Cell Therapy Proteins
Products
Overview
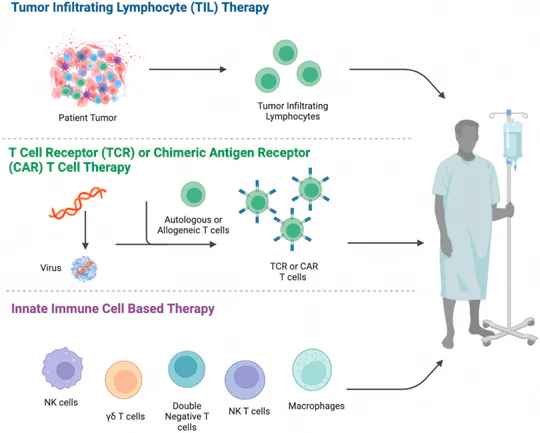
Cell therapy includes immunocellular therapy and stem cell therapy. It utilizes cells from the patient or a donor, which, after being cultured, expanded, activated, or genetically edited ex vivo, are reinfused into the patient. This stimulates or enhances the body’s immune function, thereby achieving a method of controlling diseases. Based on different mechanisms of action, typical types of cell therapy include CAR-T, TILs, TCR-T, CAR-NK, etc.
KACTUS Proteins for Cell Therapy Development
Supporting you from discovery through manufacturing.
Immunization Proteins for Drug Discovery
During the drug discovery phase of cell therapy, especially for reprogrammed cell therapeutic drugs, such as immune cells loaded with CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor), it is often necessary to obtain the correct scFv (Single-chain Variable Fragment) sequence through immunization with relevant target antigen proteins. This enables the drug product cells to accurately identify tumor cells expressing antigens. KACTUS offers a series of high-quality target antigen protein options for customers to choose from.
MHC Complexes
Intracellular antigen targets are a major direction in cell therapy. Peptide segments, resulted from the degradation of intracellular antigens, form complexes with MHC and are presented on the cell surface for TCR recognition. Targeting MHC peptide complexes can achieve the killing of tumor cells.
KACTUS peptide-MHC complexes cover a variety of popular targets, and include monomers, tetramers, fluorescently-labeled tetramers, and other forms, which can be used for immunization or screening research in the development of T-cell therapeutic drugs. KACTUS also offers custom MHC expression, custom TCR expression, and peptide-ready MHCs to build your own peptide-MHC in house.
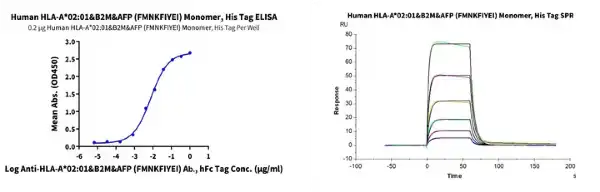
Figure 2. Through ELISA and SPR experiments, we have verified that the monomer of HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) complex can bind separately with Anti-AFP (HLA-A*02:01) Antibody and HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP TCR. The EC50 and affinity constant are 7.6 ng/mL and 0.923 μM, respectively.
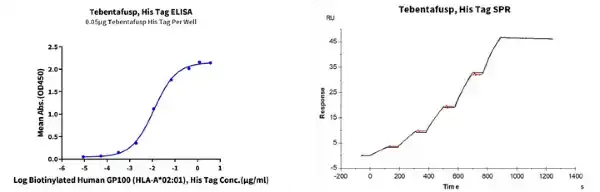
Figure 3. (Left) Through ELISA validation, it has been confirmed that gp100 TCR & CD3 scfv fusion protein can bind to the monomer of HLA-A*02:01&B2M&GP100 (YLEPGPVTA) complex, with an EC50 of 11.8 ng/mL. (Right) In the SPR analysis, gp100 TCR & CD3 scfv fusion protein can bind to the tetramer of the HLA-A*02:01&B2M&GP100 (YLEPGPVTA) complex, with an affinity constant of 0.196 nM.
CAR-T Target Proteins
KACTUS’ high-activity CAR-T target proteins can be applied during the early animal immunization stage for antibody discovery.
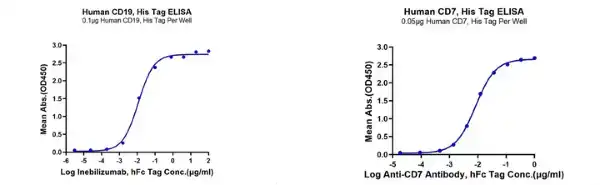
Figure 4. CAR-T target proteins, Human CD19 and Human CD7 proteins, can both bind well with the corresponding antibodies.
VLP SuperAntigens
Cell therapy targets include multiple transmembrane proteins (such as the GPCR family) and some targets for which it is difficult to obtain ideal antibody sequences through direct immunization. Our virus-like particle (VLP) display technology can maintain the correct conformation of multiple transmembrane proteins while enhancing the immunogenicity of the protein. In addition, the VLP framework can be designed specifically for your antigen with our custom VLP services.
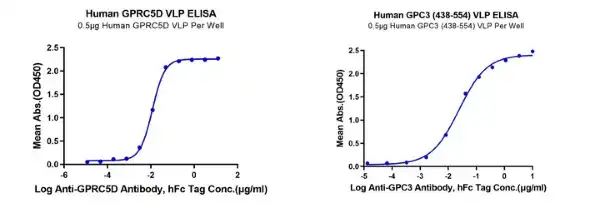
Proteins for Cell Therapy Production & Analysis
Production preparation is a crucial step to obtain immunocellular drugs and is also key to the successful registration of cell drugs. KACTUS provides high-activity cytokines for cell culture and cell matrix proteins required for stem cell differentiation.
Laminin 521 for Stem Cell Culture
KACTUS offers recombinant Laminin 521 at research-grade, preclinical-grade, and cell therapy-grade. Laminin 521 is an important matrix adhesion protein for maintaining stem cells in culture.

Figure 5. The cell culture matrix protein Laminin 521 can effectively promote the growth of human iPSCs.
Figure 6. The cell culture matrix protein Laminin 521 can maintain the differentiation potential of stem cells.
Cytokines for Cell Culture
Cell culture is a necessary step for the preparation of cell-based therapies. Immunotherapy involving T cells, NK cells, and stem-cell derived immunocytes requires the preparation of stem cells such as ESCs, MSCs, and iPSCs. KACTUS offers a variety of cytokine products for cell culture.
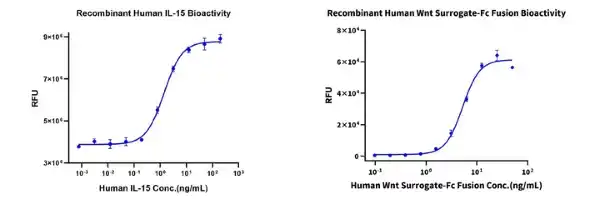
Figure 7. (Left) We demonstrate via cell analysis that our Human IL-15 can promote the proliferation of MO7e cells, with an ED50 of 1-2 ng/mL. (Right) Through cellular level analysis, Human Wnt Surrogate can induce the activity of the Topflash reporter gene in HEK293 cells, with an ED50 of 5.2 ng/mL.
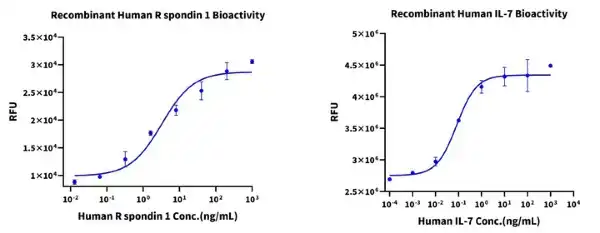
Figure 8. (Left) Via cellular-level analysis, we demonstrate that in the presence of Wnt Surrogate (5 ng/mL), Human R-spondin 1 Protein induced the activity of the Topflash reporter gene in HEK293 cells, with an ED50 between 1.0-10.0 ng/mL. (Right) Via cellular-level analysis, we validated that Human IL-7 Protein can promote the proliferation of 2E8 cells, with an ED50 value between 0.1-0.5 ng/mL.
Fluorescent or Biotinylated Proteins For Antibody Screening & Cell Therapy Analysis
Proteins labeled with fluorescence or biotin can be used for various detection processes in the production and quality inspection of therapeutic cells, such as antibody screening (such as scFv, etc.), CAR affinity research, CAR-T positivity rate detection, TCR screening or detection, and Blocking Assay, etc. KACTUS provides high-quality proteins labeled with different fluorescent markers like FITC, PE, as well as biotin-labeled proteins, to meet the needs of various analytical scenarios including cellular level analyses.
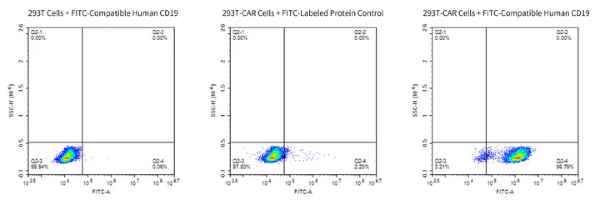
Figure 9. Through cellular-level flow cytometry detection, we demonstrated that FITC-Compatible Human CD19 protein can specifically bind with Anti-CD19-CAR T cells.

Figure 10. Through cellular-level flow cytometry detection, we demonstrated the fluorescently labeled HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC) tetramer complex can bind well with HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 TCR cells.
GMP-Grade CRISPR Enzymes for Cellular Gene Editing
Allogeneic off-the-shelf cellular therapy products, such as UCAR-T, require the use of gene-editing technologies to knock out genes related to immune rejection reactions on donor T cells, to avoid inducing immune rejection reactions like GvHD and HvGR.
KACTUS offers GMP-Grade CRISPR Cas9 and GMP-Ready Cas12a for genetic modification of cells, including UCAR-T cell therapy. Regulatory support documentation is available. Moreover, our GMP-Grade Cas9 has been registered with the FDA Drug Master files (DMF #036578). Additionally, check out our CRISPR Cas9 ELISA kit to detect residual Cas9 nuclease in your cell product.
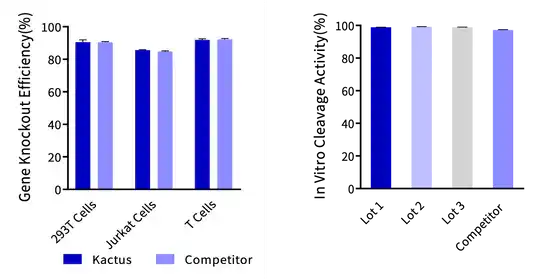
Figure 11. (Left) Cas9 Nuclease is used for gene knockout in 293T cells, Jurkat cells, and T cells, and its gene knockout efficiency in various cell types is comparable to that of leading suppliers. (Right) Cas9 Nuclease In Vitro DNA Cleavage Experiment. The in vitro cleavage efficiency of Cas9 nuclease is equivalent across all three batches.
Cas9 ELISA Kit
Quantitatively detect the residue of Cas9 nuclease in extracellular or intracellular spaces of gene-edited cell drugs before reinfusion into the human body. The detection range of our Cas9 ELISA kit is 0.25 ng/mL – 16 ng/mL, with a sensitivity that can reach 0.125 ng/mL.
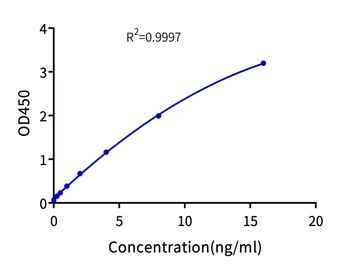
Figure 12. Polynomial fitting of the Cas9 ELISA standard curve. The R² is 0.9997.
GMP-Grade MaxNuclease for DNA/RNA Degradation
In gene therapy, MaxNuclease principally serves to eliminate contaminants like host DNA and plasmid DNA present during the pharmaceutical production process. This GMP-grade nuclease is produced within a facility maintaining stringent GMP-Grade production standards, avoiding the use of materials derived from animals. The analytical methods applied have undergone systematic validation, and the final enzyme is subject to extensive quality control release testing to ensure it meets the requirements for use from research and development through to large-scale commercial production. Additionally, KACTUS has submitted MaxNuclease to the FDA Drug Master Files (DMF #036799).
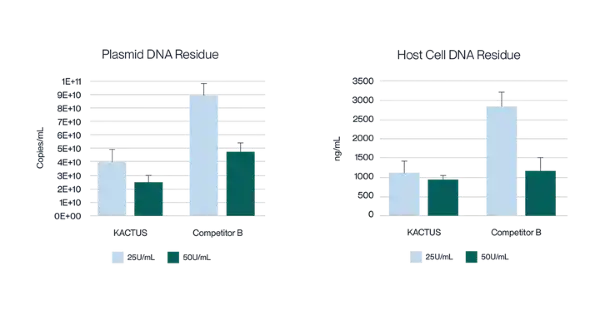
Figure 13. Virus harvest solution was treated with 25U/mL and 50U/mL endonuclease at 37°C for 2 hours, respectively. Detection of plasmid DNA (pDNA) residue (left) and host cell DNA (HCD) (right) residue was analyzed. KACTUS MaxNuclease has higher degradation activity versus Competitor B demonstrated by lower pDNA and HCD residue for both 25U/mL and 50U/mL working concentrations.
MaxNuclease ELISA Kit
The quantification of residual MaxNuclease in gene therapy drugs is achievable with our associated ELISA kit, which provides a wide detection range of 46.88pg/mL to 3000pg/mL and sensitivity reaching up to 23.44pg/mL.
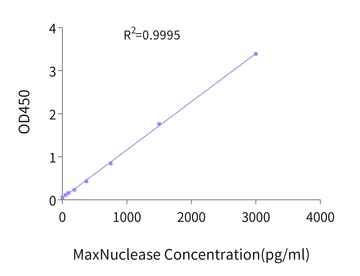
Figure 14. Example standard curve for MaxNuclease ELISA kit.
Browse Cell Therapy Products by Category
Class I and Class II MHC Monomers & Tetramers
Mammalian-Expressed Catalog & Custom Peptide-MHC Complexes
Class I and Class II Alleles
Product Features

Choice of Allele
Biotinylation & Fluorescent Labels
Verified Bioactivity
Shop by Allele
Class I Alleles – Human
HLA-A*01:01
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM426 | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&CT83 (NTDNNLAVY) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and NTDNNLAVY peptide |
| MHC-HM427 | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&MAGE-A3 (EVDPIGHLY) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and EVDPIGHLY peptide |
| MHC-HM427T | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&MAGE-A3 (EVDPIGHLY) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and EVDPIGHLY peptide |
| MHC-HM426T | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&CT83 (NTDNNLAVY) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and NTDNNLAVY peptide |
| MHC-HM428 | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&DSG3 (YTDNWLAVY) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YTDNWLAVY peptide. |
HLA-A*02:01
HLA-A*02:03
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM432TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:03&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM432 | Human HLA-A*02:03&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:03),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM432T | Human HLA-A*02:03&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:03),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM432B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:03&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:03),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
HLA-A*03:01
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM438 | Human HLA-C 03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
| MHC-HM438B | Biotinylated Human HLA-C*03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
| MHC-HM438T | Human HLA-C*03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305 (HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119 (B2M) and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
HLA-A*11:01
HLA-A*24:02
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM46RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*24:02&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM46R | Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*24:02&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM433 | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&GP100 Intron 4 (VYFFLPDHL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VYFFLPDHL peptide |
| MHC-HM433B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&GP100 Intron 4 (VYFFLPDHL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VYFFLPDHL peptide |
| MHC-HM434 | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&MAGE-A3 (IMPKAGLLI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and IMPKAGLLI peptide |
| MHC-HM434B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&MAGE-A3 (IMPKAGLLI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and IMPKAGLLI peptide |
| MHC-HM434T | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&MAGE-A3 (IMPKAGLLI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and IMPKAGLLI peptide |
| MHC-HM430B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&Survivin 2B (AYACNTSTL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and AYACNTSTL peptide |
| MHC-HM430 | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&Survivin 2B (AYACNTSTL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and AYACNTSTL peptide |
| MHC-HM430T | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&Survivin 2B (AYACNTSTL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and AYACNTSTL peptide |
HLA-B*15:01
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM448 | Human HLA-B*15:01&B2M&SARS-CoV-2 epitope (NQKLIANQF) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly21-Thr301(HLA-B*15:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and NQKLIANQF peptide |
| MHC-HM448B | Biotinlylated Human HLA-B*15:01&B2M&SARS-CoV-2 epitope (NQKLIANQF) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly21-Thr301(HLA-B*15:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and NQKLIANQF peptide |
HLA-C*03:04
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM438 | Human HLA-C 03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
| MHC-HM438B | Biotinylated Human HLA-C*03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
| MHC-HM438T | Human HLA-C*03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305 (HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119 (B2M) and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
HLA-E*01:03
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM406B | Biotinylated Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPRTLVL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VMAPRTLVL peptide |
| MHC-HM406 | Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPRTLVL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VMAPRTLVL peptide |
| MHC-HM42RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-E*01:03&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM40C | Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPKTLVL) Monomer Negative Control Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VMAPKTLVL peptide |
| MHC-HM42R | Human Peptide Ready HLA-E*01:03&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM406TB | Biotinylated Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPRTLVL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VMAPRTLVL peptide |
| MHC-HM406T | Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPRTLVL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VMAPRTLVL peptide |
HLA-G
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| HLG-HM41C | Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HM41CTB | Biotinylated Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HM41CT | Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HM41CB | Biotinylated Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HM41CTP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-RM41C | Rhesus macaque HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-CM41C | Cynomolgus HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| MHC-HM45RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-G&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| HLG-RM41CT | Rhesus macaque HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-CM41CT | Cynomolgus HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| MHC-HM45R | Human Peptide Ready HLA-G&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| HLG-CM41CB | Biotinylated Cynomolgus HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HE41F | Human HLA-G Free Heavy Chain Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(C66S) |
Class I Alleles – Mouse
Qa-1b
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-MM452 | Mouse Qa-1b&B2M&Qdm (AMAPRTLLL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | His23-Pro296(Qa-1b), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and AMAPRTLLL peptide |
H-2Kb
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-MM453 | Mouse H-2K(b)&B2M&OVA (SIINFEKL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | His24-Pro297(H-2K(b)), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and SIINFEKL peptide |
Class II Alleles or Other Alleles
For other class I alleles, non-classical alleles, or class II alleles click here
Shop by Peptide Sequence
AFP (FMNKFIYEI)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM407B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M) and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM432TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:03&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM407TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM432 | Human HLA-A*02:03&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:03),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM432T | Human HLA-A*02:03&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:03),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM432B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:03&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:03),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM407T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
| MHC-HM407 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP (FMNKFIYEI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FMNKFIYEI peptide |
AFP (PLFQVPEPV)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM408B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP (PLFQVPEPV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and PLFQVPEPV peptide |
| MHC-HM408T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP (PLFQVPEPV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and PLFQVPEPV peptide |
| MHC-HM408 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP (PLFQVPEPV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and PLFQVPEPV peptide |
CT83 (NTDNNLAVY)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM426 | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&CT83 (NTDNNLAVY) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and NTDNNLAVY peptide |
| MHC-HM426T | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&CT83 (NTDNNLAVY) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and NTDNNLAVY peptide |
DSG3 (YTDNWLAVY)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM428 | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&DSG3 (YTDNWLAVY) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YTDNWLAVY peptide |
GP100 (YLEPGPVTA)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM402B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&GP100 (YLEPGPVTA) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YLEPGPVTA peptide |
| MHC-HM402 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&GP100 (YLEPGPVTA) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YLEPGPVTA peptide |
| MHC-HM402T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&GP100 (YLEPGPVTA) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YLEPGPVTA peptide |
| MHC-HM433 | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&GP100 Intron 4 (VYFFLPDHL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VYFFLPDHL peptide |
| MHC-HM433B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&GP100 Intron 4 (VYFFLPDHL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VYFFLPDHL peptide |
GP100 Intron 4 (VYFFLPDHL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM433 | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&GP100 Intron 4 (VYFFLPDHL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VYFFLPDHL peptide |
| MHC-HM433B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&GP100 Intron 4 (VYFFLPDHL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VYFFLPDHL peptide |
HBV (FLLTRILTI)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM409 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HBV (FLLTRILTI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FLLTRILTI peptide |
| MHC-HM409B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HBV (FLLTRILTI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FLLTRILTI peptide |
| MHC-HM409T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HBV (FLLTRILTI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and FLLTRILTI peptide |
HLA-E (VMAPRTLVL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM406B | Biotinylated Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPRTLVL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VMAPRTLVL peptide |
| MHC-HM406 | Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPRTLVL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VMAPRTLVL peptide |
| MHC-HM406TB | Biotinylated Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPRTLVL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VMAPRTLVL peptide |
| MHC-HM406T | Human HLA-E*01:03&B2M&Peptide (VMAPRTLVL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VMAPRTLVL peptide |
HLA-G (RIIPRHLQL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| HLG-HM41C | Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HM41CTB | Biotinylated Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HM41CT | Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HM41CB | Biotinylated Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-HM41CTP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-RM41C | Rhesus macaque HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-CM41C | Cynomolgus HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-RM41CT | Rhesus macaque HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-CM41CT | Cynomolgus HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
| HLG-CM41CB | Biotinylated Cynomolgus HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RIIPRHLQL peptide |
HLA-G Free Heavy Chain
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| HLG-HE41F | Human HLA-G Free Heavy Chain Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(C66S) |
HPV16 E6 (KLPQLCTEL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM436 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HPV 16 E6 (KLPQLCTEL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and KLPQLCTEL peptide |
| MHC-HM436T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HPV 16 E6 (KLPQLCTEL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and KLPQLCTEL peptide |
HPV16 E7 (YMLDLQPET)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM24MT | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HPV16 E7 (YMLDLQPET) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YMLDLQPET peptide |
| MHC-HM424B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HPV16 E7 (YMLDLQPET) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YMLDLQPET peptide |
| MHC-HM424 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HPV16 E7 (YMLDLQPET) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YMLDLQPET peptide |
HPV16 E7 (YMLDLQPET)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM24MT | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HPV16 E7 (YMLDLQPET) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YMLDLQPET peptide |
| MHC-HM424B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HPV16 E7 (YMLDLQPET) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YMLDLQPET peptide |
| MHC-HM424 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&HPV16 E7 (YMLDLQPET) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and YMLDLQPET peptide |
KRAS G12A (VVVGAAGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM441 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12A (VVVGAAGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAAGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM441T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12A (VVVGAAGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAAGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM441B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12A (VVVGAAGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAAGVGK peptide |
KRAS G12C (VVVGACGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM439B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12C (VVVGACGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGACGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM439 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12C (VVVGACGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGACGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM439T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12C (VVVGACGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGACGVGK peptide |
KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM438 | Human HLA-C 03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
| MHC-HM438B | Biotinylated Human HLA-C*03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
| MHC-HM438T | Human HLA-C*03:04&B2M&KRAS G12D (GADGVGKSAL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305 (HLA-C 03:04), Ile21-Met119 (B2M) and GADGVGKSAL peptide |
KRAS G12D (VVGADGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM420B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM420 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM454B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119 (B2M) and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM455B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM454 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM455 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM420TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM420T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM420B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM420 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM454B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119 (B2M) and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM454 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM420TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM420T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGADGVGK peptide |
KRAS G12R (VVVGARGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM440B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12R (VVVGARGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGARGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM440 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12R (VVVGARGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGARGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM440T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12R (VVVGARGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGARGVGK peptide |
KRAS G12S (VVVGASGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM442 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12S (VVVGASGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGASGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM442B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12S (VVVGASGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGASGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM442T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12S (VVVGASGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGASGVGK peptide |
KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM422 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM418B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM422B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM418TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE005 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE005B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE006B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE006 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM456 | Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM422T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM456B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM456TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305 (HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119 (B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421F | FITC-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM418T | Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM418 | Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM418B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM418TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE005TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE005 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE005B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305 (HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119 (B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421F | FITC-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM421T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM418T | Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM418 | Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS G12V (VVVGAVGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAVGVGK peptide |
KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM423B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM423 | Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM429B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM429 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE001B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HE001 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM429TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM429F | FITC-Labeled Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM429T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
| MHC-HM423T | Human HLA-A*03:01&B2M&KRAS WT (VVVGAGGVGK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M)and VVVGAGGVGK peptide |
LMP2 (CLGGLLTMV)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM413T | Chimeric HLA-A*02:01 (mα3) &B2M&LMP2 (CLGGLLTMV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr206(Human HLA-A*02:01 α1&α2) & Asp207-Glu299(Mouse H-2Ld α3), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and CLGGLLTMV peptide |
| MHC-HM413 | Chimeric HLA-A*02:01 (mα3) &B2M&LMP2 (CLGGLLTMV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr206(Human HLA-A*02:01 α1&α2) & Asp207-Glu299(Mouse H-2Ld α3), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and CLGGLLTMV peptide |
| MHC-HM411T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&LMP2 (CLGGLLTMV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and CLGGLLTMV peptide |
| MHC-HM411B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&LMP2 (CLGGLLTMV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and CLGGLLTMV peptide |
| MHC-HM411 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&LMP2 (CLGGLLTMV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and CLGGLLTMV peptide |
LMP2 (SSCSSCPLTK)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM410B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&LMP2 (SSCSSCPLTK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SSCSSCPLTK peptide |
| MHC-HM410T | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&LMP2 (SSCSSCPLTK) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SSCSSCPLTK peptide |
| MHC-HM410 | Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&LMP2 (SSCSSCPLTK) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SSCSSCPLTK peptide |
MAGE-A1 (KVLEYVIKV)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM445B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A1 (KVLEYVIKV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and KVLEYVIKV peptide |
| MHC-HM445TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A1 (KVLEYVIKV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and KVLEYVIKV peptide |
| MHC-HM445 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A1 (KVLEYVIKV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and KVLEYVIKV peptide |
| MHC-HM445T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A1 (KVLEYVIKV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and KVLEYVIKV peptide |
MAGE-A3 (EVDPIGHLY)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM427 | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&MAGE-A3 (EVDPIGHLY) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and EVDPIGHLY peptide |
| MHC-HM427T | Human HLA-A*01:01&B2M&MAGE-A3 (EVDPIGHLY) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*01:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and EVDPIGHLY peptide |
MAGE-A3 (IMPKAGLLI)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM434 | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&MAGE-A3 (IMPKAGLLI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and IMPKAGLLI peptide |
| MHC-HM434B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&MAGE-A3 (IMPKAGLLI) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and IMPKAGLLI peptide |
| MHC-HM434T | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&MAGE-A3 (IMPKAGLLI) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and IMPKAGLLI peptide |
MAGE-A4 (GVYDGREHTV)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM401B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A4 (GVYDGREHTV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GVYDGREHTV peptide |
| MHC-HM401 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A4 (GVYDGREHTV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GVYDGREHTV peptide |
| MHC-HM401TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A4 (GVYDGREHTV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and GVYDGREHTV peptide |
| MHC-HM401T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A4 (GVYDGREHTV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and GVYDGREHTV peptide |
MAGE-A4 (KVLEHVVRV)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM106 | Chimeric HLA-A*02:01 (mα3) &mB2M&MAGE-A4 (KVLEHVVRV) Monomer Protein | C-His | Gly25-Thr206(Human HLA-A*02:01 α1&α2) & Asp207-Glu299(Mouse H-2Ld α3), Ile21-Met119(mB2M) and KVLEHVVRV peptide |
| MHC-HM437B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A4 (KVLEHVVRV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and KVLEHVVRV peptide |
| MHC-HM437 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A4 (KVLEHVVRV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and KVLEHVVRV peptide |
MAGE-A8 (KVLEHVVRV)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM106 | Chimeric HLA-A*02:01 (mα3) &mB2M&MAGE-A4 (KVLEHVVRV) Monomer Protein | C-His | Gly25-Thr206(Human HLA-A*02:01 α1&α2) & Asp207-Glu299(Mouse H-2Ld α3), Ile21-Met119(mB2M) and KVLEHVVRV peptide |
| MHC-HM437B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A4 (KVLEHVVRV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and KVLEHVVRV peptide |
| MHC-HM437 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MAGE-A4 (KVLEHVVRV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and KVLEHVVRV peptide |
MART-1 (ELAGIGILTV)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM435 | HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MART-1 (ELAGIGILTV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and ELAGIGILTV peptide |
| MHC-HM435T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&MART-1 (ELAGIGILTV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and ELAGIGILTV peptide |
NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM151 | Chimeric HLA-A*02:01 (mα3) &mB2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC) Monomer Protein | C-His | Gly25-Thr206(Human HLA-A*02:01 α1&α2) & Asp207-Glu299(Mouse H-2Ld α3), Ile21-Met119(mB2M) and SLLMWITQC peptide |
| MHC-HE446 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and SLLMWITQC peptide |
| MHC-HE446T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and SLLMWITQC peptide |
| MHC-HM405TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and SLLMWITQC peptide |
| MHC-HM405T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and SLLMWITQC peptide |
| MHC-HM405B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLMWITQC peptide |
| MHC-HM405 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQC) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLMWITQC peptide |
NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQV)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM40N | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLMWITQV peptide |
| MHC-HM40NT | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQV) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLMWITQV peptide |
| MHC-HM40NB | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 (SLLMWITQV) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLMWITQV peptide |
p53-R175H (HMTEVVRHC)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM415B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&P53 R175H (HMTEVVRHC) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and HMTEVVRHC peptide |
| MHC-HM415TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&P53 R175H (HMTEVVRHC) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and HMTEVVRHC peptide |
| MHC-HM415T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&P53 R175H (HMTEVVRHC) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and HMTEVVRHC peptide |
| MHC-HM415 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&P53 R175H (HMTEVVRHC) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and HMTEVVRHC peptide |
p53 WT (HMTEVVRRC)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM416B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&P53 WT (HMTEVVRRC) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and HMTEVVRRC peptide |
| MHC-HM416TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&P53 WT (HMTEVVRRC) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and HMTEVVRRC peptide |
| MHC-HM416T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&P53 WT (HMTEVVRRC) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and HMTEVVRRC peptide |
| MHC-HM416 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&P53 WT (HMTEVVRRC) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and HMTEVVRRC peptide |
PRAME (ALYVDSLFFL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM447B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&PRAME (ALYVDSLFFL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and ALYVDSLFFL peptide |
| MHC-HM447T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&PRAME (ALYVDSLFFL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and ALYVDSLFFL peptide |
| MHC-HM447 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&PRAME (ALYVDSLFFL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and ALYVDSLFFL peptide |
PRAME (SLLQHLIGL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM443B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&PRAME (SLLQHLIGL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLQHLIGL peptide |
| MHC-HM443 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&PRAME (SLLQHLIGL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLQHLIGL peptide |
| MHC-HM443T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&PRAME (SLLQHLIGL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLQHLIGL peptide |
| MHC-HM443TP | PE-Labeled Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&PRAME (SLLQHLIGL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and SLLQHLIGL peptide |
SARS-CoV-2 Epitope (NQKLIANQF)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM448 | Human HLA-B*15:01&B2M&SARS-CoV-2 epitope (NQKLIANQF) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly21-Thr301(HLA-B*15:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and NQKLIANQF peptide |
| MHC-HM448B | Biotinlylated Human HLA-B*15:01&B2M&SARS-CoV-2 epitope (NQKLIANQF) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly21-Thr301(HLA-B*15:01), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and NQKLIANQF peptide |
Survivin (LMLGEFLKL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM412T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&Survivin (LMLGEFLKL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and LMLGEFLKL peptide |
| MHC-HM412B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&Survivin (LMLGEFLKL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and LMLGEFLKL peptide |
| MHC-HM412 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&Survivin (LMLGEFLKL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and LMLGEFLKL peptide |
Survivin 2B (AYACNTSTL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM430B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&Survivin 2B (AYACNTSTL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and AYACNTSTL peptide |
| MHC-HM430 | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&Survivin 2B (AYACNTSTL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and AYACNTSTL peptide |
| MHC-HM430T | Human HLA-A*24:02&B2M&Survivin 2B (AYACNTSTL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and AYACNTSTL peptide |
WT-1 (RMFPNAPYL)
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM431B | Biotinylated Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&WT-1 (RMFPNAPYL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RMFPNAPYL peptide |
| MHC-HM431T | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&WT-1 (RMFPNAPYL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RMFPNAPYL peptide |
| MHC-HM431 | Human HLA-A*02:01&B2M&WT-1 (RMFPNAPYL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01),Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RMFPNAPYL peptide |
| MHC-HM414T | Chimeric HLA-A*02:01 (mα3) &B2M&WT-1 (RMFPNAPYL) Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr206(Human HLA-A*02:01 α1&α2) & Asp207-Glu299(Mouse H-2Ld α3), Ile21-Met119(B2M)and RMFPNAPYL peptide |
| MHC-HM414 | Chimeric HLA-A*02:01 (mα3) &B2M&WT-1 (RMFPNAPYL) Monomer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr206(Human HLA-A*02:01 α1&α2) & Asp207-Glu299(Mouse H-2Ld α3), Ile21-Met119(B2M) and RMFPNAPYL peptide |
Custom Peptide
For MHCs with custom peptide sequences,click here.
Alternatively, try a Peptide-Ready MHC to load your peptide in-house onto an MHC tetramer or monomer.
Product Validation Data
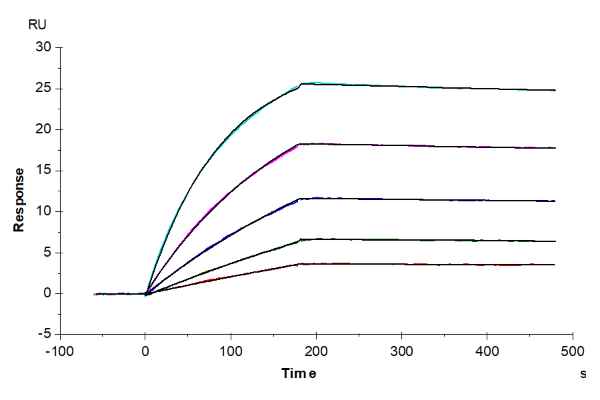
Human NY-ESO-1 (HLA-A*02:01) Tetramer
Anti-NY-ESO-1 (HLA-A*02:01) Antibody, hFc Tag captured on CM5 Chip via Protein A can bind Human NY-ESO-1 (HLA-A*02:01) Tetramer, His Tag with an affinity constant of 0.09 nM as determined in SPR assay (Biacore T200).
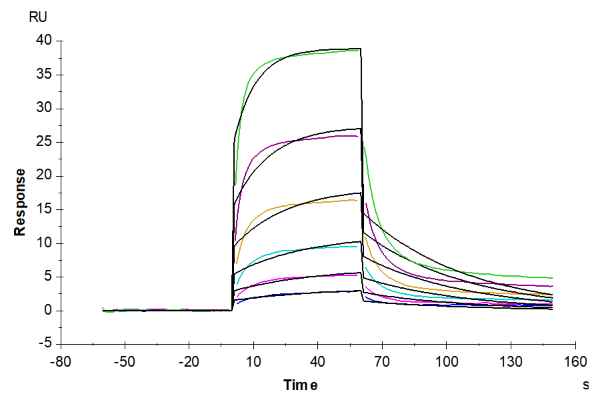
Human KRAS G12V (HLA-A*03:01)
Human KRAS G12V (HLA-A*03:01) , His Tag captured on CM5 Chip via anti-his antibody can bind Anti-KRAS G12V (HLA-A*03:01) Antibody with an affinity constant of 0.11 μM as determined in SPR assay (Biacore T200).
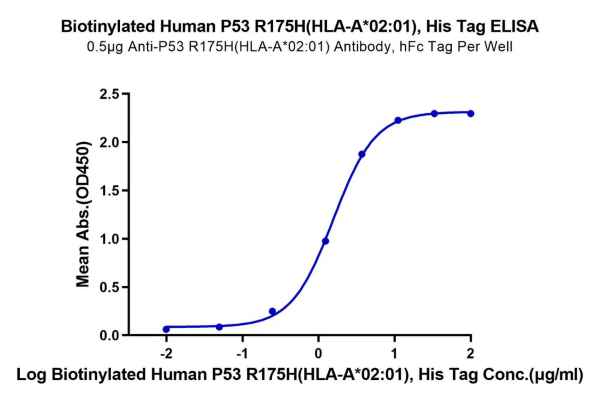
Biotinylated Human P53 R175H (HLA-A*02:01)
Immobilized Anti-P53 R175H (HLA-A*02:01) Antibody, hFc Tag at 5μg/mL (100μL/well) on the plate. Dose response curve for Biotinylated Human P53 R175H (HLA-A*02:01) , His Tag with the EC50 of 1.6μg/mL determined by ELISA.
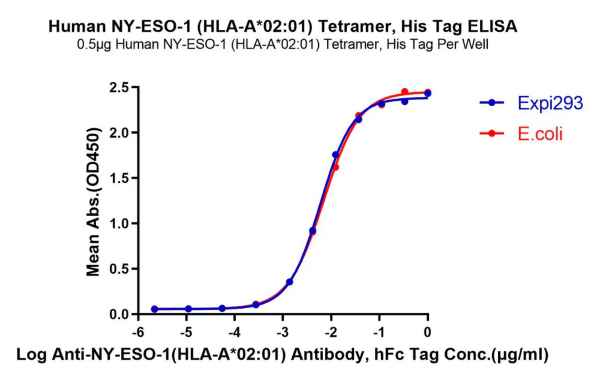
Human NY-ESO-1 (HLA-A*02:01) Tetramer
As verified by ELISA, the activity of NY-ESO-1 (HLA-A*02:01) tetramer expressed in mammalian cells and E. coli is comparable, providing you with more choices for research.
Peptide-Ready MHC: Load your own peptide
Load your own MHC monomer or tetramer in-house with our peptide-free MHCs.
→ Quick & simple peptide loading procedure
→ Monomer / Tetramer
→ Fluorescent Labeling
→ Class I and Class II Alleles
→ Biotinylation
MHC Product Types

Monomers
Our MHC peptide monomers are mammalian-expressed to ensure the natural configuration and have a His-Avi tag at the C-terminus. The Avi tag is a 15-amino acid sequence, which has a high affinity for biotin and can be specifically biotinylated by BirA.
Tetramers
MHC tetramers are complexes of four peptide-MHC biotinylated monomers bound to streptavidin molecules. The enhanced avidity of MHC tetramers and TCR interactions can have a significant impact for detecting antigen-specific T cells. They allow for direct detection, phenotyping, and enumeration of antigen-specific T cells within a polyclonal T cell population. KACTUS offers class I and class II tetramers.
Fluorescent Tetramer
Fluorescent MHC tetramers can be used to identify T cells that recognize a particular peptide-MHC complex. By labeling T cells with MHC tetramers, the frequency and distribution of antigen-specific T cells can be determined and sorted by FACS in a cell population. MHC tetramers can also be used to monitor immune responses to vaccines, infections and diseases by measuring the frequency of antigen-specific T cells over time to track the efficacy of a treatment.
MHC-I Virus-Like Particles
In combination with our Virus-Like Particles (VLP) technology platform, we have introduced multivalent fluorescent MHC I. These MHC I-VLP complexes are about 750 Å in diameter, compared to the MHC I monomer size of 70 Å. Each VLP contains approximately 250 copies of MHC I, resulting in boosted fluorescence quantum yield for enhanced detection of TCR binding. We currently offer FITC- and APC-equivalent options for MHC I-VLP fluorescence labeling.

Peptide-Ready MHC
Neoantigens offer a distinct advantage in their unique tumor-specific and normal tissue-absent feature, presenting ideal targets for effective and personalized tumor-specific immunotherapy. We have developed Peptide-Ready MHCs (prMHC), which are composed only of the α heavy chain and β2-microglobulin (β2m) light chain for loading your own neoantigen.

Chimeric MHC
Chimeric MHCs have the human α3 immunoglobulin-like domain replaced with the mouse α3 domain. This modification enhances antigen specificity for antibody discovery. These mammalian-expressed Chimeric MHCs retain their normal conformation to increase the likelihood of generating peptide-specific antibodies while decreasing the frequency of non-specific antibodies and making screening less labor-intensive.
Custom MHC Complexes
Choice of mammalian or E. coli expression systems
Monomers, Tetramers, Biotinylation, Fluorescent Labels
Multi-faceted biological activity verification (ELISA, SPR, FACS, etc.)
Choice of Class I or Class II Alleles
Choice of PE, APC, or other fluorescent label
Various species: Human, mouse, monkey, etc.
Soluble TCR Expression & SPR Analysis
→ Production of various formats of soluble TCRs, including scFv-TCR, TCR-His, etc.
→ TCR engineering to optimize soluble TCR expression based on TCR modeling
→ SPR analysis of soluble TCR & Peptide-Ready MHC/Peptide-MHC interactions
HLA-G and LILRs
→ HLA-G Monomers and Tetramers
→ LILRAs and LILRBs
→ APOE Proteins
→ Custom HLA-G & LILR Proteins
Major Histocompatibility Complex
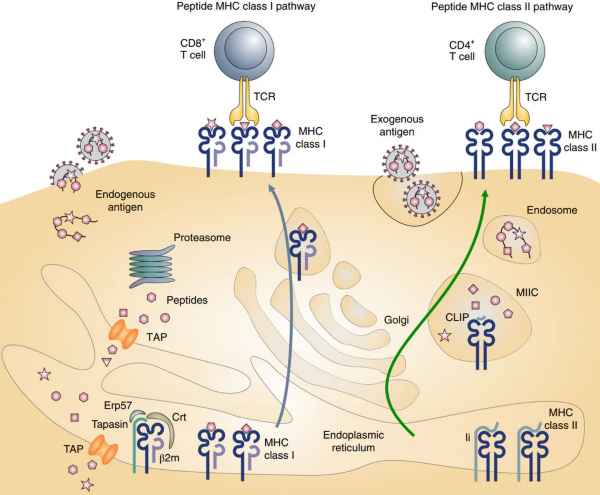
The MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex) is a major histocompatibility complex, which is a highly polymorphic family of cell surface proteins, also known as HLA in humans. MHC can bind to peptide fragments of intracellular antigens to form MHC-peptide complexes, which are then transported to the cell surface and recognized by the corresponding T cell receptor (TCR) to initiate an immune response.
In humans, the main types of MHC involved in antigen presentation are MHC I and MHC II. MHC I, after binding antigen peptides, is recognized by CD8+ T cells, while MHC II, after binding peptides, is recognized by CD4+ T cells. MHC-peptide complexes represent a category of intracellular antigen targets. Their unique binding pattern with TCR plays a crucial role not only in adaptive immune processes but also holds significance for TCR-related therapies such as TCR-T development.
MHC Class I (MHC-I)
MHC-I molecules play a crucial role in the immune system by presenting peptide antigens to cytotoxic T cells. These heterotrimers consist of a transmembrane MHC heavy chain, a light chain known as β2-microglobulin (β2m), and an 8-10 peptide antigen. The heavy chain contains two peptide binding domains (α1 and α2), an immunoglobulin-like domain (α3), and a transmembrane region. The folding of the α1 and α2 domains forms a groove where peptide antigens bind to the MHC-I molecule. β2m stabilizes the peptide binding groove and MHC I presentation.
A single nucleated cell expresses 5×10⁵ copies of each MHC I molecule, presenting a variety of peptides simultaneously on the cell surface to CTLs. Accumulating genomic mutations in cancers result in the production of tumor-specific antigens or neoantigens, which can be presented by MHC I molecules of tumor cells to CTLs.
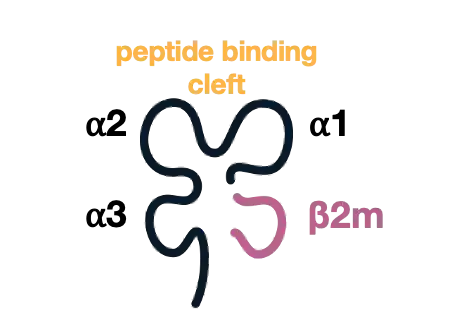
MHC Class 1 complex (MHC-I) containing an α-chain spanning the cell membrane and an extracellular β2m (β2-microglobulin) connected to this chain.
References
1. Kurosawa et al., Development of a T‐cell receptor mimic antibody targeting a novel Wilms tumor 1‐derived peptide and analysis of its specificity. Cancer Sci. 2020 Oct; 111(10): 3516–3526.
2. Doubrovina et al., Mapping of novel peptides of WT-1 and presenting HLA alleles that induce epitope-specific HLA-restricted T cells with cytotoxic activity against WT-1(+) leukemias. Blood. 2012 Aug 23;120(8):1633-46
Quick and simple in-house peptide loading for custom MHC monomers or tetramers
What are prMHCs?
KACTUS peptide-ready MHCs (prMHC) are MHC monomers and tetramers absent of antigenic peptides. The prMHCs are stabilized and ready for loading the neoantigen peptide of your choosing. They are ideal for generating custom MHC peptide tetramers and high throughput peptide screening. The prMHCs are expressed from HEK293 cells and have >95% purity.
Do you offer a peptide-loading protocol?
KACTUS offers a quick and simple protocol for loading peptides in-house. Contact us to receive the protocol.

Class I Peptide-Ready MHC (prMHC).
What can I do with a prMHC?
Assess MHC/TCR Binding Affinity
Enabling rapid and high-quality creation of custom Class I and II MHC tetramers, our Peptide-Ready MHCs (prMHC) provide a streamlined and user-friendly approach to developing new custom MHC monomers and tetramers in just a few minutes directly in your lab. Simply by mixing your peptide of interest with one of our prMHCs and incubating at room temperature, you generate a Peptide-MHC complex, which can be utilized for the creation of custom MHC tetramers and monomers or employed in high-throughput screening of peptides. This innovative system holds applications across various realms including epitope discovery, neoantigen vaccine research, and verification of T cell staining, among others.
Generate a custom MHC peptide monomer or tetramer
In neoantigen identification, assessing the immune functionality of the antigenic peptide is critical, which includes evaluating its binding affinity to MHC and its reactivity with TCR. To facilitate this, KACTUS has introduced a range of functional Peptide-Ready MHCs products. These can serve as a ready-to-use loading system to assist in loading antigen peptides and subsequently form a new, complete MHC peptide complex, thereby significantly aiding your neoantigen research studies by ensuring efficiency and reliability.
High Throughput Peptide Screening
prMHCs are instrumental in the functional screening of peptides for MHC class I binding, a critical component in vaccine design and immune monitoring. They provide the distinct ability to discriminate between MHC binding and non-binding peptides, which is particularly pivotal when screening immunogenic peptides derived from infectious agents or cancer neoantigens. Subsequently, the generated Peptide-MHC complexes can be used for immune monitoring.
Shop Alleles
Browse available alleles in our stabilized peptide-free form.
HLA-A*02:01
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM43RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*02:01&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM43R | Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*02:01&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM43RTC | APC-equivalent Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*02:01&B2M Tetramer Protein | C-His | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*02:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
HLA-A*03:01
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM44RTP | PE-Labeled Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*03:01&B2M Tetramer Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM44RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*03:01&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*03:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
HLA-G
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM45RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-G&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM45R | Human Peptide Ready HLA-G&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-G) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
HLA-A*11:01
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM41RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*11:01&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM41RTP | PE-Labeled Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*11:01&B2M Tetramer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM41R | Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*11:01&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*11:01) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
HLA-A*24:02
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM46RTF | FITC-equivalent Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*24:02&B2M Tetramer Protein | C-His | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM46RTC | APC-equivalent Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*24:02&B2M Tetramer Protein | C-His | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM46RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*24:02&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM46R | Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*24:02&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Thr305(HLA-A*24:02) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
HLA-E*01:03
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| MHC-HM42RB | Biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-E*01:03&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
| MHC-HM42R | Human Peptide Ready HLA-E*01:03&B2M Monomer-Protein | C-His-Avi | Gly25-Ile305(HLA-E*01:03) & Ile21-Met119(B2M) |
Other Alleles
KACTUS supports expression of other MHC alleles including class II alleles and non-human species.
Browse All Available Products
Browse our selection of in-stock Peptide-Ready MHC Complexes.
| Order Now | Type | Allele | Species | Tag | Express system | Purity |
| MHC-HM43R | Monomer | HLA-A*02:01&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM43RB | Biotinylated Monomer | HLA-A*02:01&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM43RTC | APC-Equivalent Tetramer | HLA-A*02:01&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM44R | Monomer | HLA-A*03:01&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM44RB | Biotinylated Monomer | HLA-A*03:01&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM41R | Monomer | HLA-A*11:01&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM41RB | Biotinylated Monomer | HLA-A*11:01&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM42R | Monomer | HLA-E*01:03&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM42RB | Biotinylated Monomer | HLA-E*01:03&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM45R | Monomer | HLA-G&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM45RB | Biotinylated Monomer | HLA-G&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM46R | Monomer | HLA-A*24:02&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
| MHC-HM46RB | Biotinylated Monomer | HLA-A*24:02&B2M | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 | > 95% via Tris-Bis Page & HPLC |
Performance Validation of prMHCs
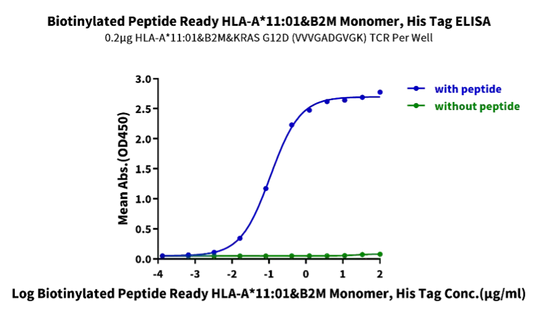
Figure 1. Demonstrated via ELISA assay, biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*11:01&B2M Monomer loaded peptide (VVVGADGVGK) has a high affinity with HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D TCR. The EC50 is 110 ng/mL.
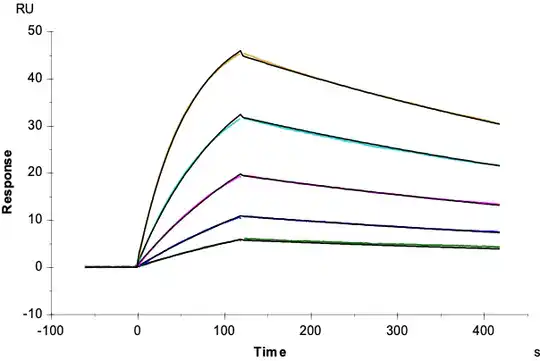
Figure 2. Demonstrated via SPR assay, biotinylated Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*11:01&B2M Monomer loaded with peptide (VVVGADGVGK) has a high affinity with HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D TCR. The affinity constant is 8.5 nM.
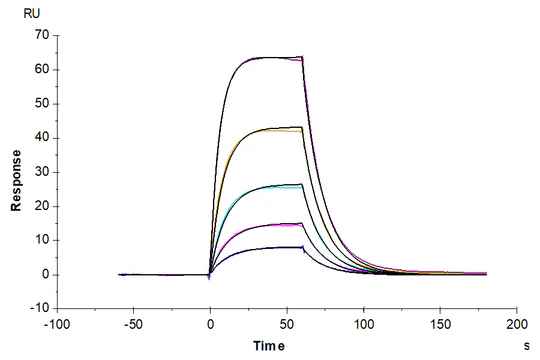
Figure 3. Demonstrated via SPR assay, Human Peptide Ready HLA-A*02:01&B2M& Monomer loaded with peptide (FMNKFIYEI) has a good affinity with HLA-A*02:01&B2M&AFP TCR. The affinity constant is 0.32 µM.
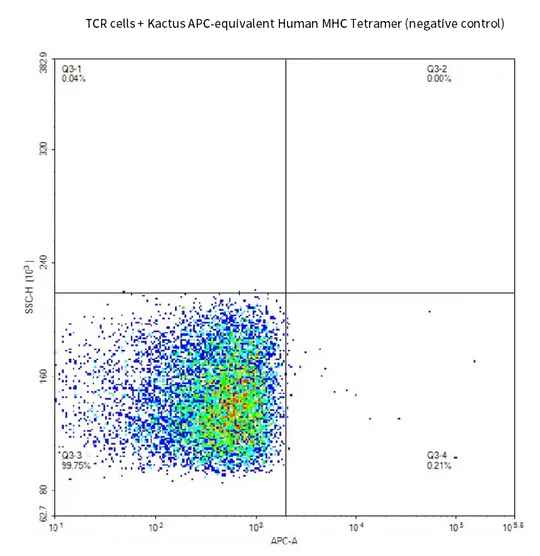
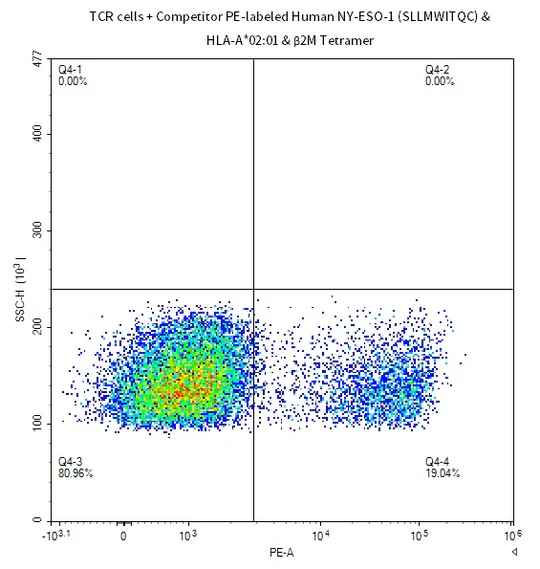
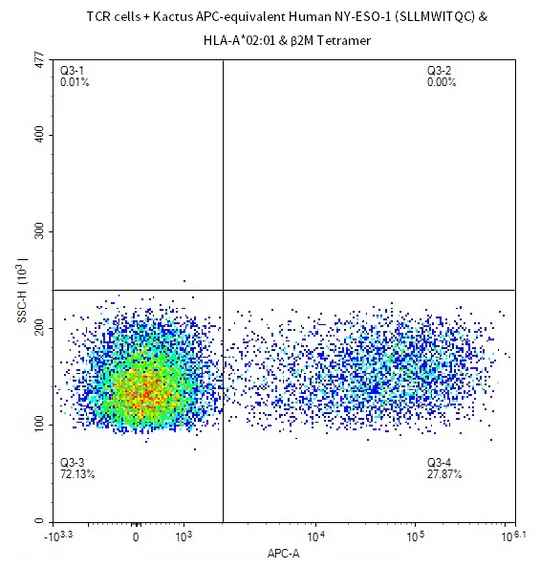
Figure 4. Demonstrated via FACS assay, fluorescent-labeled Human Peptide-Ready HLA-A*02:01&B2M Tetramer loaded with peptide (SLLMWITQC) can bind with HLA-A*02:01&B2M&NY-ESO-1 TCR cells.
Stability Testing of KACTUS prMHCs
Freeze Thaw Stability
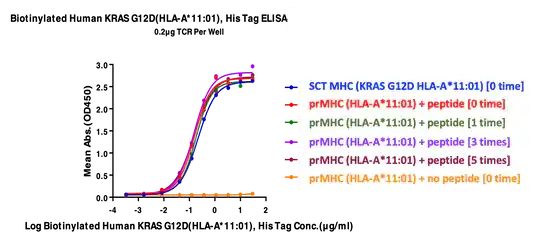
KRAS G12D peptide was added to biotinylated human HLA-A*11:01 and freeze thawed up to five times. Activity was analyzed via ELISA. Immobilized TCR was added to the plate at 2μg/mL (100μL/well). Results are a dose response curve for Biotinylated
Human KRASG12D (HLA-A*11:01), His Tag with EC50s of 0.22/0.16/0.18/0.15/0.15/19 μg/mL.
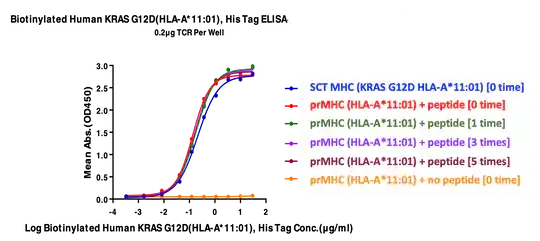
Biotinylated human HLA-A*11:01 was freeze-thawed up to five times after which KRAS G12D peptide was added. Activity was analyzed via ELISA. Immobilized TCR was added to the plate at 2μg/mL (100μL/well). Results are a dose response curve for Biotinylated Human KRASG12D (HLA-A*11:01), His Tag with EC50s of 0.21/0.13/0.18/0.16/0.16 μg/mL.
Stability Testing at 4C
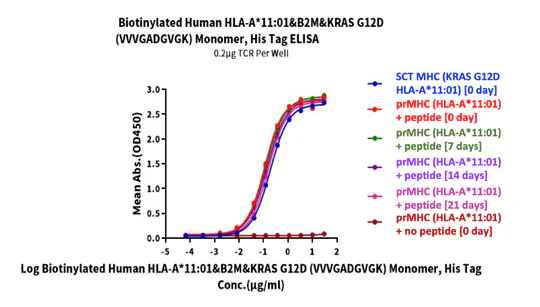
KRAS G12D peptide was added to biotinylated human HLA-A*11:01 and incubated at 4℃ for 0, 7, 14, and 21 days. Activity was analyzed via ELISA. Immobilized TCR was added to the plate at 2µg/mL (100µL/well). Results show a dose-response curve for Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) monomer, His Tag with EC50s of 0.19/0.11/0.13/0.14/0.16 µg/mL.
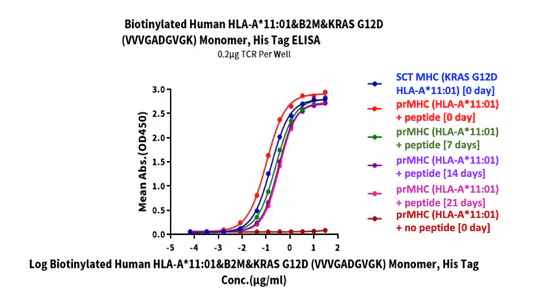
Biotinylated human HLA-A*11:01 was incubated at 4°C for 0, 7, 14, and 21 days, after which KRAS G12D peptide was added. Activity was analyzed via ELISA. Immobilized TCR was added to the plate at 2µg/mL (100µL/well) on the plate. Results show a dose-response curve for Biotinylated Human HLA-A*11:01&B2M&KRAS G12D (VVVGADGVGK) monomer, His tag with EC50s of 0.16/0.11/0.26/0.32/0.36 µg/mL.
Stability Testing at 37C
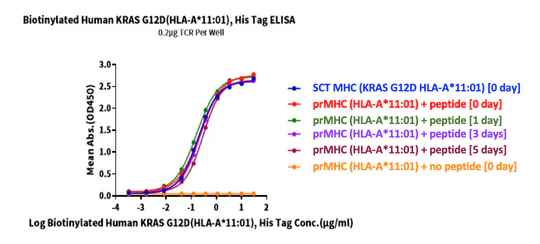
KRAS G12D peptide was added to biotinylated human HLA-A*11:01 and incubated at 37℃ for 0, 1, 3, and 5 days. Activity was analyzed via ELISA. Immobilized TCR was added to the plate at 2µg/mL (100µL/well). Results show a dose response curve for biotinylated human KRAS G12D (HLA-A*11:01), His tag with EC50s of 0.19/0.22/0.16/0.22/0.29/10.56 µg/mL.
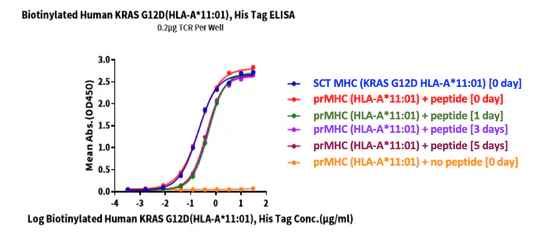
Biotinylated human HLA-A*11:01 was incubated at 37℃ for 0, 1, 3, and 5 days, after which KRAS G12D peptide was added. Activity was analyzed via ELISA. Immobilized TCR was added to the plate at 2µg/mL (100µL/well). Results show a dose-response curve for Biotinylated Human KRAS G12D (HLA-A*11:01), His tag with EC50s of 0.19/0.22/0.52/0.46/0.43 µg/mL.
Neoantigen Peptides and Their Role in MHC/TCR Interactions
Neoantigens are highly specific targets and ideal targets for immunotherapy. Degraded neoantigen peptides can bind with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, forming complexes that are subsequently transported to the cell surface. These complexes are recognized by T-cell receptor (TCR), triggering an immune response. MHC polypeptide complexes constitute a category of neoantigen targets, and their distinctive interaction with TCR holds immense importance in the advancement of neoantigen-based immunotherapies, including TCR-T cell therapy, antibody drugs, and tumor vaccines.
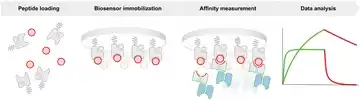
Identification of the affinity of peptide loaded MHC with TCR [1].
prMHC FAQs
Our Products
What prMHC products does KACTUS provide?
KACTUS provides catalog and customized prMHC monomers, biotinylated monomers, and fluorescent tetramers.
What quality control is done for KACTUS prMHCs?
We analyze prMHC products for molecular weight (Tris-Bis PAGE), purity (Tris-Bis PAGE & SEC-HPLC), endotoxin, and concentration. Our prMHC products have > 95% purity and < 1 EU/µg.
Does KACTUS provide custom prMHC class I and prMHC class II molecules?
Yes, KACTUS provides custom prMHC-I and prMHC-II for all available MHC alleles. Contact us at info@stratech.co.uk to request a custom MHC.
What is the shelf life of a prMHC?
prMHCs can be stored for at least 12 months at -80°C.
About Peptide-Ready MHCs
What are prMHCs?
Peptide-ready MHCs (prMHC) is an MHC that doesn’t contain any pre-loaded peptide and can be loaded with custom peptides for TCR binding and cell staining.
What is a prMHC monomer?
A prMHC monomer consists of an α-chain and β-2 microglobulin. It is a single subunit of prMHC tetramer.
What is a biotinylated prMHC monomer?
It is a prMHC monomer with biotin at the C-terminal Avi tag.
What is a fluorescent prMHC tetramer?
A fluorescent prMHC tetramer is a complex of four prMHC monomers with fluorophores conjugated to each monomer subunit of the prMHC complex.
Expression of prMHCs
Are KACTUS prMHCs a proprietary design?
Yes, KACTUS prMHCs are a propriety design based on our SAMS™ Protein Engineering Platform.
Are prMHCs made using single-chain expression?
Yes, prMHC are a single-chain design of α-chain and β-2 microglobulin developed by our protein engineering team.
How are prMHCs purified?
prMHCs are affinity-purified via His tag at the C-terminus with additional size exclusion chromatography steps.
Are the prMHCs expressed in mammalian cells?
Yes, prMHCs are purified from HEK293 cells.
Are the prMHC tetramers made by in vitro assembly using streptavidin?
No, prMHC tetramerize in vivo during expression in HEK293, a KACTUS propriety design.
Fluorescent Labeling
Which fluorophores are available for prMHC tetramers?
We currently offer APC-equivalent, FITC-equivalent and PE conjugation for prMHC tetramers.
What are the properties of APC-equivalent fluorophores?
APC-equivalent is a 90 kDa protein, with excitation peak at 609 nm and emission peak at 643 nm.
Is APC-equivalent labeling done in vitro for prMHC tetramers?
No, APC-equivalent is an in vivo label, part of KACTUS proprietary single chain design for fluorescent prMHC tetramer.
Protocols & Applications
Can you provide a tetramer staining protocol using prMHC?
Yes, contact orders@stratech.co.uk for a protocol.
Can you provide a prMHC peptide loading protocol?
Yes, contact orders@stratech.co.uk for a protocol.
Can KACTUS prMHCs be used for peptide screening?
Yes, KACTUS prMHCs can be used for peptide screening.
References
[1] Moritz A, Anjanappa R, Wagner C, Bunk S, Hofmann M, Pszolla G, Saikia A, Garcia-Alai M, Meijers R, Rammensee HG, Springer S, Maurer D. High-throughput peptide-MHC complex generation and kinetic screenings of TCRs with peptide-receptive HLA-A*02:01 molecules. Sci Immunol. 2019 Jul 19;4(37):eaav0860.
Unlock the Potential of First-in-Class Drug Discovery with Recombinant HLA-G and LILR Products
Novel Combination of Targets in Immune Response and Drug Discovery
LILRs
Leukocyte Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors (LILRs) are a family of receptors primarily expressed on immune cells, playing critical roles in modulating immune responses. They are type I transmembrane glycoproteins characterized by the presence of extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains. LILRs can be activating (LILRAs) or inhibitory (LILRBs), with the inhibitory receptors possessing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) in their cytoplasmic tails. These receptors recognize a variety of ligands, including major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules, and their interaction with these ligands can influence the function of various immune cells, including dendritic cells, macrophages, and T and B lymphocytes.
Through these interactions, LILRs contribute to the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune responses, playing roles in immune tolerance, inflammation, and the defense against pathogens. Their dysregulation has also been implicated in various diseases, including autoimmune conditions, cancer, and infectious diseases. This highlighting their importance in immune
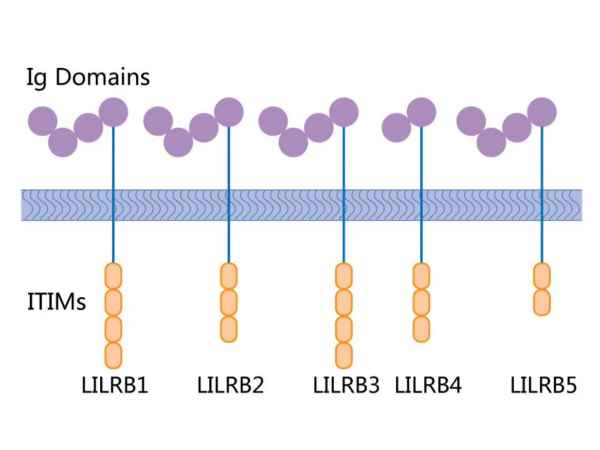
Figure 1. LILRB binding ligands.
HLA-G
MHC-I proteins present antigenic peptides and are recognized by associated receptors. This enables the immune system to detect self-antigens and eliminate targets lacking self-antigens or expressing foreign antigens. Human leukocyte antigen G (HLA-G) is a non-classical human MHC class Ib molecule. It is an important immune tolerance molecule in the body, contributing to immune escape or immune cell anergy. In recent years, it has been regarded as a new type of immune checkpoint.
HLA-G, like other immune checkpoints, mediates its function by binding to receptors on immune cells. The known receptors of HLA-G are leukocyte Ig-like receptor subfamily B member 1 (LILRB1) and member 2 (LILRB2) which belong to the Leukocyte Ig-like receptor (LILR) family. LILRs are one kind of these receptors that either activates (LILRA members) or suppresses (LILRB members) immune cell functions. When HLA-G binds to LILRBs, tumor cells can escape the surveillance of the immune system. As LILRBs have a similar immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) like immune checkpoint proteins such as CTLA4 and PD-1, they’ve become hot targets for drug development, especially for discovery of first-in-class drugs.
Multiple clinical/preclinical studies show the potential broad anti-tumor effects of LILR family proteins, such as BND-22 (Biond), IO-202 (Immune Onc), JTX-8064 (Jounce Therapeutics) and NC410 (NextCure). In addition, since the expression profile of HLA-G is significantly different from that of PD-L1, HLA-G antibodies might be able to enhance tumor sensitivity to anti-PD-L1 therapy. This would be a novel breakthrough for patients with tumors that do not respond to anti-PD-L1 therapy.
Performance Validation
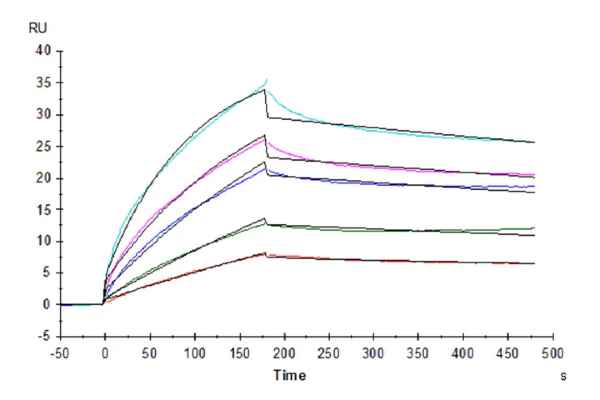
Figure 2. Human LILRB2, hFc Tag captured on CM5 Chip via Protein A can bind Human HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer with an affinity constant of 4.62 nM as determined in SPR assay (Biacore T200).

Figure 3. Rhesus macaque LILRB1, hFc Tag captured on CM5 Chip via Protein A can bind Rhesus macaque HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer, His Tag with an affinity constant of 1.74 nM as determined in SPR assay (Biacore T200).
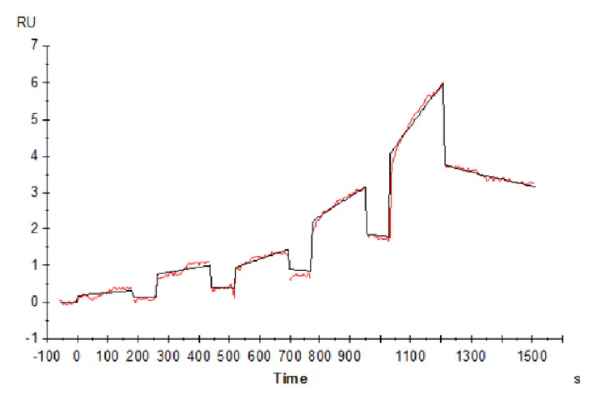
Figure 4. Cynomolgus LILRB2, His Tag immobilized on CM5 Chip can bind Cynomolgus HLA-G Complex Tetramer, His Tag with an affinity constant of 852 nM as determined in SPR assay (Biacore T200).
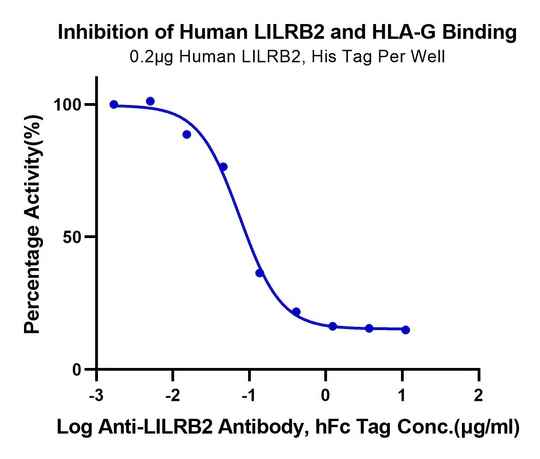
Figure 5. Serial dilutions of Anti-LILRB2 Antibody were added into Human LILRB2, His Tag : Biotinylated HLA-G Complex Tetramer, His Tag binding reactioins. The half maximal inhibitiory concentration (IC50) is 75.3ng/ml.
Product Lists
HLA-G Products
KACTUS has developed a full portfolio of mammalian-expressed HLA-G monomers and tetramers including biotinylated versions. Our HLA-G monomers and tetramers are mammalian-expressed from HEK293 cells and have >95% purity with low endotoxin (<1EU/ug). HLA-G monomers and tetramers can be used for antibody discovery, TCR binding, and flow cytometry. We also offer custom HLA-G tetramers. Contact us today to learn more.
| Catalog # | Species | Tag | Target | Express System |
| HLG-HE41F | Human | C-His-Avi | HLA-G Free Heavy Chain | E.coli |
| HLG-HM41CB | Human | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer | HEK293 |
| HLG-CM41CB | Cynomolgus | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer | HEK293 |
| HLG-CM41C | Cynomolgus | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer | HEK293 |
| HLG-HM41C | Human | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer | HEK293 |
| HLG-RM41C | Rhesus macaque | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Monomer | HEK293 |
| HLG-HM41CTB | Human | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer | HEK293 |
| HLG-CM41CT | Cynomolgus | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer | HEK293 |
| HLG-HM41CT | Human | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer | HEK293 |
| HLG-HM41CTP | Human | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer | HEK293 |
| HLG-RM41CT | Rhesus macaque | C-His-Avi | HLA-G&B2M&Peptide (RIIPRHLQL) Tetramer | HEK293 |
| MHC-HM45RB | Human | C-His-Avi | Peptide Ready HLA-G&B2M Monomer | HEK293 |
| MHC-HM45R | Human | C-His-Avi | Peptide Ready HLA-G&B2M Monomer | HEK293 |
LILRA, LILRB, and APOE Products
Using our SAMS protein engineering platform, we have developed a large portfolio of LILRA and LILRB catalog products. These products are expressed from HEK293 cells and are available in multiple species, including human, mouse, cynomolgus, and rhesus macaque as well as biotinylated versions. Contact us today to request a custom LILR.
| Catalog # | Target | Species | Biotinylated | Tag | Exact Sequence | Express System |
| APO-MM102 | APOE/Apolipoprotein E | Mouse | No | C-His | Glu19-Gln311 | HEK293 |
| APO-MM202 | APOE/Apolipoprotein E | Mouse | No | C-hFc | Glu19-Gln311 | HEK293 |
| APO-HM101B | APOE3/Apolipoprotein E | Human | Yes | N-His | Lys19-His317 | HEK293 |
| APO-HM101 | APOE3/Apolipoprotein E | Human | No | N-His | Lys19-His317 | HEK293 |
| APO-HM203 | APOE3/Apolipoprotein E | Human | No | N-hFc | Lys19-His317 | HEK293 |
| APO-HM202 | APOE4/Apolipoprotein E | Human | No | N-hFc | Lys19-His317 | HEK293 |
| APO-HM102 | APOE4/Apolipoprotein E | Human | No | N-His | Lys19-His317 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A1 | LILRA1/CD85i/LIR-6 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Pro17-Asn461 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A1B | LILRA1/CD85i/LIR-6 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Pro17-Asn461 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A2 | LILRA2/CD85h/ILT1 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gly24-Asn449 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A2B | LILRA2/CD85h/ILT1 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gly24-Asn449 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A3B | LILRA3/CD85e | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gly24-Glu439 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A3 | LILRA3/CD85e | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gly24-Glu439 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM1A4 | LILRA4/CD85g | Cynomolgus | No | C-His | Glu24-Asn446 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A4 | LILRA4/CD85g | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Glu24-Asn446 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A4B | LILRA4/CD85g | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Glu24-Asn446 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A5B | LILRA5/CD85f/ILT11 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gly42-Arg268 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A5 | LILRA5/CD85f/ILT11 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gly42-Arg268 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A6 | LILRA6/CD85b/ILT8 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gly24-Asn447 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4A6B | LILRA6/CD85b/ILT8 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gly24-Asn447 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM1A6 | LILRA6/CD85b/ILT8 | Cynomolgus | No | C-His | Gly41-His474 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM1B3 | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Rhesus macaque | No | C-His | Met1-His474 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM1B1 | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Rhesus macaque | No | C-His | Ser17-His456 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM2B1 | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Rhesus macaque | No | C-hFc | Ser17-His456 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM2B3 | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Rhesus macaque | No | C-hFc | Met1-His474 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM13D | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Human | No | C-His | Leu116-Val461 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM2B1 | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Human | No | C-hFc | Gly24-His458 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM3B1 | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Human | No | C-mFc | Gly24-His458 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B1B | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gly24-His458 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B1 | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gly24-His458 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM1RB | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 | Cynomolgus | No | C-His | Gly41-His474 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM11D | LILRB1/CD85j/ILT2 Domain1&2 | Human | No | C-His | Gly24-Gly221 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM1B2 | LILRB2/CD85d/ILT4 | Cynomolgus | No | C-His | Gly24-Arg457 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM2B2 | LILRB2/CD85d/ILT4 | Cynomolgus | No | C-hFc | Gly24-Arg457 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM2B2 | LILRB2/CD85d/ILT4 | Human | No | C-hFc | Gln22-His458 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM3B2 | LILRB2/CD85d/ILT4 | Human | No | C-mFc | Gln22-His458 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B2 | LILRB2/CD85d/ILT4 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gln22-His458 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B2B | LILRB2/CD85d/ILT4 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gln22-His458 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM12D | LILRB2/CD85d/ILT4 Domain1&2 | Human | No | C-His | Gln22-Val229 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B3 | LILRB3/CD85a/ILT5 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gly24-Glu443 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B3B | LILRB3/CD85a/ILT5 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gly24-Glu443 | HEK293 |
| LIL-CM1B4 | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 | Cynomolgus | No | C-His | Gln22-Glu259 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM2B4 | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 | Human | No | C-hFc | Gln22-Arg256 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B4 | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gln22-His257 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B4B | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gln22-His257 | HEK293 |
| LIL-MM1B4 | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 | Mouse | No | C-His | Gly24-Lys238 | HEK293 |
| LB4-HM1D1 | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 Domain 1 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gln22-Thr118 | HEK293 |
| LB4-HM1D1B | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 Domain 1 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gln22-Thr118 | HEK293 |
| LB4-HM4D4 | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 Domain 1+hinge | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Gln22-Lys123 | HEK293 |
| LB4-HM4D4B | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 Domain 1+hinge | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gln22-Lys123 | HEK293 |
| LB4-HM1D3B | LILRB4/CD85k/ILT3 Domain 2 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Gly119-Glu259 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B5 | LILRB5/CD85c/LIR-8 | Human | No | C-His-Avi | Arg18-His456 | HEK293 |
| LIL-HM4B5B | LILRB5/CD85c/LIR-8 | Human | Yes | C-His-Avi | Arg18-His456 | HEK29 |
Obtain a physiologically relevant culture surface for pluripotent stem cell maintenance, expansion, and differentiation.
Research-Grade & Preclinical-Grade Laminin 521
Matrix protein for maintenance of pluripotent stem cells.
KACTUS has successfully developed a high-quality Laminin 521 product that can be applied to scientific research (research-grade) and preclinical development (preclinical-grade). It can effectively support the normal growth and passage of PSCs, maintain good stemness, and ensure the homogeneous growth of cells with genetic stability. Laminin 521 can be applied to the cultivation of stem cells and other primary cells and the development of related stem cell products.
Order Now
KACTUS Laminin 521 Features
Use on Various Cell Types
Applicable to a wide range of cells: iPSCs, hMSCs & most anchorage-dependent progenitor cell types
Expect Quality
> 95% Purity
Low Internal Toxicity (<10EU/mg)
Transition to Feeder-Free Culture
Compatible with a variety of feeder-free stem cell culture media
Maintain Growth
Maintain homogeneous growth and karyotype stability of stem cells
Recombinant Laminin for Stem Cell Culture
Due to their unique ability for self-renewal and directional differentiation, stem cells can be applied in many fields such as embryonic development research, drug screening modeling, and cell therapy. At the same time, stem cell culture methods continue to be optimized. Laminin 521 is an important matrix adhesion protein, which can recreate a suitable growth environment for primary cells such as stem cells, and is currently one of the most commonly used trophoblast-free culture substrates.
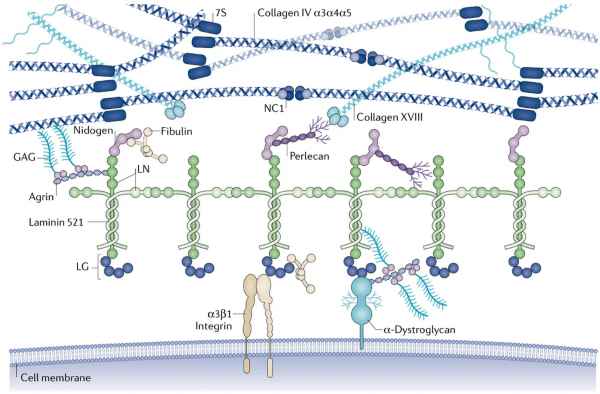
Figure 1. The main components of globular basement membrane (GBM) [2].
Laminin 521 can maintain the pluripotency of stem cells, promote cell proliferation, support the clonal expansion of pluripotent human stem cells and the growth of skin keratinocytes. It is also involved in the regulation of important physiological processes such as cell adhesion, migration, differentiation, phenotype maintenance, and matrix-mediated signal transduction [3]. Compared with Laminin 511, Laminin 521 can support the monolayer maintenance and expansion of stem cells in the absence of apoptosis inhibitors (such as ROCK inhibitors). It can be an excellent alternative to Laminin 511 and to some extent, is more suitable for human pluripotency stem cell culture than Laminin 511.
What are the applications of Laminin 521?
Stem Cell Expansion Culture
Laminin 521 can support the low-density growth and self-renewal of stem cells in a chemically defined, animal-free environment. It is suitable for the culture of hSC, iSC and cloned stem cells, such as hPSC [4], MSC, hematopoietic stem cells, etc.
Directed Differentiation of Stem Cells
Laminin 521 promotes the differentiation of hPSCs into different cell types such as hepatocytes, cardiomyocytes, retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells [5] and endothelial cells [6]. hESCs grown on Laminin 521 can exhibit molecular phenotypic characteristics of hepatocytes and undergo cell self-organization [7].
Organoid Culture
Indeterminate media replacing Matrigel is a major target for organoid culture, and full-length laminin (rather than laminin-derived peptides) has been shown to be a key component for the correct formation of organoids in gel models. Lucendo-Villarin and collaborators developed an economical automated platform for the generation of human hepatic spheroids from pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatic progenitors, endothelial cells, and hepatic stellate cells with the help of laminin 521, which can be used in disease modeling and drug screening research [8].
Growth Maintenance of Differentiated Primary Cells
Laminin 521 can support the growth and proliferation of differentiated primary cells, such as cardiomyocytes, retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells, nerve cells, endothelial cells, islet cells, etc. For example, the basement membrane damage of the isolated islets will cause islet function decline and cell death, but when cultured on a matrix containing Laminin 521, it can significantly promote the survival and function maintenance of islet cells [9], and has now been successfully applied in the original Generation islet cell culture system. Likewise, cardiac progenitor cells differentiated in vitro can proliferate on Laminin 521-containing matrices and transform into mature cardiomyocytes.
Drug Research
Laminin 521 is a new anti-GBM disease pulmonary hemorrhage autoantibody target. Studies have shown that in anti-glomerular basement membrane disease, circulating antibodies can recognize Laminin 521 in addition to type IV collagen, indicating that Laminin 521 is Another major autoantigen against GBM [10], autoantibodies against Laminin 521 may promote lung injury and lead to pulmonary hemorrhage by increasing the total amount of IgG bound to the alveolar basement membrane, which provides theoretical clues for the development of related drugs.
Maintain Expression of Stem Cell Markers & iPSC Growth In Vitro
KACTUS Laminin 521 was pre-coated with 0.5µg/cm² in a 6-well dish, seeding the thawed iPSC cells at a concentration of 1×10⁴/cm². After 5 days of culture, stem cell markers were detected via flow cytometry.
Figure 2. Normal expression of stem cell markers OCT3/4, SOX2, SSEA4, TRA-1-60, etc.:

Figure 3. Laminin 521 can effectively maintain the growth of human iPSCs.
What is Laminin 521?
Laminin 521 (LN521, LAMB2, LN-11) is a heterotrimeric glycoprotein composed of α5, β2 and γ1 chains, expressed in stem cells and most basement membranes (especially in the nerve sheath, muscle nerve junction and glomerular basement membrane GBM). It is a key matrix protein that supports the growth of stem cells and maintains the stability and performance of the basement membrane.
Laminin 521 can form a huge net-like material environment together with nestin, collagen, fibronectin, glycosaminoglycan, and other extracellular matrix components. It is a key supportor of various tissues such as muscle fiber, epithelium, nerve, capillaries, fat, etc. In addition, the LG1-5 region of Laminin 521 can bind to cell membrane surface integrin α6β1 or α3β1, etc., start the downstream PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, and promote cell proliferation.
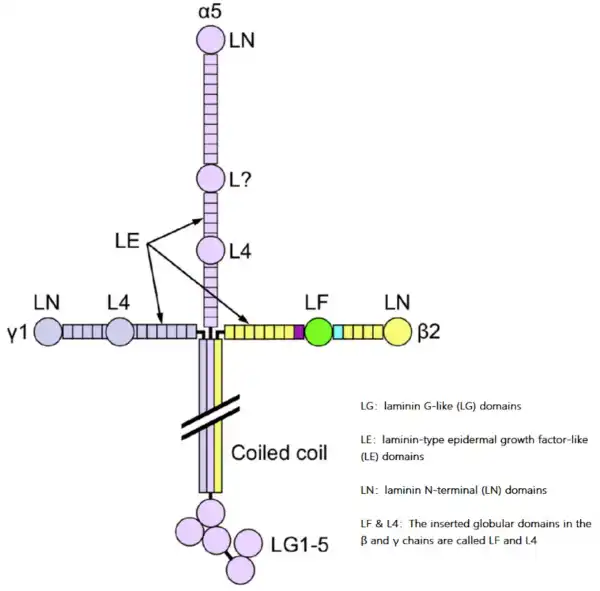
Figure 4. Laminin 521 structure [1].
How do I use Laminin 521?
General recommended procedure:
1. Coat the cell culture flask/dish with Laminin 521 (a typical dosage is 0.5 μg/cm² but this can vary depending on the experiment).
2. Wash the cells and incubate with digestive enzymes or EDTA.
3. Separate into a single cell suspension, centrifuge, and resuspend in appropriate fresh medium.
4. Seed cells on culture flask/dish coated with Laminin 521.
References
[1] Pulido D, Briggs DC, Hua J, Hohenester E. Crystallographic analysis of the laminin β2 short arm reveals how the LF domain is inserted into a regular array of LE domains. Matrix Biol. 2017 Jan;57-58:204- 212.
[2] Naylor RW, Morais MRPT, Lennon R. Complexities of the glomerular basement membrane. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Feb;17(2):112-127.
[3] Yap L, Tay HG, Nguyen MTX, Tjin MS, Tryggvason K. Laminins in Cellular Differentiation. Trends Cell Biol. 2019 Dec;29(12):987-1000.
[4] Dziedzicka D, Markouli C, Barbé L, Spits C, Sermon K, Geens M. A High Proliferation Rate is Critical for Reproducible and Standardized Embryoid Body Formation from Laminin-521-Based Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cultures. Stem Cell Rev Rep . 2016 Dec;12(6):721-730.
[5] Lynch VJ, Nnamani MC, Kapusta A, Brayer K, Plaza SL, Mazur EC, Emera D, Sheikh SZ, Grützner F, Bauersachs S, Graf A, Young SL, Lieb JD, DeMayo FJ, Feschotte C, Wagner GP . Ancient transposable elements transformed the uterine regulatory landscape and transcriptome during the evolution of mammalian pregnancy. Cell Rep. 2015 Feb 3;10(4):551-61.
[6] Nguyen MTX, Okina E, Chai X, Tan KH, Hovatta O, Ghosh S, Tryggvason K. Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells to Endothelial Progenitor Cells on Laminins in Defined and Xeno-free Systems. Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Oct 11;7(4):802-816.
[7] Cameron K, Tan R, Schmidt-Heck W, Campos G, Lyall MJ, Wang Y, Lucendo-Villarin B, Szkolnicka D, Bates N, Kimber SJ, Hengstler JG, Godoy P, Forbes SJ, Hay DC. Laminins Drive the Differentiation and Self-Organization of hESC-Derived Hepatocytes. Stem Cell Reports. 2015 Dec 8;5(6):1250-1262.
[8] Meseguer-Ripolles J, Kasarinaite A, Lucendo-Villarin B, Hay DC. Protocol for automated production of human stem cell derived liver spheres. STAR Protoc. 2021 Apr 30;2(2):100502.
[9] Brandhorst D, Brandhorst H, Lee Layland S, Acreman S, Schenke-Layland K, Johnson PRV. Basement membrane proteins improve human islet survival in hypoxia: Implications for islet inflammation. Acta Biomater. 2022 Jan 1;137:92- 102.
[10] Shen CR, Jia XY, Luo W, Olaru F, Cui Z, Zhao MH, Borza DB. Laminin-521 is a Novel Target of Autoantibodies Associated with Lung Hemorrhage in Anti-GBM Disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Aug ;32(8):1887-1897.
About CAR-T Therapy
Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T-cell (CAR-T) therapy is a novel immunotherapy approach that has achieved remarkable success in the treatment of a variety of hematological malignancies. The basis of CAR-T therapy is to make the immune system attack cancer cells. Briefly, patient T cells are isolated and genetically engineered to express a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) that recognizes specific tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) such as CD19, a cell surface protein that is uniformly and strongly expressed on malignant B cells. Two new FDA-approved CD19-specific drugs, KymriahTM and YescartaTM, demonstrate the importance of TAAs in CAR-T cell therapy research.
Utilizing our SAMSTM platform, KACTUS has developed a series of recombinant proteins covering multiple CAR-T cell therapeutic targets, including difficult-to-express proteins such as CD19 and BCMA. We offer various types of highly active CAR-T target antigen proteins, including site-directed labeled proteins, fluorescent labeled proteins, biotin-labeled proteins, etc., which can flexibly meet different research and development needs such as CAR-T positive rate detection.
Performance Validation
Human FITC Compatible CD19
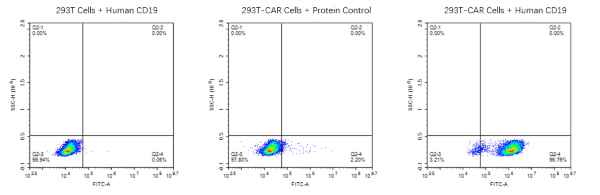
Figure 1. Use Human CD19-FITC Compatible protein to detect the expression rate of Anti-CD19-CAR positive cells. Non-transfected 293T cells and FITC-labeled protein control were used as negative control.
PE-Labeled Human EGFR VIII
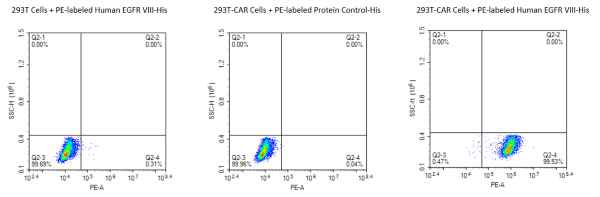
Figure 2. 293T-CAR Cells were incubated with PE-Labeled Human EGFR VIII, His Tag and PE-labeled protein control. Non-transfected 293T cells and PE-labeled protein control were used as negative control.
Biotinylated Human MSLN
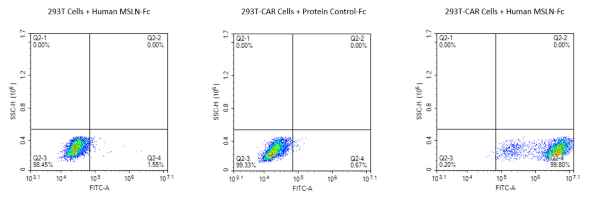
Figure 3. Anti-MSLN CAR-293T cells were incubated with Biotinylated human MSLN-hFc-Avi Tag. Non-transfected 293T cells and Fc-labeled protein control were used as negative control. SA-FITC was used to evaluate the binding activity of Biotinylated Human MSLN.
| Catalog No. | Description | Product Tag | Exact Sequence |
| ITG-HM461 | Human Integrin alpha 6 beta 1 (ITGA6&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe24-Gly1012 (ITGA6) acidic tail & GIn21-Asp728 (ITGB1) basic tail |
| ITG-MM4V3B | Biotinylated Mouse Integrin alpha V beta 3 (ITGAV&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val988(ITGAV)acidic tail & Glu26-Asp717(ITGB3)basic tail |
| ITG-HM18B | Human Integrin alpha 8 beta 1 (ITGA8&ITGB1) -Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe39-Leu1012(ITGA8) acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1) basic tail |
| ITG-CM1V3 | Cynomolgus Integrin alpha V beta 3 (ITGAV&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe31-Pro993(ITGAV)acidic tail & Gly27-Asp718(ITGB3)basic tail |
| ITG-HM2V3 | Human Integrin alpha V beta 3 (ITGAV&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-hFc | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV)acidic tail & Gly27-Asp718(ITGB3)basic tail |
| ITG-HM110 | Human Integrin alpha 10 beta 1 (ITGA10&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe23-Ser1122(ITGA10)acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1)basic tail |
| ITG-MM110 | Mouse Integrin alpha 10 beta 1 (ITGA10&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe23-Leu1119(ITGA10)acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1)basic tail |
| ITG-MM1V3 | Mouse Integrin alpha V beta 3 (ITGAV&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe31-Val988(ITGAV)acidic tail & Glu26-Asp717(ITGB3)basic tail |
| ITG-MM2V3 | Mouse Integrin alpha V beta 3 (ITGAV&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-hFc | Phe31-Val988(ITGAV)acidic tail & Glu26-Asp717(ITGB3)basic tail |
| ITG-HM4V6B | Biotinylated Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 (ITGAV&ITGB6) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV) acidic tail & Gly22-Asn707(ITGB6) basic tail |
| ITG-MM1A1 | Mouse Integrin alpha 1 beta 1 (ITGA1&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe29-Pro1141(ITGA1)acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1)basic tail |
| ITG-MM1LB | Mouse Integrin alpha L beta 2 (ITGAL&ITGB2) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Tyr24-His1087 (ITGAL) acidic tail & Gln24-Asn702 (ITGB2) basic tail |
| ITG-HM4V3B | Biotinylated Human Integrin alpha V beta 3 (ITGAV&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV) acidic tail & Gly27-Asp718(ITGB3) basic tail |
| ITG-HM4V5B | Biotinylated Human Integrin alpha V beta 5 (ITGAV&ITGB5) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV)acidic tail & Gly24-Asn719(ITGB5)basic tail |
| ITG-HM4V8B | Biotinylated Human Integrin alpha V beta 8 (ITGAV&ITGB8) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV) acidic tail & Glu43-Arg684(ITGB8) basic tail |
| ITG-HM451B | Biotinylated Human Integrin alpha 5 beta 1 (ITGA5&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe42-Tyr995(ITGA5)acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1)basic tail |
| ITG-RM1V8 | Rhesus macaque Integrin alpha V beta 8 (ITGAV&ITGB8) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe31-Pro993(ITGAV) acidic tail & Glu43-Ser681(ITGB8) basic tail |
| ITG-RM1V6 | Rhesus macaque Integrin alpha V beta 6 (ITGAV&ITGB6) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe31-Pro993(ITGAV) acidic tail & Gly22-Asn707(ITGB6) basic tail |
| ITG-MM1V8 | Mouse Integrin alpha V beta 8 (ITGAV&ITGB8) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe31-Val988(ITGAV)acidic tail & Gly22-Ser679(ITGB8)basic tail |
| ITG-MM1V6 | Mouse Integrin alpha V beta 6 (ITGAV&ITGB6) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe31-Val988(ITGAV)acidic tail & Gly22-Asn706(ITGB6)basic tail |
| ITG-MM1AB | Mouse Integrin alpha 2 beta 1 (ITGA2&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Tyr27-Thr1129(ITGA2) acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1) basic tail |
| ITG-MM12B | Mouse Integrin alpha 2B beta 3 (ITGA2B&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Leu32-Arg988(ITGA2B) acidic tail & Glu26-Asp717(ITGB3) basic tail |
| ITG-HM4V8 | Human Integrin alpha V beta 8 (ITGAV&ITGB8) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV) acidic tail & Glu43-Arg684(ITGB8) basic tail |
| ITG-HM4V5 | Human Integrin alpha V beta 5 (ITGAV&ITGB5) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV)acidic tail & Gly24-Asn719(ITGB5)basic tail |
| ITG-HM4V6 | Human Integrin alpha V beta 6 (ITGAV&ITGB6) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV) acidic tail & Gly22-Asn707(ITGB6) basic tail |
| ITG-HM4V3 | Human Integrin alpha V beta 3 (ITGAV&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe31-Val992(ITGAV)acidic tail & Gly27-Asp718(ITGB3)basic tail |
| ITG-HM451 | Human Integrin alpha 5 beta 1 (ITGA5&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His-Avi | Phe42-Tyr995(ITGA5) acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1) basic tail |
| ITG-HM1XB | Human Integrin alpha X beta 2 (ITGAX&ITGB2) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe20-Pro1107(ITGAX) acidic tail & Gln23-Asn700(ITGB2) basic tail |
| ITG-HM1AB | Human Integrin alpha 2 beta 1 (ITGA2&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Tyr30-T1132(ITGA2) acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1) basic tail |
| ITG-HM1A1 | Human Integrin alpha 1 beta 1 (ITGA1&ITGB1) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Phe29-Pro1141(ITGA1) acidic tail & Gln21-Asp728(ITGB1) basic tail |
| ITG-HM12B | Human Integrin alpha 2B beta 3 (ITGA2B&ITGB3) Heterodimer Protein | C-His | Leu32-Arg993(ITGA2B) acidic tail & GLy27-Asp718(ITGB3) basic tail |
Soluble TCR Expression & SPR Characterization Services
Service Features

Production of various formats of soluble TCRs, including scFv-TCR, TCR-His, etc.
TCR engineering to optimize soluble TCR expression based on TCR modeling
SPR analysis of soluble TCR & Peptide-Ready MHC/Peptide-MHC interactions
SPR Characterization Services to Combat TCRs with Low Binding Affinity
TCRs often have low binding affinity to Peptide-MHCs (pMHC) which makes characterization via ELISA difficult. Alternatively, SPR is well suited for characterizing TCRS with low binding affinity. In addition to soluble TCR expression, we also offer SPR analysis services for characterizing the binding between TCRs and Peptide-MHCs or Peptide-Ready MHCs.
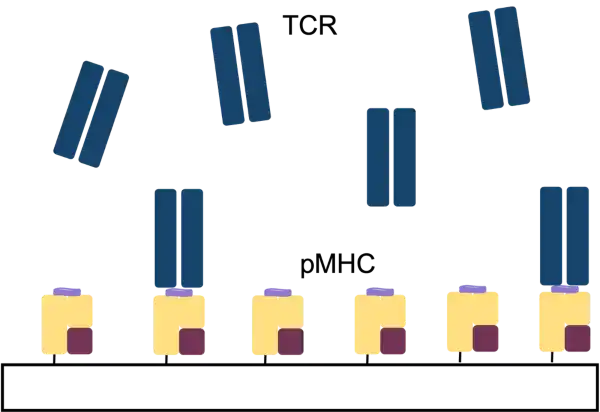
TCR Binding with Peptide-Ready MHC & Peptide-MHC
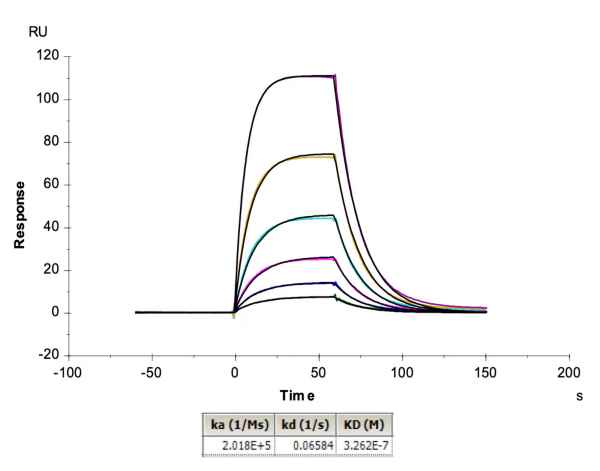
(A)
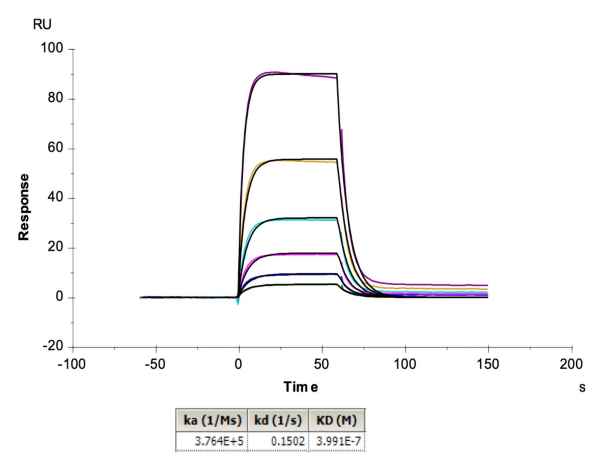
(B)
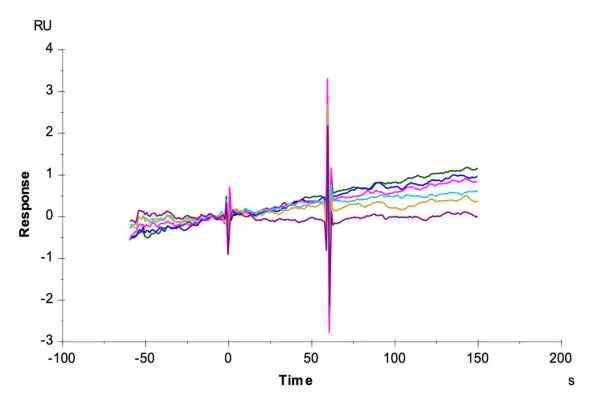
(C)
| Figure | Ligand | Analyte | ka (1/Ms) | kd (1/s) | KD (M) |
| A | prMHC + FMNKFIYEI | AFP specific TCR | 202000 | 0.0658 | 3.26e-7 |
| B | AFP pMHC | AFP specific TCR | 376000 | 0.15 | 3.99e-7 |
| C | prMHC (no peptide) | AFP specific TCR | / | / | No Binding |
Figure 1. HLA-A*02:01 neoantigen loading efficiency in Peptide-Ready MHC loaded with FMNKFIYEI peptide (A), Peptide-MHC with FMNKFIYEI peptide (B), and MHC with no peptide (C).
Peptide-MHCs, Peptide-Ready MHCs, & Soluble TCR Expression
Get full support for your TCR therapy drug development endeavors with our comprehensive customized TCR and Peptide-MHC complex expression services.
Expression Validation: gp100 TCR & Anti-CD3 Bispecific Fusion Protein
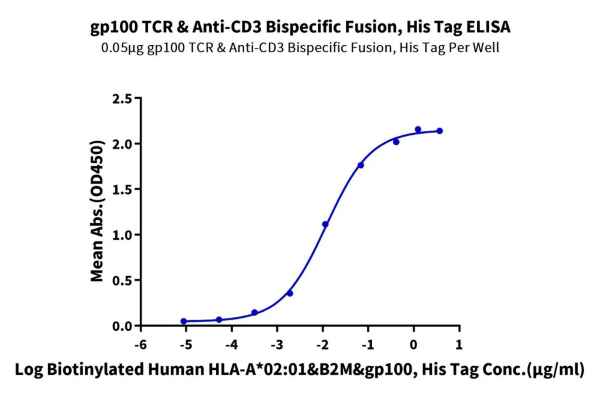
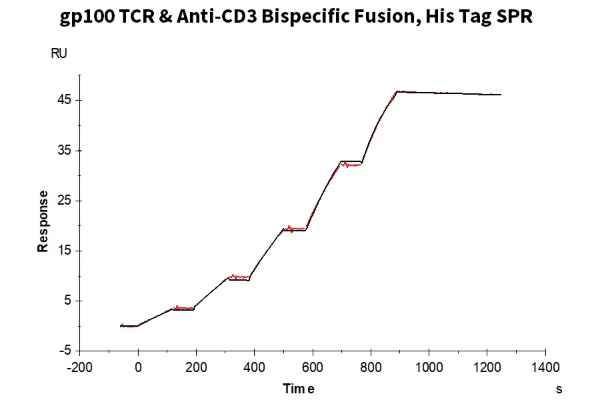
Figure 2. We have successfully expressed Tebentafusp, which not only binds to the GP100 (HLA-A*02:01) complex but also simultaneously binds to CD3 heterodimers, demonstrating excellent bidirectional binding activity. In ELISA (left) and SPR (right) analyses, Tebentafusp can bind to both monomers and tetramers of Human GP100 (HLA-A*02:01) complex, with an EC50 and affinity constant of 11.8 ng/mL and 0.196 nM, respectively.
About TCR Therapy
What is TCR Therapy?
TCR therapy is a novel immunotherapy developed based on the recognition pattern between the body’s TCR and antigens. It includes two forms: T cell transfer therapy (TCR-T) and TCR protein drugs (TCR-scfv, TCR mimic antibodies, etc.). Among them, the principle of TCR-T involves first screening and validating TCR sequences that can recognize antigens. Through genetic engineering, these sequences are integrated into the patient’s T cells, equipping them with the ability to selectively bind to and eliminate tumor cells expressing the target antigens. In this context, “antigen” refers to complexes formed by MHC (or HLA) with intracellular antigen peptides. Through this unique recognition mechanism, TCR-T can target a wider range of intracellular antigens, leading to more pronounced effects in solid tumors.
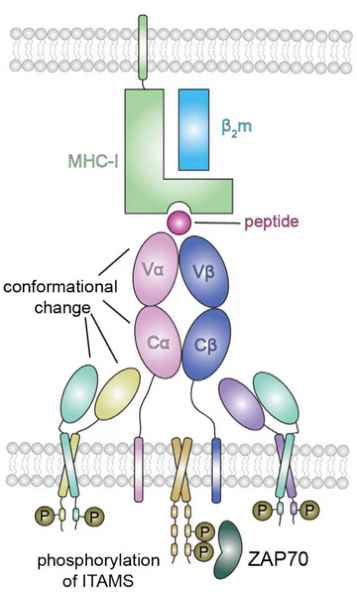
Figure 3. TCR Recognition of MHC-Peptide Complex [2]
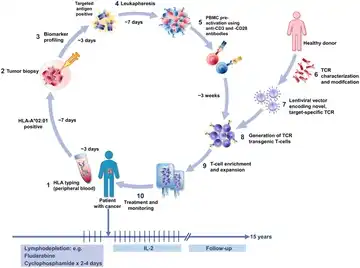
Figure 4. TCR-T Treatment Process [3]
Advantages of TCR Therapy
High specificity and sensitivity are prominent features of TCR-T therapy, especially in generating robust T cell responses against low-density antigen populations. Additionally, it exhibits a lower probability of cytokine release syndrome. Furthermore, compared to CAR, TCRs often possess lower affinity and faster dissociation, enabling continuous triggering of recognition responses and facilitating the amplification of immune signals.
CR-scfv & TCR Mimic Antibodies
TCR-scfv (single chain variable fragment) and TCR mimic antibodies represent a novel class of protein engineering techniques, focusing directly on the development of protein drugs using TCR or TCR-like structures. This approach eliminates the need for genetic engineering and T cell transfer, resulting in a simpler manufacturing process and providing a more streamlined treatment option for clinical use. A representative drug in this category is Tebentafusp, currently the only approved TCR therapy on the market. It can simultaneously recognize the GP100 peptide-(HLA*02:01) complex and CD3.
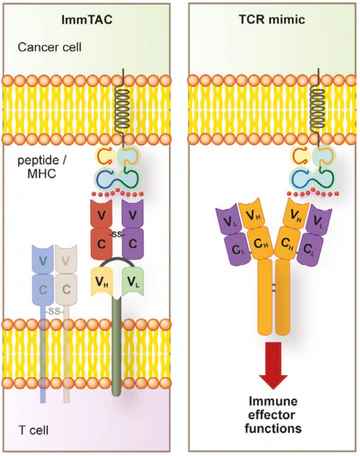
Figure 5. TCR-T Treatment Process [3]
References
[1] http://www.scgcell.com/
[2] Natarajan K, Jiang J, May NA, Mage MG, Boyd LF, McShan AC, Sgourakis NG, Bax A, Margulies DH. The Role of Molecular Flexibility in Antigen Presentation and T Cell Receptor-Mediated Signaling. Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 17;9:1657.
[3] Tsimberidou AM, Van Morris K, Vo HH, Eck S, Lin YF, Rivas JM, Andersson BS. T-cell receptor-based therapy: an innovative therapeutic approach for solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jun 30;14(1):102.
[4] Chandran SS, Klebanoff CA. T cell receptor-based cancer immunotherapy: Emerging efficacy and pathways of resistance. Immunol Rev. 2019 Jul;290(1):127-147.
References
[1] Fang KK, Lee JB, Zhang L. Adoptive Cell Therapy for T-Cell Malignancies. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;15(1):94.
[2] Mangal JL, Handlos JL, Esrafili A, Inamdar S, Mcmillian S, Wankhede M, Gottardi R, Acharya AP. Engineering Metabolism of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Cells for Developing Efficient Immunotherapies. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 5;13(5):1123.
[3] Maalej KM, Merhi M, Inchakalody VP, Mestiri S, Alam M, Maccalli C, Cherif H, Uddin S, Steinhoff M, Marincola FM, Dermime S. CAR-cell therapy in the era of solid tumor treatment: current challenges and emerging therapeutic advances. Mol Cancer. 2023 Jan 30;22(1):20.