| Name |
Catalog Number |
Formulation |
GenBank ID |
Specificity |
| 14-3-3 alpha/beta siRNA Set I |
Y71-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_003404 |
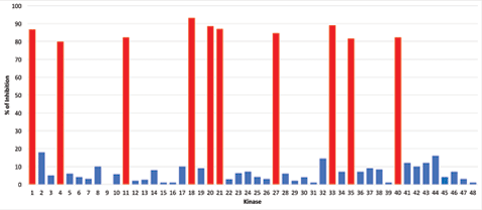
14-3-3 alpha/beta siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human 14-3-3 alpha/beta expression. |
| 14-3-3 epsilon siRNA Set I |
Y75-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_006761 |
14-3-3 epsilon siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human 14-3-3 epsilon expression. |
| 14-3-3 sigma siRNA Set I |
Y86-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_006142 |
14-3-3 sigma siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human 14-3-3 sigma expression. |
| 14-3-3 theta siRNA Set I |
Y84-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_006826 |
14-3-3 theta siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human 14-3-3 theta expression. |
| 14-3-3 zeta siRNA Set I |
Y92-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_003406 |
14-3-3 zeta siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human 14-3-3 zeta expression. |
| 4EBP1 siRNA Set I |
E35-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_004095 |
4EBP1 siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human 4EBP1 expression. |
| AATK siRNA Set I |
A02-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_007377 |
AATK siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human AATK expression. |
| ABL1 siRNA Set I |
A03-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_009594 |
ABL1 siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ABL1 expression. |
| ABL2 siRNA Set I |
A04-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_005158 |
ABL2 siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ABL2 expression. |
| ACK siRNA Set I |
A05-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_005781 |
ACK siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ACK expression. |
| ACVR2A siRNA Set I |
A35-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_001616 |
ACVR2A siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ACVR2A expression. |
| ACVR2B siRNA Set I |
A36-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_001106 |
ACVR2B siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ACVR2B expression. |
| ADD1 siRNA Set I |
A38-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_001119 |
ADD1 siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ADD1 expression. |
| AFX siRNA Set I |
A42-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_001170931 |
AFX siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human AFX expression. |
| AKT1/PKB alpha siRNA Set I |
A16-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_005163 |
AKT1/PKB alpha siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human AKT1/PKB alpha expression. |
| AKT2/PKB beta siRNA Set I |
A17-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_001626 |
AKT2/PKB beta siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human AKT2/PKB beta expression. |
| AKT3 siRNA Set I |
A18-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_005465 |
AKT3 siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human AKT3 expression. |
| ALK1 siRNA Set I |
A09-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_000020 |
ALK1 siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ALK1 expression. |
| ALK2 siRNA Set I |
A06-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_001105 |
ALK2 siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ALK2 expression. |
| ALK3 (BMPR1A) siRNA Set I |
B04-911 |
The siRNAs are supplied as a lyophilized powder and shipped at room temperature. |
NM_004329 |
ALK3 (BMPR1A) siRNAs are designed to specifically knock-down human ALK3 (BMPR1A) expression. |