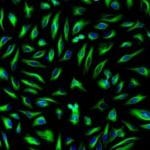
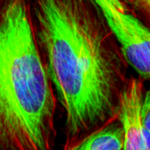
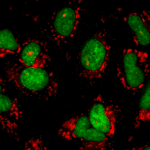
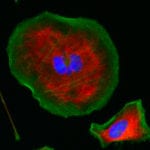
Bioconjugation is the technique of covalently binding molecules, at least one of which is a biomolecule such as a protein. These linked biomolecules serve functions ranging from drug delivery to imaging cellular functions. Bioconjugate synthesis involves optimization of procedural design and material selection. The stability of the resulting molecule will need to be sufficient to maintain its chemical integrity throughout all further experimental processing, including permeabilization and fixation if necessary. To retain experimental relevance, the conjugation procedure also must not compromise the essential functional properties of the unlabeled molecules.