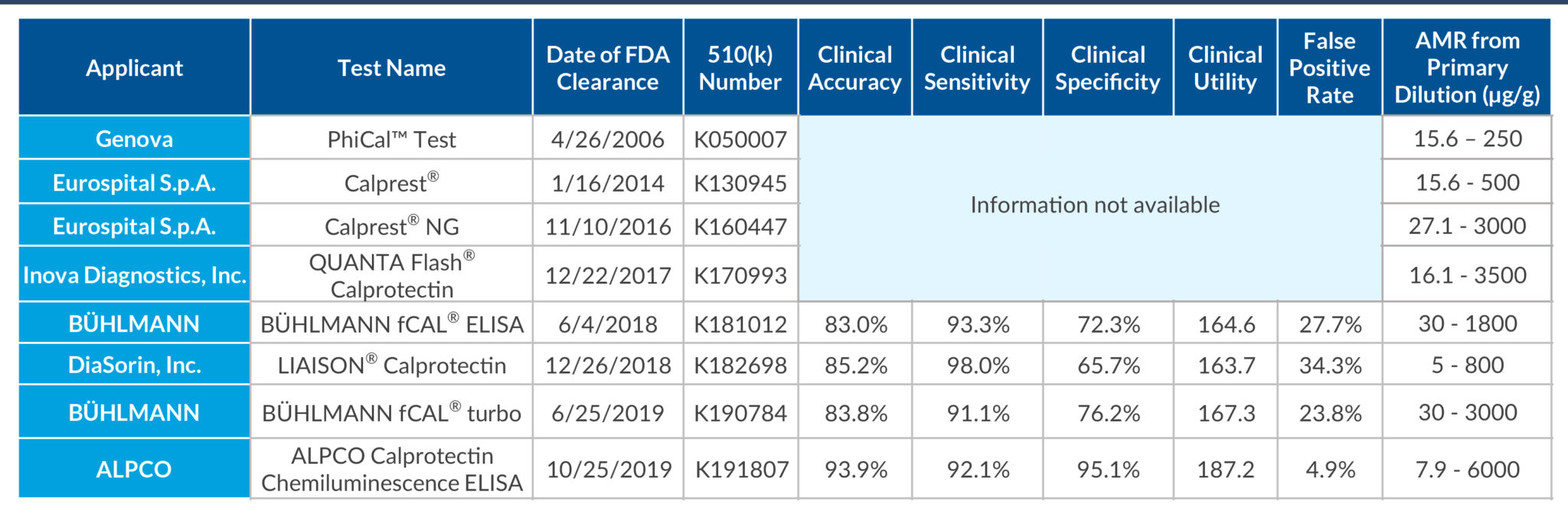
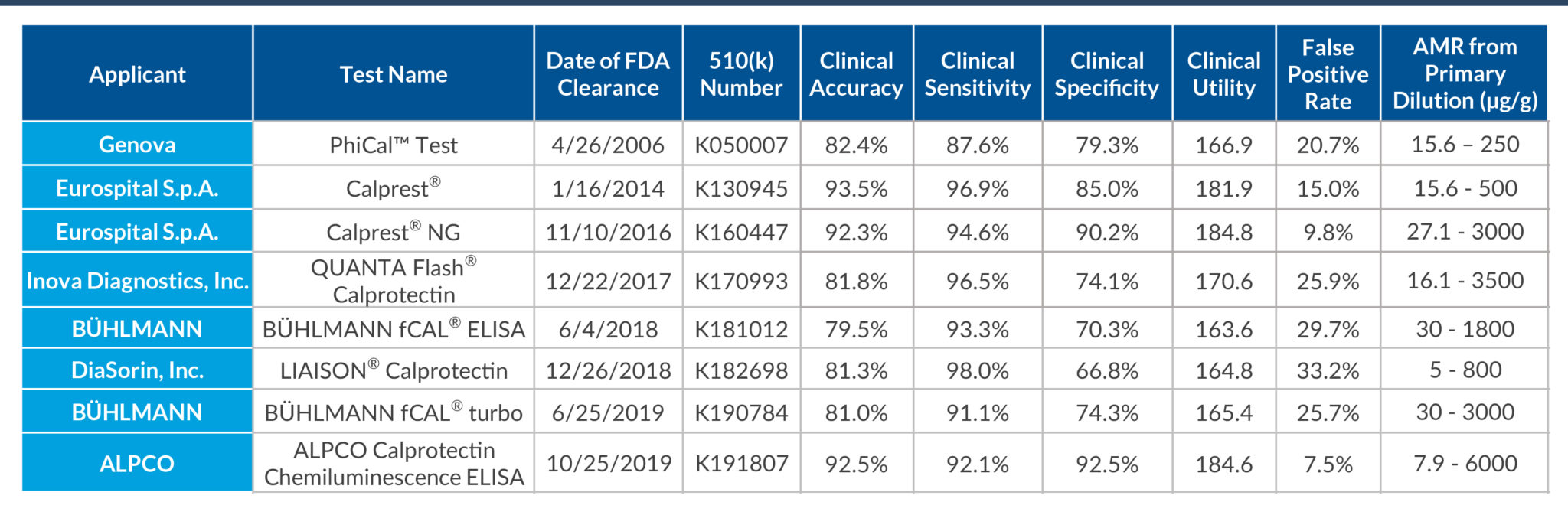
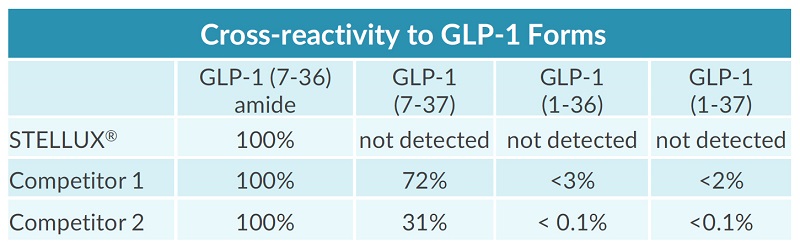
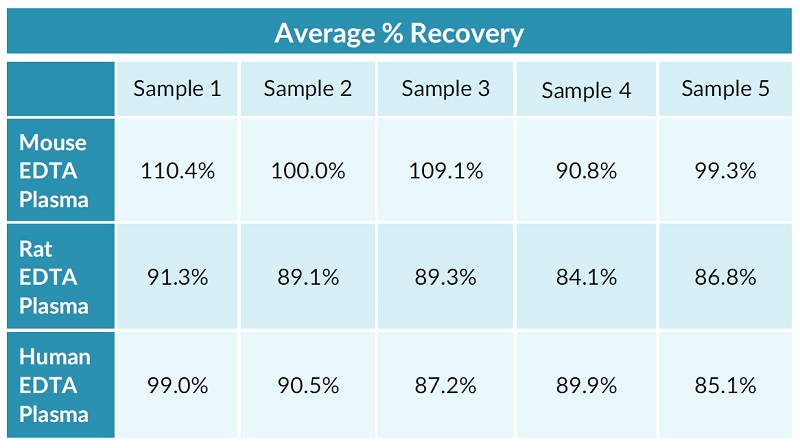
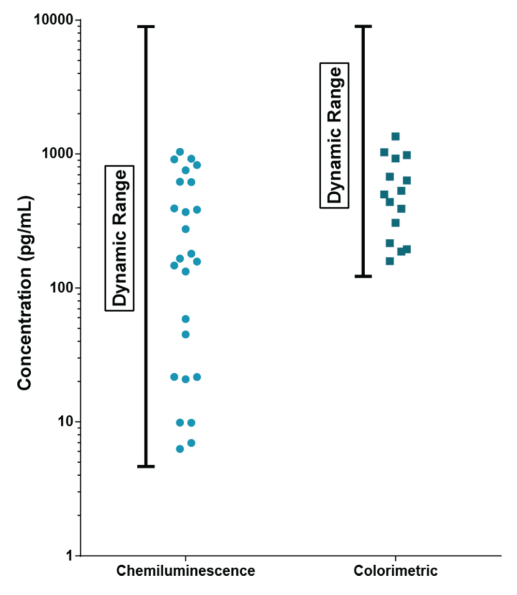
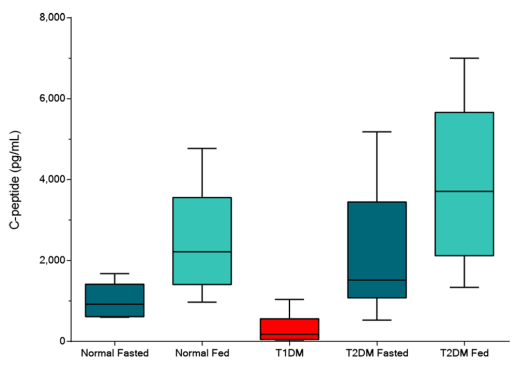
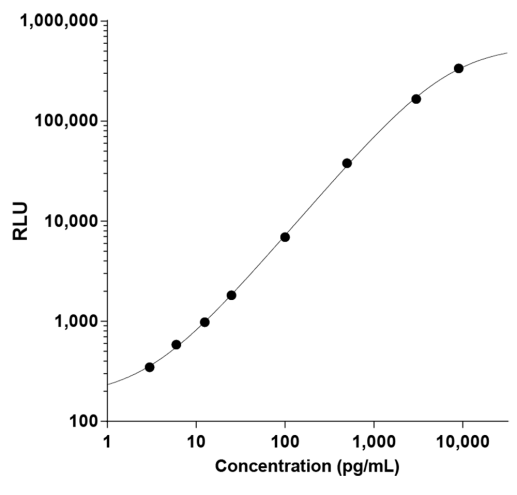
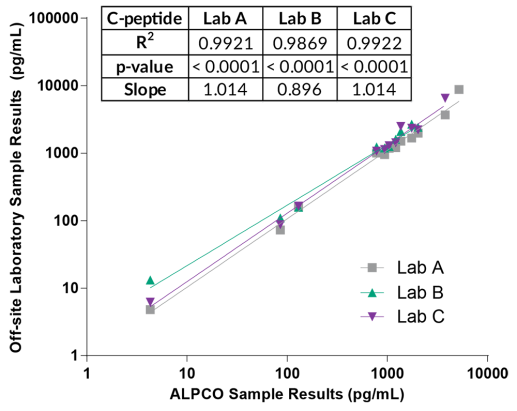
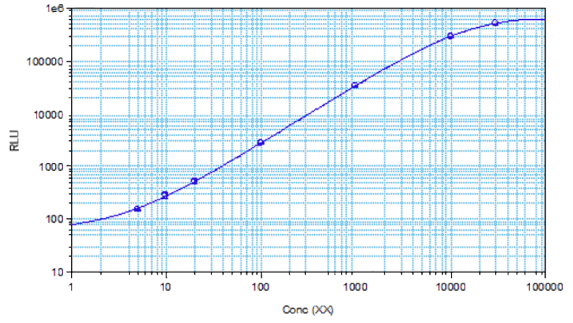
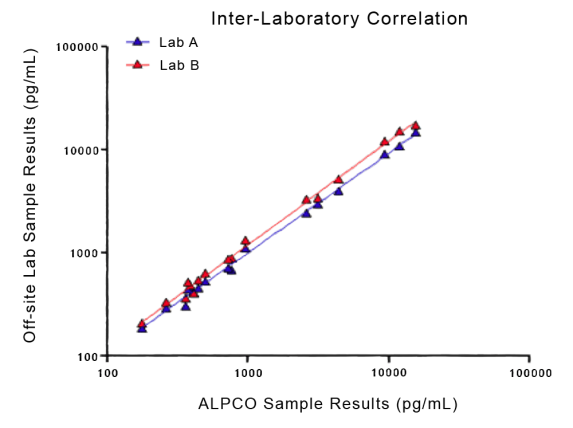
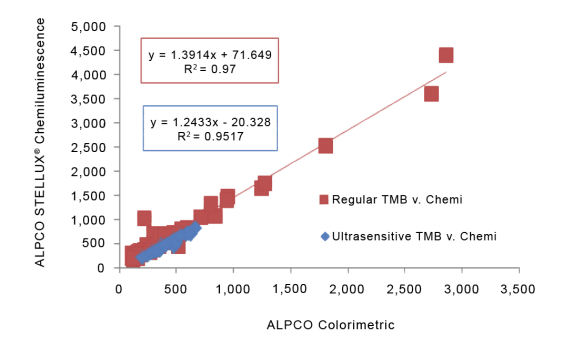
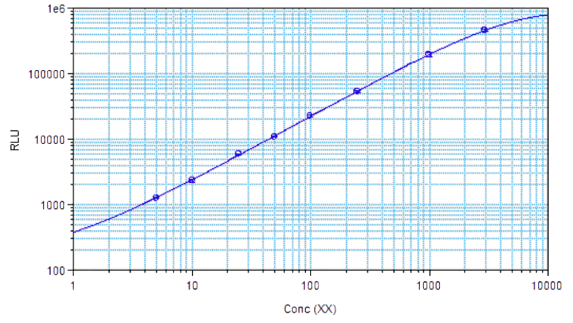
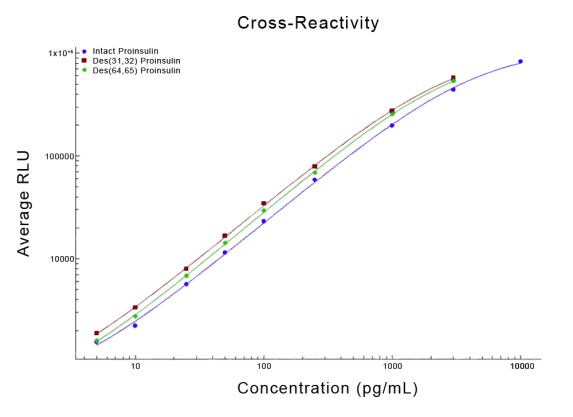
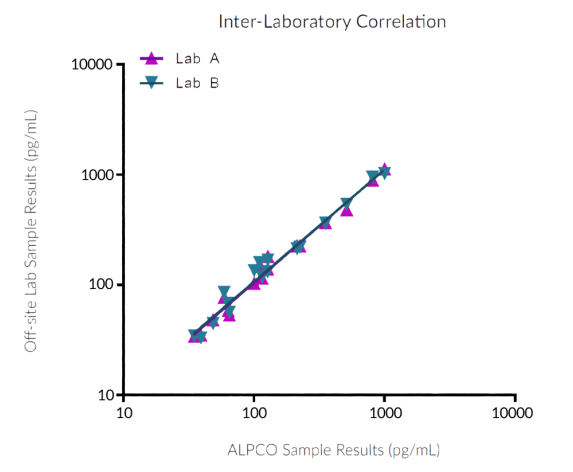
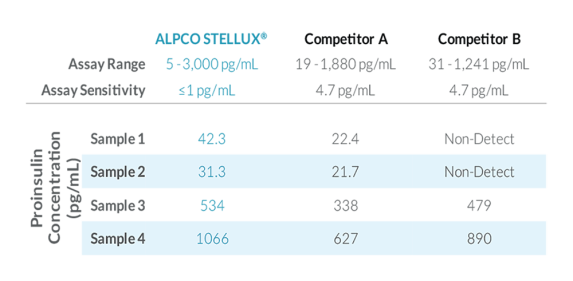
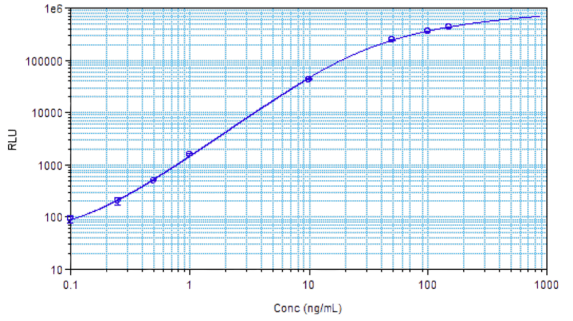
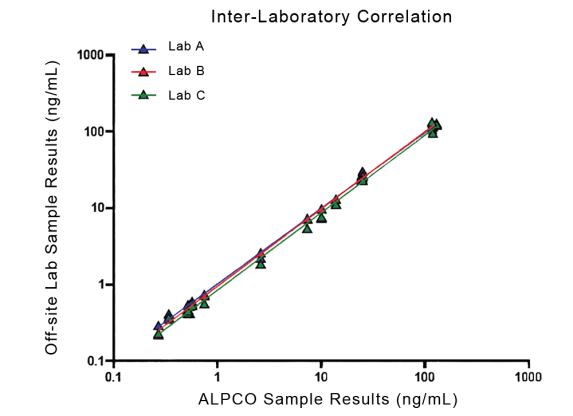
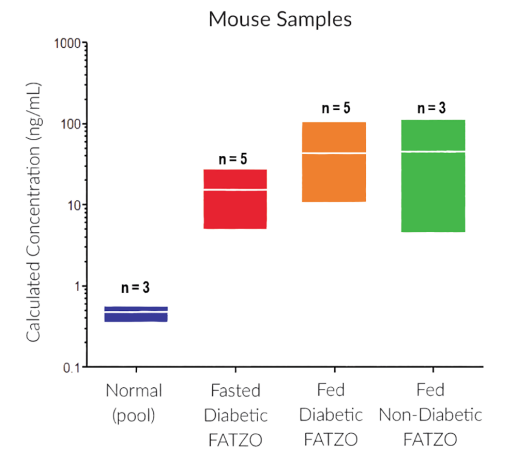
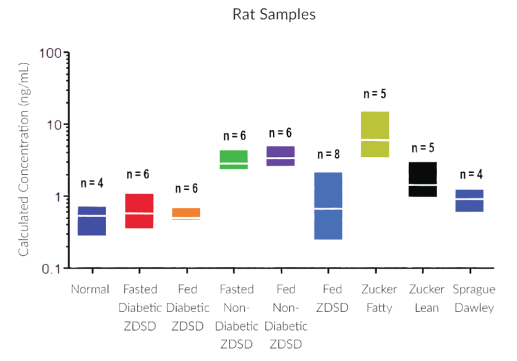
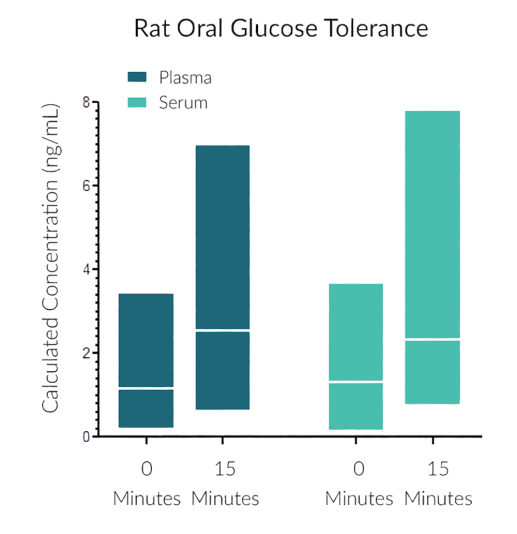
STELLUX® is our chemiluminescence ELISA platform aimed at detecting key biomarkers in life science research.
We provide a variety of testing solutions to further study the endocrine system, including its complex array of hormones and associated disorders.