ELISA, or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, is a plate-based immunoassay used to detect and quantify biomolecules such as antibodies, proteins, hormones or peptides, as well as for the characterization of protein-protein and protein-nucleic acid interactions. In an ELISA, the target of interest, typically an antigen, is immobilized onto a solid surface and subsequently probed with an antibody conjugated to an enzyme such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or alkaline phosphatase (AP). Quantification is achieved by incubation with a substrate, which is catalyzed by the enzyme, resulting in a measurable byproduct.
ELISA
Overview of ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
ELISA assays are traditionally performed in 96-well polystyrene microtiter plates. These plates are designed to passively bind and immobilize antigens, typically through direct adsorption to the surface of the microtiter plate or indrectly via pre-coated “capture” antibodies. Once immobilized, primary antibodies are introduced to the sample, forming an immune complex with the antigens. Primary antibodies can either be covalently labeled to an enzyme, such as HRP, or can itself be indirectly detected using enzyme-labeled secondary antibodies or streptavidin conjugates if the primary antibody is labeled with biotin. Detection is achieved by evalutating the conjugated enzyme activity via incubation with the appropriate substrate, which produces a measurable byproduct. Substrates vary in sensitivity and compatability with imaging equipment, and should be considered carefully when designing an ELISA.
Direct vs. Indirect Detection
The method for detecting a primary antibody-antigen complex in an ELISA, can be either direct or indirect (Figure 1). In direct detection methods, a single primary antibody conjugated to a reporter enzyme (e.g. HRP or AP) is used in a single-step procedure to directly detect a target antigen. With indirect detection, a dual antibody system is used sequentially to detect the target of interest. First, the sample is incubated with an unlabeled primary antibody directed against the target antigen. Then, an enzyme-labeled secondary antibody specific for the primary antibody is used to detect its presence, and thus the target antigen. If using a biotinylated primary antibody to detect the antigen, then use an enzyme-labeled streptavidin conjugate as your secondary detection reagent.
Determining which detection method to use depends upon the expression level of the target antigen. For detecting highly-expressed antigens, direct detection is a suitable method. When sensitivity is paramount, such as detecting low-abundance targets or poorly-expressed antigens, use an indirect detection method to elevate the signal.
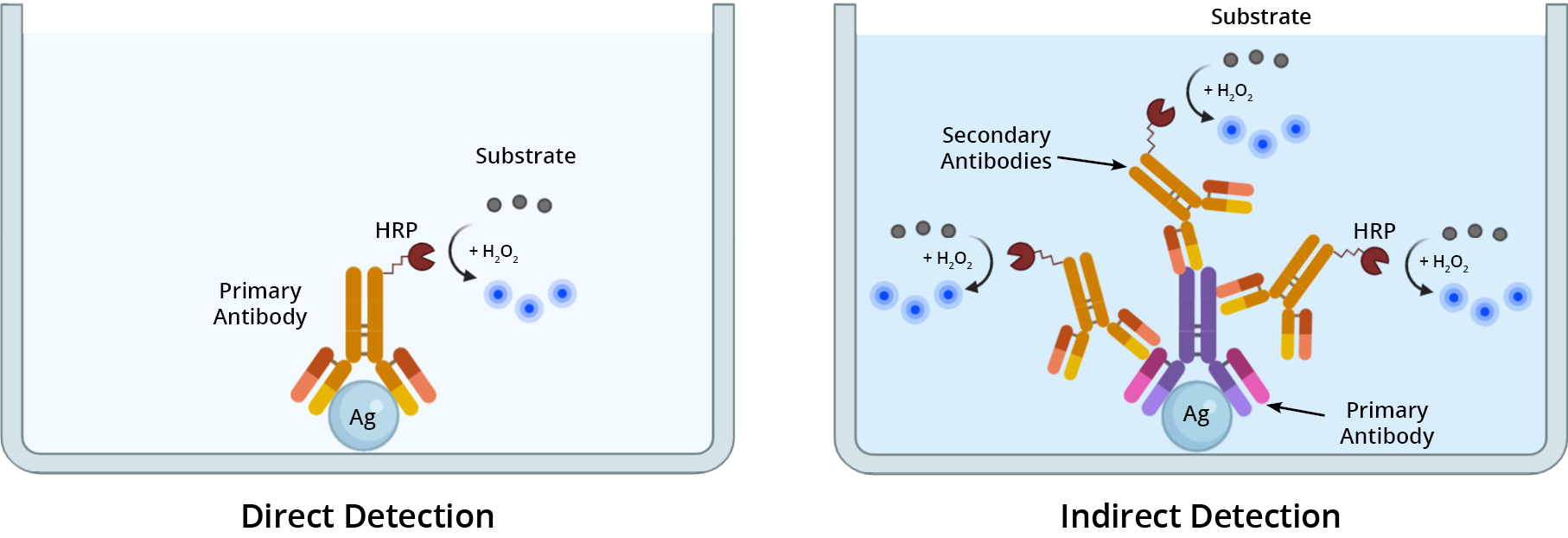
ELISA Formats
Although there are several variations of ELISA that exist, they share a similar key first step, antigen immobilization. This is achieved either through direct adsoprtion of the antigen to the well’s surface or indirectly using “capture” antibodies. In the latter method, “capture” antibodies immobilized to the well’s surface bind and retain the antigen. After immobilization, enzyme-linked antibodies are used to detect and quantify the target of interest. All things considered, ELISA are generally grouped into three categories: the direct ELISA, indirect ELISA and the sandwich ELISA.
Direct ELISA
In a direct ELISA, antigens are immobilized directly onto the plate’s surface via passive adsorption and detected using HRP-labeled primary antibodies. A coloreless substrate is introduced to the sample, which reacts with the enzyme conjugate, and produces a measurable byproduct. Depending on the choice of substrate, this byproduct can be either colorimetric, chemiluminescent or fluorescent. The magnitude of signal production is proportional to the amount of antigen in the sample. Of all the ELISA formats, direct ELISA assays are the simplest and quickest to perform, however, they are the least sensitive.
| Direct ELISA at-a-glance | |
| Applications |
|
| Advantages |
|
| Disadvantages |
|
Protocol: Colorimetric Direct ELISA

- Coat ELISA plate with testing antigens, seal plate and incubate overnight at 4°C
- Remove coating solution and wash plate 2 times with desired buffer
- Block plate with desired blocking solution for 1 hour at 4°C
- Wash plate 3 times with buffer
- Incubate with HRP-labeled primary antibody at room temperature for 1 hour
- Wash plate 4 times with buffer
- Incuabte plate with ReadiUse™ TMB Substrate Solution (Cat No. 11012) at room temperature for 15-30 minutes.
- Measure the absorbance signal at 650 nm with an ELISA microplate reader
Indirect ELISA
An indirect ELISA is essentially a modified version of a direct ELISA. In an indirect ELISA, the primary antibody used to detect the antigen is unconjugated. Instead an enzyme-labeled secondary antibody, reactive against the host-species of the primary antibody, is used to detect the primary antibody-antigen complex (indirectly detecting the antigen). A coloreless substrate is introduced to the sample, which reacts with the enzyme conjugate, and produces a measurable byproduct. Depending on the choice of substrate, this byproduct can be either colorimetric, chemiluminescent or fluroescent. The magnitude of signal production is proportional to the amount of antigen in the sample. Use of a secondary detection reagents has significant advantages over direct ELISA, namely signal amplification.
| Indirect ELISA at-a-glance | |
| Applications |
|
| Advantages |
|
| Disadvantages |
|
Protocol: Colorimetric Indirect ELISA

- Coat ELISA plate with testing antigens, seal plate and incubate overnight at 4°C
- Remove coating solution and wash plate 2 times with desired buffer
- Block plate with desired blocking solution for 1 hour at 4°C
- Wash plate 2 times with buffer
- Incubate with unconjugated primary antibody at room temperature for 1 hour
- Wash plate 4 times with buffer
- Incubate with HRP-labeled secondary antibody (in blocking buffer) at room temperature for 1 hour
- Wash plate 4 times with buffer
- Incuabte plate with ReadiUse™ TMB Substrate Solution (Cat No. 11012) at room temperature for 15-30 minutes.
- Measure the absorbance signal at 650 nm with an ELISA microplate reader
Sandwich ELISA
Sandwich ELISA assays are the most commonly used ELISA format. It requires the use of matched antibody pairs whereby each antibody is specific for different non-overlapping epitopes on the antigen. One of the antibodies, known as the capture antibody, is first coated onto the surface of a multi-well microtiter plate to facilitate the immobilization of the target antigen. Then the second antibody, known as the detection antibody, binds to the capture antibody-antigen complex (hence the term ‘sandwich’ as the antigen is bound between the matched antibody pairs). Finally, an enzyme-labeled secondary antibody conjugate specific for the detection antibody (and not the capture antibody) is added. Once the secondary binds to the detection antibody, the enzyme-labeled secondary antibody catalyzes a reaction with its respective substrate to produce a measurable signal.
| Sandwich ELISA at-a-glance | |
| Applications |
|
| Advantages |
|
| Disadvantages |
|
Protocol: Colorimetric Sandwich ELISA

- Coat wells of a PCV microtiter plate with capture antibody, seal plate and incubate overnight at 4°C
- Remove coating solution and wash plate 2 times with desired buffer
- Block plate with desired blocking solution for 1 hour at 4°C
- Wash plate 2 times with desired buffer
- Add samples to each well, incubate for 2 hours at 37°C
- Remove samples and wash plate 2 times with desired buffer
- Incubate with unconjugated detection antibody at room temperature for 1 hour
- Wash plate 4 times with desired buffer
- Incubate with HRP-labeled secondary antibody (in blocking buffer) at room temperature for 1 hour
- Wash plate 4 times with desired buffer
- Incuabte plate with ReadiUse™ TMB Substrate Solution (Cat No. 11012) at room temperature for 15-30 minutes.
- Measure the absorbance signal at 650 nm with an ELISA microplate reader
Antibodies and Other Probes for ELISA
Monoclonal antibodies, polyclonal antibodies or a combination of both are typically used in ELISA assays as either detection or capture antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies are inherently monovalent, with specificity towards a single epitope per antigen. In all ELISA formats, monoclonal antibodies are commonly used as detection antibodies. Because they seldom cross-react with other proteins and are less likely to generate non-specific signals. In contrast, polyclonal antibodies, which are a complex mixture of antibodies, recognize multiple epitopes found in a single antigen. While they are often used in sandwich ELISA assays as ‘capture antibodies’ to pull down as much of the antigen as possible, they can also be used as detection antibodies. Polyclonal antibodies are highly susceptible to batch-to-batch variation, and should be thoroughly tested and validated prior to using.
Secondary Conjugates for ELISA
Enzyme conjugated secondary antibodies or streptavidin conjugates are frequently used in both indirect and sandwich ELISA assays. Their capacity to amplify weak signals makes them advantageous at detecting poorly-expressed antigens.
HRP and Poly-HRP Secondary Antibodies
The enzyme horseradish peroxidase ((HRP, Cat No. 11025) is commonly conjugated to secondary antibodies or streptavidin, and used in either indirect or sandwich ELISA assays. The widespread adoption of HRP as a reporter in ELISA is primarly due to three factors. First, HRP has the capacity to amplify weak signal and enhance the detectability of poorly-expressed antigens. Second, the relatively small size of HRP (∼44 kDa) compared to other reporter enzymes (e.g. alkaline phosphatase (~140 kDa)) further improves intracellular penetration into samples, reduces steric hindrance and minimizes immunoreactivity loss. Third, is the high turnover rate and good stability of HRP that enables rapid and strong signal generation. AAT Bioquest offers highly purified and cross-adsorbed secondary antibodies conjugated to HRP and poly-HRP. MegaWox™ poly-HRP secondary conjugates are designed to deliver high levels of sensitivity and low background in ELISA assays. Use MegaWox™ poly-HRP conjugates in immunoassays where sample volume is limited or when the target molecule is poorly-expressed.
Table 1. Ordering Info for HRP secondary antibodies Products
| Cat# | Product Name | Unit Size |
| 11035 | MegaWox™ polyHRP-Goat Anti-Mouse IgG Conjugate | 1 mg |
| 11037 | MegaWox™ polyHRP-Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG Conjugate | 1 mg |
| 16728 | HRP-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L) | 1 mg |
| 16793 | HRP-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG (H+L) | 1 mg |
HRP and AP Streptavidin Conjugates
Enzyme-labeled streptavidin conjugates are used in an ELISA when the primary antibody used to detect the antigen is labeled with biotin molecules. The tetrameric conformation of streptavidin allows it to bind up to four biotin molecules with high affinity and selectivity. This multiplicity enables the amplification of weak signals and improves the detection sensitivity for medium- and low-abundance targets. Streptavidin is offered conjugated to either HRP or AP in ready-to-use formats.
ELISA Substrates and Detection Strategies
The final step in all ELISA assays is the detection step by addition of an enzyme substrate. The enzyme (e.g. HRP or AP) catalyzes the substrate into a measurable byproduct, and the magnitude of the signal produced is proportional to the amount of antigen in the sample. ELISA substrates vary in ease-of-use, sensitivity and compatability with imaging equipment such as spectrophotometers, fluorometers and luminometers.
Colorimetric ELISA Substrates
Colorimetric (or chromogenic) substrates react with enzymes to generate an observable colored byproduct that can be measured using an absorbance plate reader. AAT Bioquest provides colorimetric substrates for horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (AP) ranging in sensitivity and optical densities.
Table 3. Available Colorimetric Enzyme Substrates for ELISA
| Enzyme | Substrate | Absorbance (nm) | Color | Detection Limit | Unit Size | Cat No. |
| AP | pNPP | 405 | Yellow | ∼10 ng/well (100 ng/mL) | 25 mg | 11619 |
| HRP | ABTS | 420 | Blue-Green | ∼250 pg/well (2.5 ng/mL) | 1 L | 11001 |
| HRP | TMB | 650, 450 | Blue, Yellow | 4∼12.5 pg/well (40-120 pg/mL) | 100 mL | 11012 |
| HRP | TMB | 650, 450 | Blue, Yellow | 4∼12.5 pg/well (40-120 pg/mL) | 1 L | 11003 |
Fluorimetric ELISA Substrates
Fluorimetric (or fluorogenic) substrates react with enzymes to generate highly fluorescent byproducts that can be measured using a fluorescence plate reader. The degree of photon emission following light excitation is proportional to the amount of antigen in the sample. AAT Bioquest provides fluorimetric substrates for horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (AP) ranging in sensitivity and fluorescence properties.
Table 4. Available Fluorimetric Enzyme Substrates for ELISA
| Enzyme | Substrate | Ex (nm) | Em (nm) | Unit Size | Cat No. |
| AP | MUP, disodium salt | 360 nm | 448 nm | 25 mg | 11610 |
| AP | MUP, disodium salt | 360 nm | 448 nm | 10 g | 11612 |
| AP | MUP, free acid | 360 nm | 448 nm | 25 mg | 11614 |
| AP | MUP, free acid | 360 nm | 448 nm | 5 g | 11617 |
| AP | DiFMUP | 360 nm | 450 nm | 5 mg | 11627 |
| AP | FDP | 497 nm | 516 nm | 5 mg | 11600 |
| AP | PhosLite™ Green | 345 nm | 520 nm | 1 mg | 11630 |
| AP | SunRed™ Phosphate | 652 nm | 660 nm | 5 mg | 11629 |
| HRP | Amplite™ Blue | 324 nm | 409 nm | 25 mg | 11005 |
| HRP | Amplite™ ADHP | 570 nm | 583 nm | 25 mg | 11000 |
| HRP | Amplite™ Red | 570 nm | 583 nm | 1000 Assays | 11011 |
| HRP | Amplite™ IR | 646 nm | 667 nm | 1 mg | 11009 |
Chemiluminescent ELISA substrates
Chemiluminescent substrates react with enzymes to generate luminescent byproducts that can be measured using a luminometer. Since the emission of a photon is a result of a chemical reaction and not light excitation, there is minimal background interference. AAT Bioquest provides chemiluminescent substrates for horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (AP) ranging in sensitivity and chemiluminescence properties.
Product Ordering Information
Table 6. General ELISA Kits For Product Ordering Information
| Cat# | Product Name | Ex (nm) | Em (nm) | Size |
| 11540 | Amplite™ Fluorimetric Goat Anti-Mouse IgG-HRP Conjugate ELISA Assay Kit *Red Fluorescence* | 571 | 585 | 1000 Tests |
| 11541 | Amplite™ Fluorimetric Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG-HRP Conjugate ELISA Assay Kit *Red Fluorescence* | 571 | 585 | 1000 Tests |
| 36370 | Screen Quest™ Colorimetric ELISA cAMP Assay Kit | 650 | 1 plate | |
| 36371 | Screen Quest™ Colorimetric ELISA cAMP Assay Kit | 650 | 10 plates | |
| 36373 | Screen Quest™ Fluorimetric ELISA cAMP Assay Kit | 571 | 585 | 1 plate |
| 36374 | Screen Quest™ Fluorimetric ELISA cAMP Assay Kit | 571 | 585 | 10 plates |
| 36379 | Screen Quest™ FRET No Wash cAMP Assay Kit | 390 | 650 | 1 plate |
| 36380 | Screen Quest™ FRET No Wash cAMP Assay Kit | 390 | 650 | 10 plates |