STELLUX™ Chemiluminescence ELISA for Broad Range and Sensitive Detection of Human Insulin
Related Products
- 80-INSHU-CH01 Insulin Chemiluminescence ELISA
- 80-INSMR-CH01 Insulin Rodent ( Mouse / Rat ) Chemiluminescence ELISA
- 80-PINHUI-CH01 Proinsulin (Intact) Chemiluminescence ELISA
- 80-PINHUT-CH01 Proinsulin (Total) Chemiluminescence ELISA
- 80-INSMR-CH10 STELLUX™ Chemi Rodent Insulin ELISA Jumbo
Quantification of insulin in serum or plasma over a wide range of disease states or pre and post drug treatment is vital in furthering diabetes research. Many commercial human insulin ELISAs require extra sample dilution steps to ensure concentrations fall within a limited standard curve range. This results in increased sample preparation time, as well as potential re-dilution and re-testing of samples. ALPCO has developed a broad range, high sensitivity, and small volume human insulin ELISA to address these issues.
Critical Performance Attributes
Until recently, an immunoassay that could accurately measure a wide range of insulin concentrations from 5-50,000 pg/mL in human samples was not commercially available. Furthermore, a 2012 HTStec’s ELISA Assay Trends report indicated an increase in assay sensitivity and reduction of sample consumption as being the two highest ranking factors of consumer importance when improving ELISA performance.8 Factors which ALPCO took into careful consideration while developing a new chemiluminescent method for analyte detection.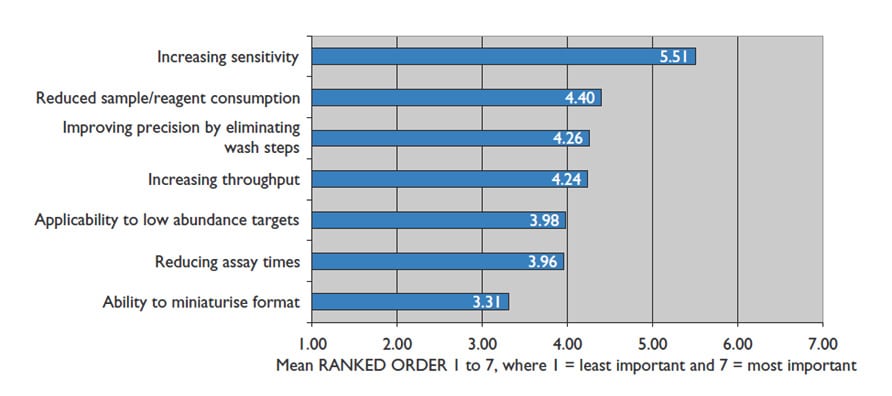
STELLUX™ Solution
The STELLUX™ Chemiluminescent Human Insulin ELISA offers an optimal solution for accurate, sensitive and wide range detection of insulin using as little as 25 µL of sample. The broad dynamic range significantly decreases sample preparation time by eliminating dilution steps and takes the guesswork out of determining ideal dilution factors, while the low sample size of the assay ensures reduced sample consumption. These features aid in preserving the customer’s precious samples and helps labs save time and money with higher throughput. Moreover, the increased sensitivity enables consumers to accurately measure a variety of samples ranging from normal, to those with impaired glucose tolerance and those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
The Chemi Human Insulin assay (80-INSHU-CH01) is currently for Research Use Only and was developed for the quantitative determination of insulin in human serum, plasma, and tissue culture samples over a dynamic range of 5-30,000 pg/mL with results achieved in 1 hour and 35 minutes. Analytical (LOD) and functional sensitivities are 1.51 pg/mL and 10 pg/mL respectively.
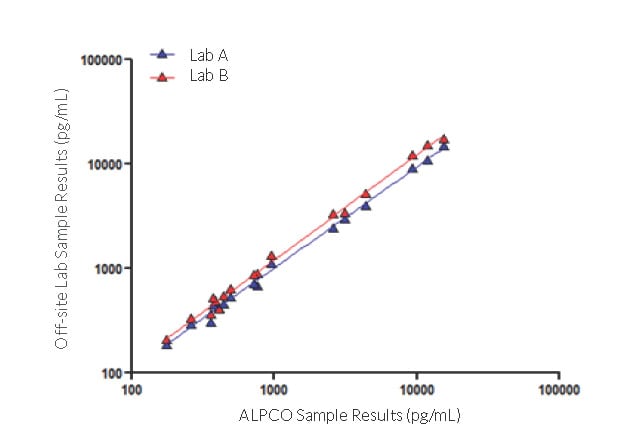
Sample correlation was evaluated at two independent laboratories and results generated from this study were compared to results generated in-house at ALPCO. As seen in Figure 3, there is a high degree of inter-laboratory correlation with an r2 value of 0.999.
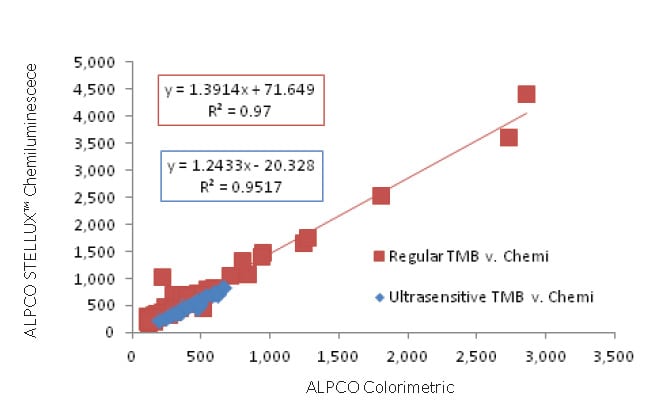
Additionally, correlation between the ALPCO human insulin colourimetric ELISAs and the STELLUX™ chemiluminescent platform was evaluated. Results showed the ability to quantitate samples similarly on both kits, ensuring customers will be able to smoothly transition from the colourimetric method to the chemiluminescence platform.
Benefit of Chemiluminescence
Unlike other test platforms, ALPCO’s line of chemiluminescent assays does not require expensive high-end instrumentation. The STELLUX™ ELISAs are 96-well black plate assays utilising a standard chemiluminescent (glow) reader common in most laboratories. Aside from the increased sensitivity and broad dynamic range, the chemiluminescent platform also allows for analyte detection with a variety of different sample types including serum, heparin plasma, and tissue culture supernatants with minimal sample preparation required.
These features make the STELLUX™ chemiluminescent kits ideal for use in a range of testing facilities including contract research organisations, core reference laboratories, academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies performing pre-clinical research. Moreover, multiple lots are validated against each other for parameters that include functional sensitivity, inter and intra assay precision, accuracy, LLOQ, ULOQ, and linearity of dilution. This gives consumers reassurance on the robustness of the assay. Plus, the high correlation to ALPCO’s colourimetric insulin ELISAs makes for an easier transition to the new STELLUX™ chemiluminescent platform for existing users, while the inter-laboratory correlation builds confidence in the accuracy of results.
Summary
ALPCO’s STELLUX™ Chemiluminescent Human Insulin ELISA offers broad range detection with just a 25 µL sample volume, significantly reducing sample preparation time by eliminating dilution steps and the guesswork involved in determining ideal dilution factors. It also provides the best sensitivity on the market with quantitative detection of insulin as low as 10pg/mL and no cross-reactivity to mouse/rat insulin or human intact proinsulin, ensuring results from pre-diabetic or Type I diabetic samples are accurate and dependable.
References
- Culina, et al. Insulin and type 1 diabetes: immune connections. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2013; 168: R19-R31.
- Weiss, M. A. Proinsulin and the genetics of diabetes mellitus. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2009; 284 (9):19159-19163.
- Kahn, CR. Banting Lecture: Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes. 1994; 43: 1066-1084.
- Madsbad, S. Prevalence of residual beta-cell function and its metabolic consequences in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1983; 24: 141-147.
- Wild, S. et al. Global prevalence of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27: 1047-1053.
- Aragones, G. et al. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 impairs the insulin-dependent nitric oxide pathway in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovascular Diabetology. 2012; 11:72.
- Ghasemi, R. et al. Brain Insulin Dysregulation: Implication for neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Neurobiol. Jan 20, 2013.
- Comley, J. ELISA Assays-recent innovations take analyte detection to new levels. Drug Discovery World Fall. 2012; 1-20.
- Bergman, R. et al. Accurate assessment of beta-cell function. Diabetes. 2002; 51: S212-220.
- Rickels et al. Insulin Sensitivity, Glucose Effectiveness, and Free Fatty Acid Dynamics after Human Islet Transplantation for Type 1 Diabetes. J. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 91(6): 2138-2144