Gel electrophoresis is a core molecular technique used routinely in life science research to separate and analyze charged macromolecules. By applying an electrical field to a gel-based medium, macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acid fragments can be separated and purified according to their size, charge, or conformation. Although commonly performed as an analytical procedure ensuing PCR, gel electrophoretic methods have also found much success as a preparative technique before blotting, cloning, DNA sequencing, and other various downstream applications.
Gel Electrophoresis
Principle of Gel Electrophoresis
As mentioned previously, gel electrophoresis involves using an electrical field to separate proteins and nucleic acid fragments based on size, charge, or conformation. This field is typically generated in an electrophoretic chamber (e.g., a hard plastic tank), commonly known as a gel box (Figure 1).
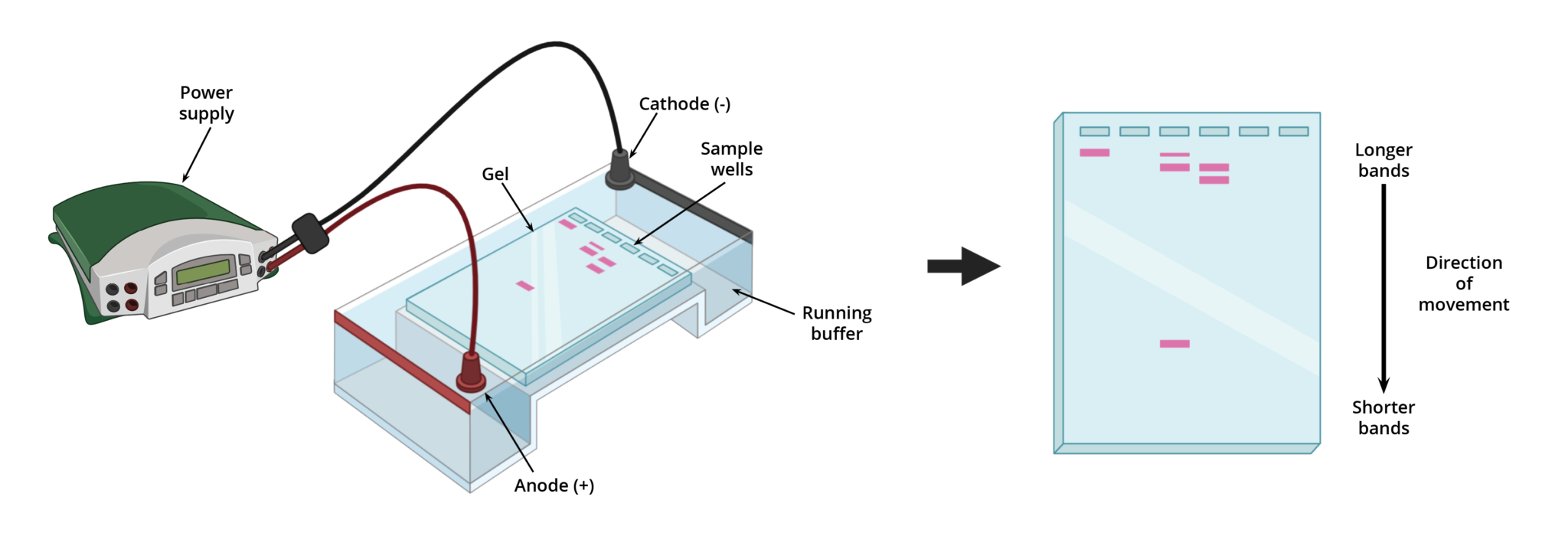
A gel box is a buffer-filled container configured with a cathode (negative terminal) at one end, an anode (positive terminal) at the opposite end, and an external power source. Gels, which behave as both an anticonvective and sieving medium, are first submerged in the buffer with its wells near the anode. Then using a pipette, samples are loaded into the wells of the gel. When the external power source is turned on, an electrical field is applied to the buffer causing charged molecules to move through the gel towards the opposite terminal (i.e., towards the anode). Depending on the size of the molecule, it will travel through the matrix at different rates and distances. Smaller molecules will migrate through the gel matrix faster than larger ones, with the shortest molecules traveling the furthest.
Types of Gel Electrophoresis
The two most common gel electrophoretic methods include agarose gel electrophoresis for separating nucleic acids and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for separating proteins, and nucleic acid fragments 500 base pairs or less. The following table summarizes key differences between agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Table 1. Summary of the key differences between agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
| Electrophoretic Method | Agarose Gel Electrophoresis | Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| Gel Type | Agarose | Polyacrylamide |
| Gel Composition | Agarose is a polysaccharide extracted from seaweed. The gel contains long chains of interlinked sugars to form a meshwork. | Polyacrylamide is a synthetic resin made by digesting acrylonitrile with nitrile hydratase. The gel is made by the chemical crosslinking of acrylamide and bis-acrylamide to produce a molecular sieve. |
| Gel Casting Method | Gel sets as it cools. Agarose powder is mixed in a buffer and microwaved. The mixture is then poured into a gel frame and allowed to set. | Gel sets by a chemical reaction once crosslinking occurs. |
| Pore Properties | Concentration dictates pore size. Pore size becomes smaller as the concentration increases. (Typical concentration is 0.5-2%). | The ratio of acrylamide to bis-acrylamide dictates pore size. (Typical concentration is 6-15%) |
| Run Configuration | The gel is run horizontally. | The gel is run vertically. |
| Application | Separates nucleic acid fragments 50-20,000 base pairs in length. | Separates proteins and nucleic acid fragments 5-500 base pairs in length (e.g., oligonucleotides, miRNA, tRNAs, etc.). |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
Visualizing DNA Samples After Separation
After separation by electrophoresis, nucleic acid fragments can be visualized using several different methods. The most well-known method for visualizing nucleic acid fragments is staining with ethidium bromide (EtBr). However, because EtBr is highly carcinogenic, cytotoxic, and mutagenic. It is environmentally hazardous and must be handled and disposed of carefully. Safer alternatives to EtBr include novel gel stains, such as Gelite™ Safe *10,000X Water Solution*, Gelite™ Safe *10,000X DMSO Solution*, Helixyte™ Green and Helixyte™ Gold, and gel staining kits, such as Gelite™ Green Nucleic Acid Gel Staining Kit and Gelite™ Orange Nucleic Acid Gel Staining Kit. Not only are these gel stains and kits less mutagenic than EtBr, but Gelite™ Safe, Helixyte™ Green, Helixyte™ Gold, and Gelite™ nucleic acid staining kits can detect nucleic acids in both agarose and polyacrylamide gels, with greater sensitivity and less background interference.
Gelite™ Safe – the most sensitive and robust DNA gel stain
Gelite™ Safe is an extremely sensitive and stable fluorescent dye for visualizing DNA in electrophoretic gels. Unlike the highly-toxic EtBr, Gelite™ Safe is explicitly designed to be less hazardous, non-cytotoxic, and non-mutagenic, providing greater sensitivity and lower background fluorescence than EtBr and SYBR® Safe. The strong DNA binding affinity of Gelite™ Safe allows for DNA to be stained before or post electrophoresis without destaining, and because Gelite™ Safe is specific to DNA, applications in which RNA is present in the sample will not obscure results. Gelite™ Safe has fluorescence excitation maxima at 280 nm and 513 nm and a broad emission profile with a maximum at 552 nm. These unique spectral properties broaden the instrument compatibility of Gelite™ Safe to include UV and blue-light transilluminators, gel documentation systems, and laser scanners, and its single formulation design allows for detection in both the green or red channels at your convenience.
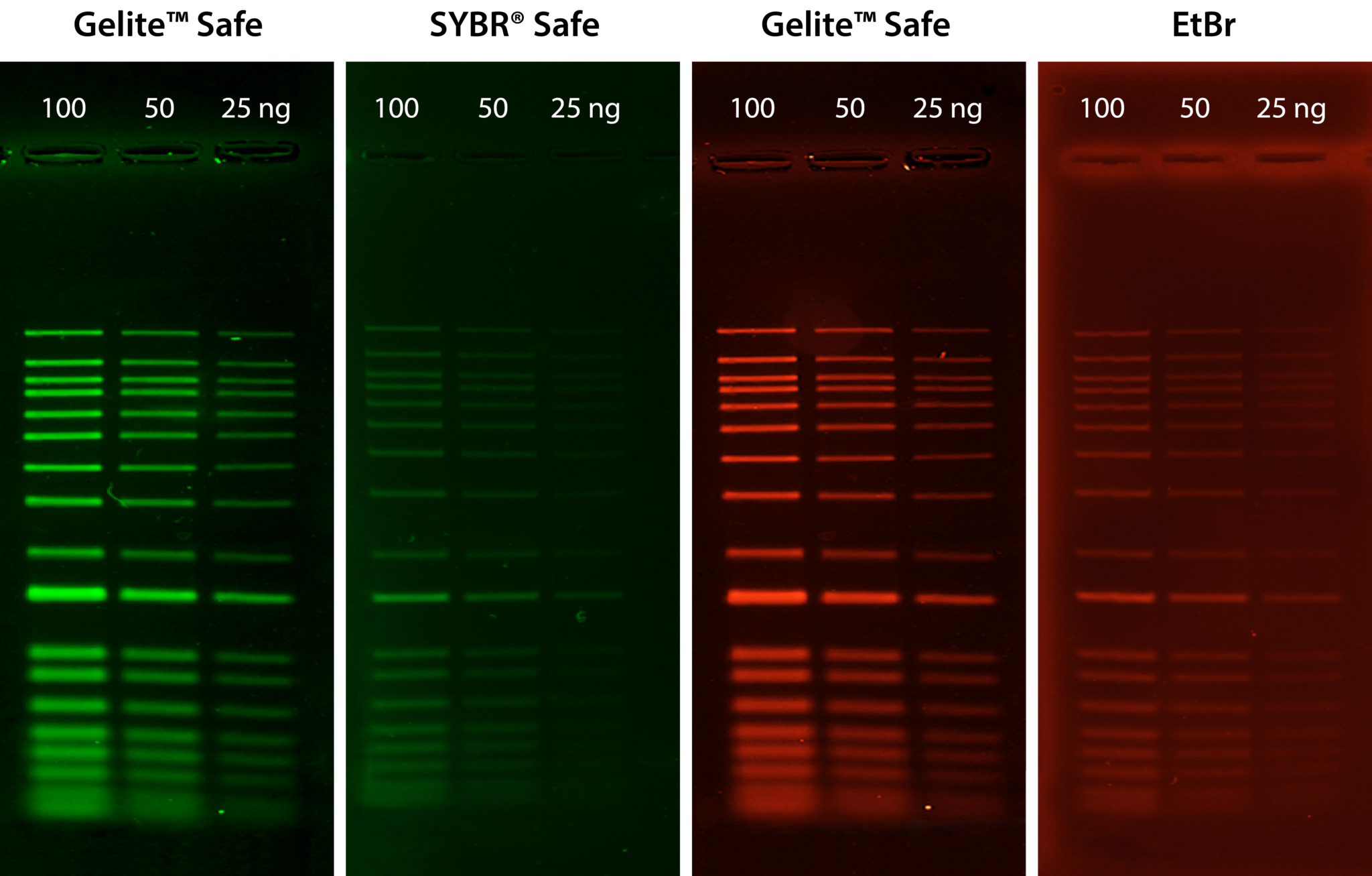
Table 1. Nucleic acid stains for agarose and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
| Product | Ex (nm)¹ | Filter² | Unit Size | Cat No. |
| Helixyte™ Green Nucleic Acid Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 254 mn | Long path green filter | 1 mL | 17590 |
| Helixyte™ Green Nucleic Acid Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 254 mn | Long path green filter | 100 µL | 17604 |
| Helixyte™ Gold Nucleic Acid Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 254 mn | Long path green filter | 1 mL | 17595 |
| Gelite™ Green Nucleic Acid Gel Staining Kit | 254 nm or 300 nm | Long path green filter | 1 Kit | 17589 |
| Gelite™ Orange Nucleic Acid Gel Staining Kit | 254 nm or 300 nm | Long path green filter | 1 Kit | 17594 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X Water Solution* | 254 nm, 300 nm or 520 nm | Ethidium Bromide, Gel Star, Gel Green, Gel Red and SYBR filters | 100 µL | 17700 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X Water Solution* | 254 nm, 300 nm or 520 nm | Ethidium Bromide, Gel Star, Gel Green, Gel Red and SYBR filters | 500 µL | 17701 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X Water Solution* | 254 nm, 300 nm or 520 nm | Ethidium Bromide, Gel Star, Gel Green, Gel Red and SYBR filters | 1 mL | 17702 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X Water Solution* | 254 nm, 300 nm or 520 nm | Ethidium Bromide, Gel Star, Gel Green, Gel Red and SYBR filters | 10 mL | 17703 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 254 nm, 300 nm or 520 nm | Ethidium Bromide, Gel Star, Gel Green, Gel Red and SYBR filters | 100 µL | 17704 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 254 nm, 300 nm or 520 nm | Ethidium Bromide, Gel Star, Gel Green, Gel Red and SYBR filters | 500 µL | 17705 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 254 nm, 300 nm or 520 nm | Ethidium Bromide, Gel Star, Gel Green, Gel Red and SYBR filters | 1 mL | 17706 |
| Gelite™ Safe DNA Gel Stain *10,000X DMSO Solution* | 254 nm, 300 nm or 520 nm | Ethidium Bromide, Gel Star, Gel Green, Gel Red and SYBR filters | 10 mL | 17707 |
- Excitation settings are for a transilluminator or laser-based gel scanner.
- Common long path green filters include the SYBR® filter and GelStar® filter.
Visualizing Protein Samples After Separation
For proteins, visualization can be achieved using either color-producing chemical reactions or dye-binding methods. Determining which method to use depends largely on the conditions of the experiment and the intended downstream application. Common strategies for detecting proteins in gel include Coomassie dye staining, silver staining, zinc staining, and fluorescent dye staining. While Coomassie dye and silver staining methods remain largely popular for total protein profiling, fluorescent dye staining methods offer greater sensitivity and linear dynamic range.
Table 3. Summary of methods for staining proteins in gel.
| Stain | Sensitivity Range | Protocol Time | Detection Method | Compatible Downstream Applications | Notes |
| Coomassie Dye | 5 – 25 ng | 10 – 135 minutes |
|
|
|
| Silver stain | 0.25 – 0.5 ng | 30 – 120 minutes |
|
|
|
| Zinc stain | 0.25 – 0.5 ng | 15 minutes |
|
|
|
| Fluorescent dye | 0.25 – 0.5 ng | 60 minutes |
|
|
|