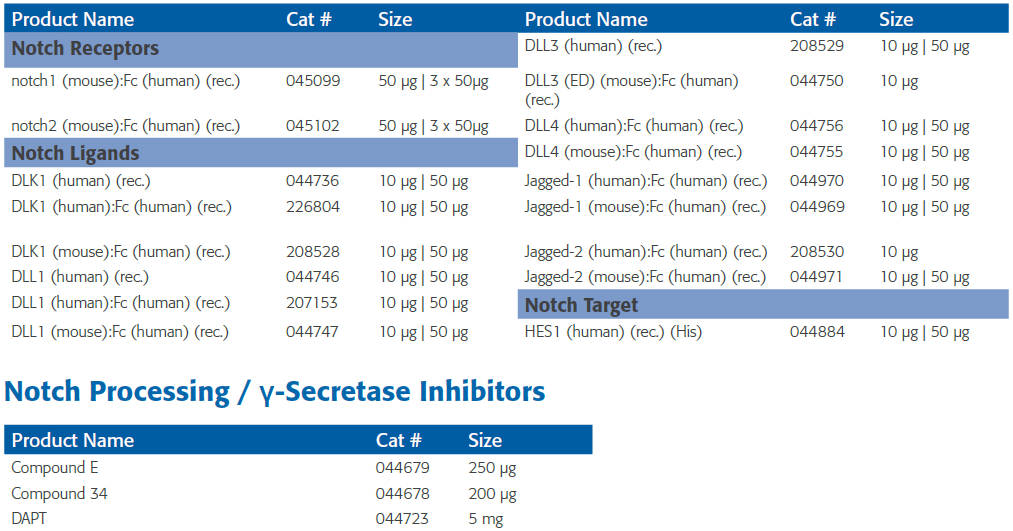
Biologically Active Notch Proteins
Selected Reviews
- Notch signaling in the central nervous system with special reference to its expression in microglia: L. Yao, et al.; CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 12, 807 (2013)
- Notching up neural stem cell homogeneity in homeostasis and disease: C. Giachino & V. Taylor; Front.Neurosci. 8, 32 (2014)