New Old Drug Identified as Candidate for Amoebic Dysentery Treatment
An inexpensive arthritis drug called auranofin has been shown in lab and animal tests to kill the parasites that cause amoebic dysentery and giardiasis1, 2. The gold-containing drug,
marketed under the trade name Ridaura, has already been demonstrated to be safe in humans, is much more powerful than existing treatments. Human trials are expected to start soon for this new application.
 |
|
|
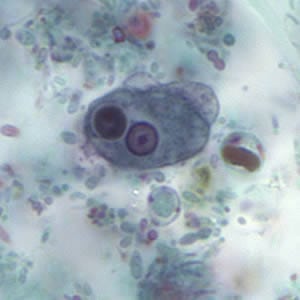
Amoebic dysentery, caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica, which is passed through contaminated food or water, strikes an estimated 50 million people around the world each year. It kills 70,000 people annually, most of them children in developing countries. The similar parasite, giardia, strikes 6% to 8% of children in developing countries, causing diarrhea, abdominal cramps and dehydration. The current treatment for both is the antibiotic metronidazole, which has side effects that include nausea, vomiting, dizziness and headache3.
To facilitate drug screening for this anaerobic protozoan, the authors developed an anaerobic screening process to test potential drugs against the parasite. The researchers utilized a large screening library of 900 compounds, all of them approved by the Food and Drug Administration for human use. This screen identified auranofin, as active against E. histolytica in culture. Araunofin was further tested in a mouse model of amebic colitis and a hamster model of amebic liver abscess. In these tests oral auranofin markedly decreased the number of parasites, the detrimental host inflammatory response, and hepatic damage. Additional studies were carried out to determine the focus of auranofin’s action. Transcriptional profiling and thioredoxin reductase assays suggested that auranofin targets the E. histolytica thioredoxin reductase, thus preventing the reduction of thioredoxin and enhancing the sensitivity of trophozoites to reactive oxygen-mediated killing1, 2.
References
- Debnath, A. et al., Nature Medicine (2012) doi:10.1038/nm.2758
- Bole, K. UCSF news release; https://www.ucsf.edu/news/2012/05/12041/lab-tests-show-arthritis-drug-effective-against-global-parasite
- Dans, L.F. and Martinez, E.G. Clin Evid (Online). 2007; 2007: 0918.
Selected Amoebic Dysentery Products from US Biological
| Catalog # | Product Name | Type | Host | Source |
| E3250-10 | Entamoeba histolytica | Mab | Mo x | |
| E3250-10A | Entamoeba histolytica | Mab | Mo x | |
| E3250-10B | Entamoeba histolytica | Mab | Mo x | |
| E3250-11 | Entamoeba histolytica | Mab | Mo x | |
| E3250-12 | Entamoeba histolytica HK-9 | Mab | Mo x | |
| E3250-13 | Entamoeba histolytica | Mab | Mo x | |
| G2034-17 | Giardia lamblia | Pab | Gt x | |
| G2034-17A | Giardia lamblia (HRP) | Pab | Gt x | |
| G2034-17B | Giardia lamblia (Biotin) | Pab | Gt x | |
| G2034-17C | Giardia lamblia (FITC) | Pab | Gt x | |
| G2034-18 | Giardia lamblia | Mab | Mo x | |
| G2034-19 | Giardia lamblia | Mab | Mo x | |
| G2034-21 | Giardia lamblia | Mab | Mo x | |
| G2034-22 | Giardia lamblia | Mab | Mo x | |
| G2034-22A | Giardia lamblia (FITC) | Mab | Mo x | |
| T5010-14A | Thioredoxin Reductase 1 (TrxR1) | Pab | Rb x | Hu |
| T5010-14B | Thioredoxin Reductase | Pab | Gt x | Hu |
| T5010-14D | Thioredoxin Reductase, Recombinant, Yeast, NTR | |||
| T5010-14E | Thioredoxin Reductase, Recombinant, E. coli (TRXR, trxB) | |||
| T5010-14F | Thioredoxin Reductase 1 | Mab | Mo x | Hu |
| T5010-14G | Thioredoxin Reductase 1 | Mab | Mo x | Hu |
| T5010-14H | TXNRD1, aa161-647, Recombinant, Human | |||
| T5010-14J | Thioredoxin Reductase 1 | Pab | Gt x | Hu |
| T5010-14K | TXNRD1, CT | Pab | Gt x | Hu |
| T5010-17A | Thioredoxin Reductase BioAssay™ Kit (TrxR) |