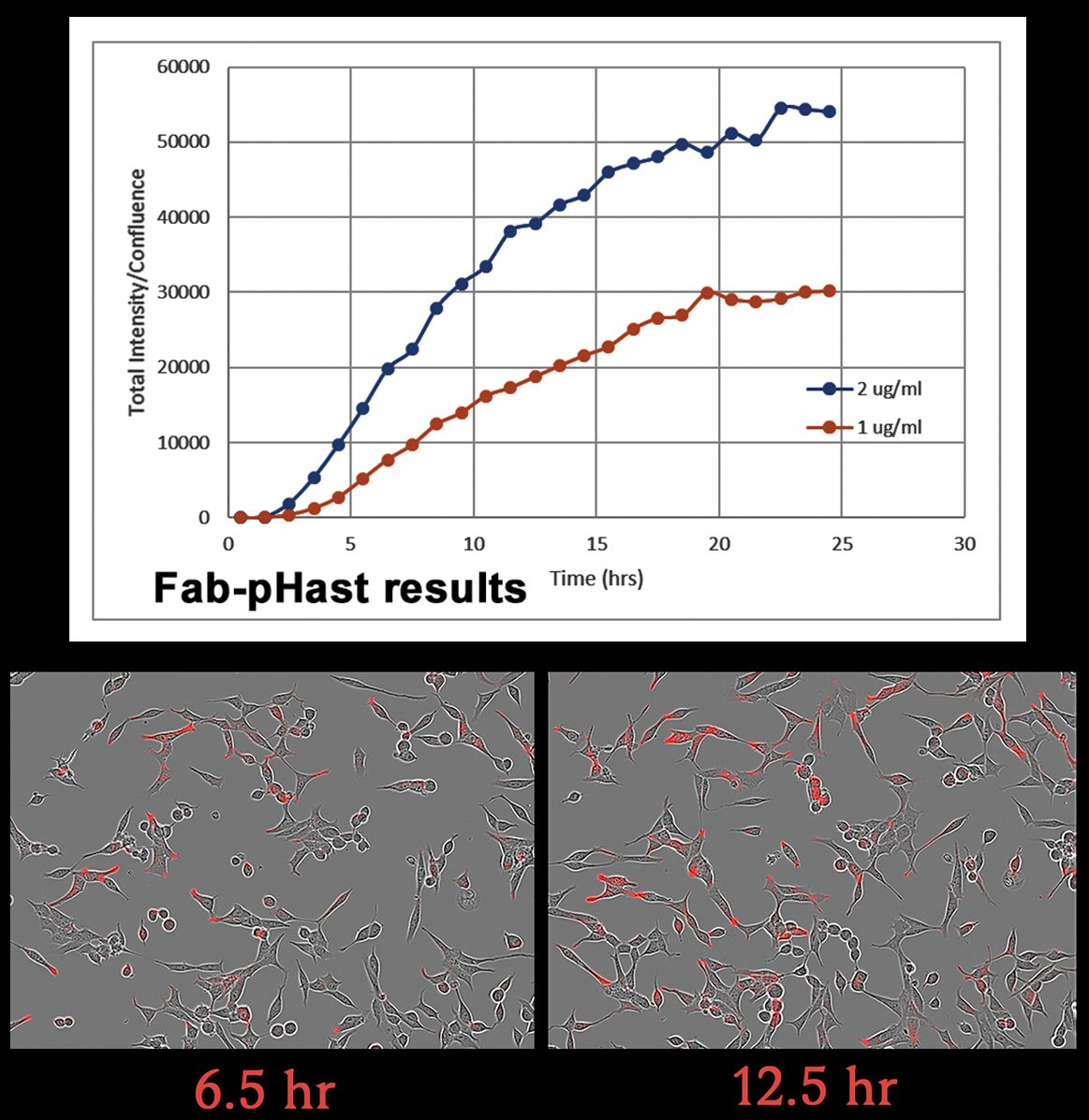
a tool to test biotinylated protein specificity, binding, and internalization with results in one (1) day
Streptavidin-pHast in conjunction with your biotinylated protein can be analyzed via fluorescent microscope, fluorescent plate reader, or flow cytometry. In order to establish the EC50 of your antibody a fluorescent plate reader is recommended.
A sample protocol for determining internalization via Fluorescent Plate reader
Streptavidin-pHast Internalization Protocol
1. Determine the number of cells needed for the planned number of plates. Cells are plated in the center 60 wells in 90 μl of media per well.
2. Plate cells in a 96-well black, clear bottom plate or all black plate. The clear bottom plate allows visualization of antibody internalization using a microscope. Cells are usually plated at 20,000 cells per well.
3. Transfer 100 μl of media into the wells around the edge of a 96-well plate. These wells simply offer some protection from evaporation for the experimental wells.
4. Incubate plates for 20-24 hours before treatment.
5. Mix an equimolar amount of Streptavidin-pHast to your biotinylated protein. Incubate at room temperature for 20 minutes. Optimization of concentration and dilutions will need to be established. High concentrations of unconjugated antibody may act as an inhibiter of fluorescent activity.
6. Serial dilute your desired concentrations of Streptavidin-pHast-Biotinylated-Protein in microcentrifuge tubes, 10X the desired concentration planned for the plate.
7. The first and last experimental columns (2 and 11 in most plates) of cells are controls, only medium or Streptavidin-pHast alone is added to these wells.
8. Add 10 μl of your 10X concentrations of Streptavidin-pHast-Biotinylated-Protein to each of your plates.
9. Mix the plate gently on a plate mixer for 1-2 min, then incubate overnight to allow internalization. (Internalization can start to be detected in 1 hour, but maximal fluorescence occurs typically 19 hours after addition of the Streptavidin-pHast conjugated proteins).
10. To achieve a higher sensitivity, replace media with PBS before reading the plate.
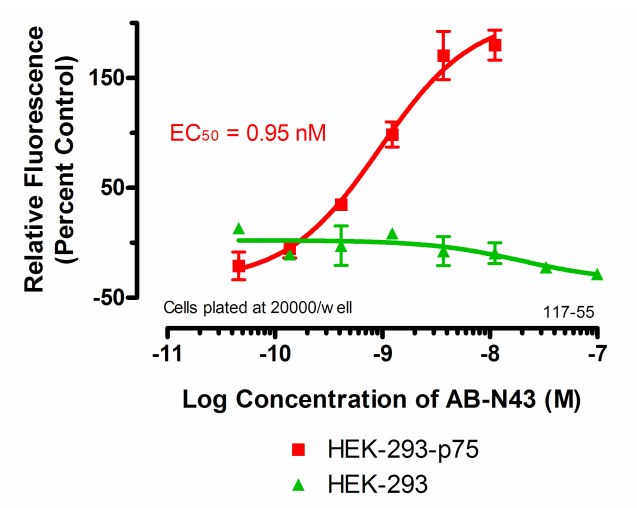
11. Read the plate in a fluorescent plate reader at Ex: 532 nm/Em: 560 nm.
12. The absorbance of the sample wells is compared to the control wells to establish a curve.
13. The EC50 of your antibody can be derived from the curve, using PRISM software
(GraphPad, San Diego).