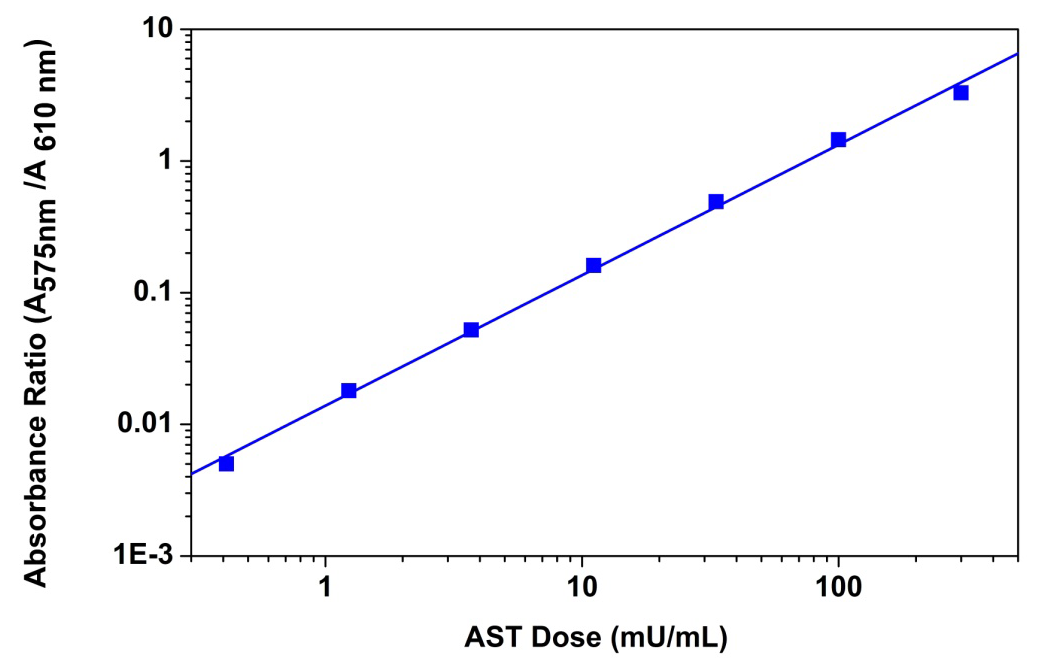
Transferases are a class of enzymes that catalyze the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from a donor molecule to an acceptor molecule. They are involved in a myriad of vital cellular processes including the transfer of thiol esters, metabolism of tryptophan and the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). Transferases are classified primarily based on the type of biochemical group transferred, there are 10 categories in all comprising over 400 unique enzymes.
Common classifications include:
- Methyltransferases and formyltransferase – enzymes that transfer single-carbon groups methyl (-CH3) and formyl (-CHO) groups
- Transketolase and transaldolase – enzymes that transfer ketone or aldehyde group
- Oxi aminotransferase or transaminase – enzymes that transfer nitrogenous groups
- Sulfotransferase – enzymes that transfer sulfur-containing groups
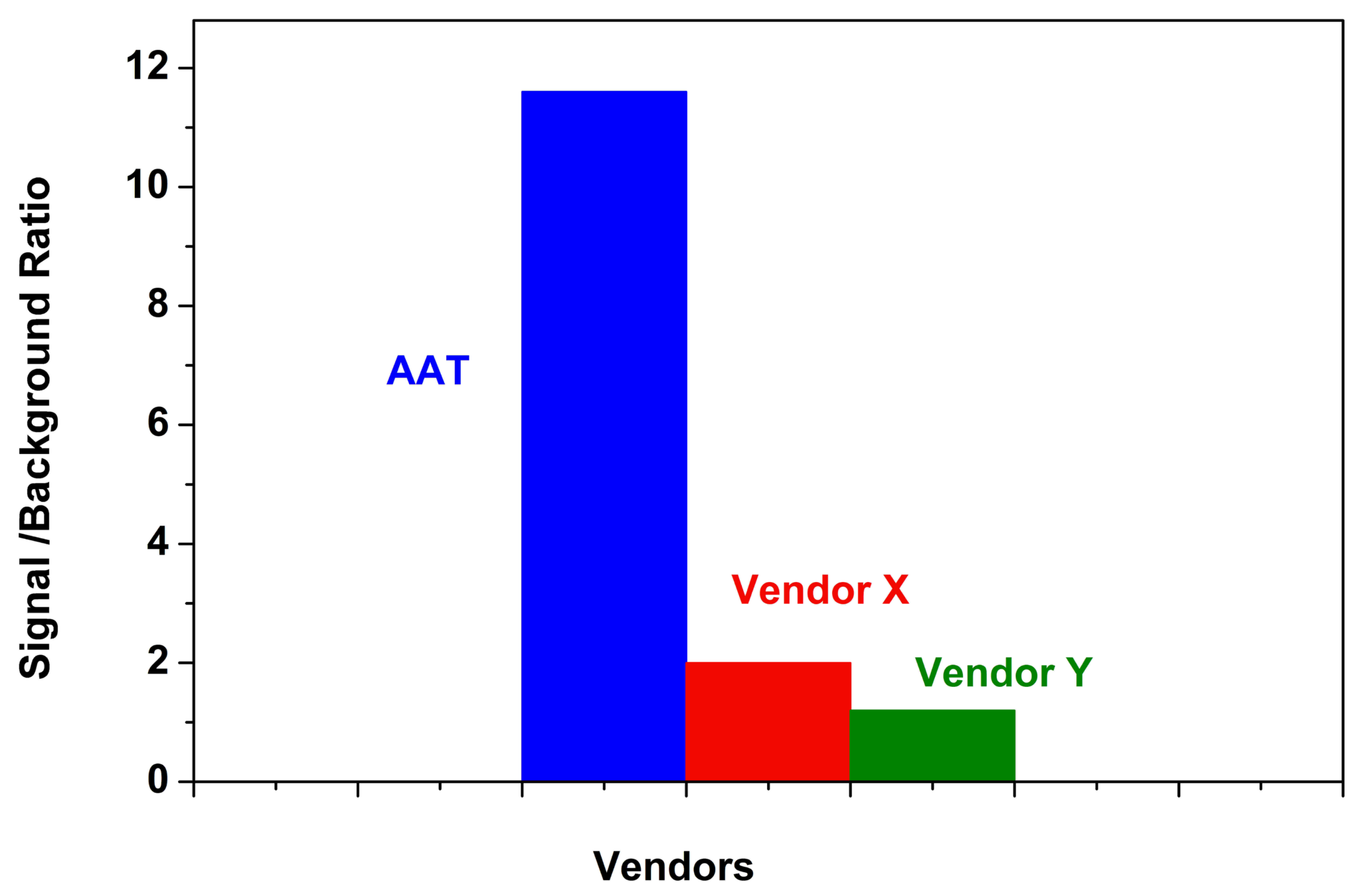
AAT Bioquest provides a series of “mix and read” transferase assay kits which are compatible with HTS liquid handling instruments, and also offers fluorogenic substrate to quantify transferase activity in solutions.
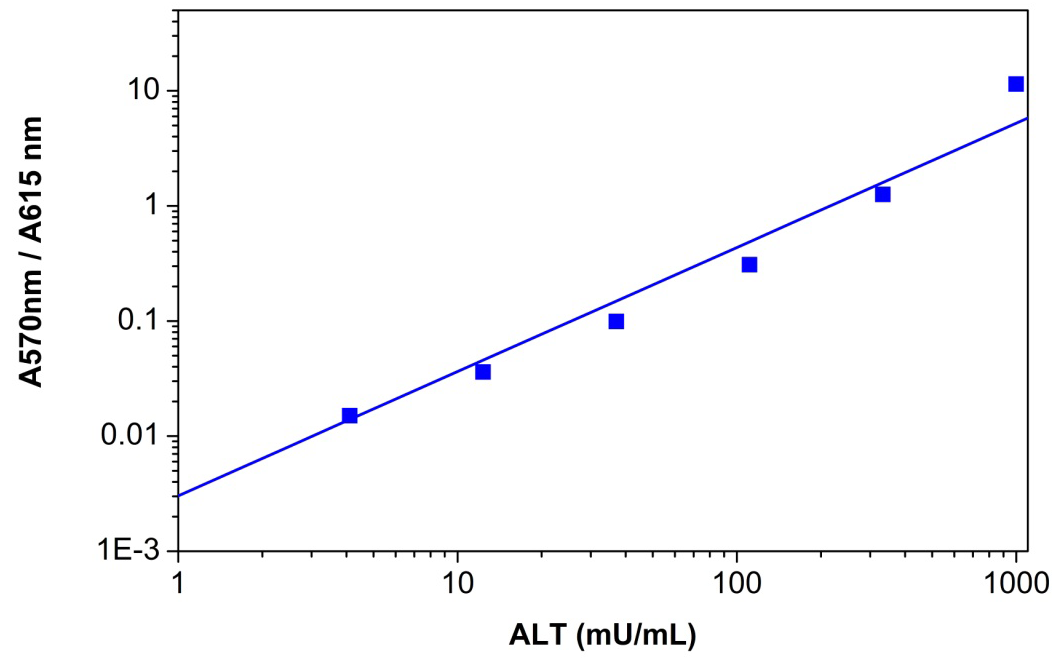
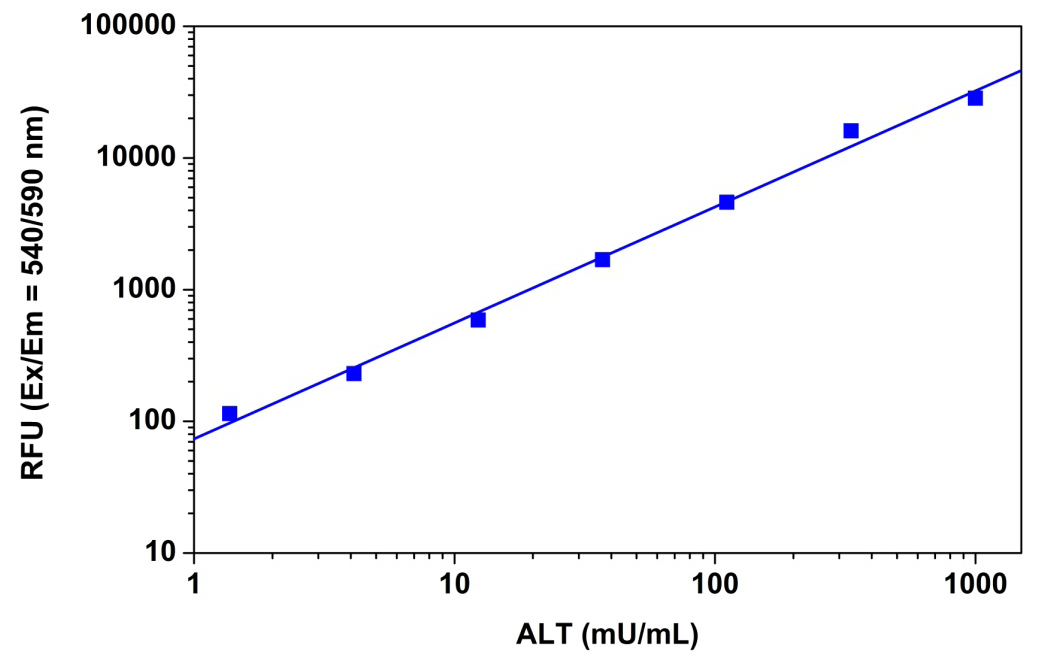
Alanine Aminotransferase
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), also called serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (GPT), catalyzes the reversible transfer of an ?-amino group between alanine and glutamate, and is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. ALT is mainly found in the liver as well as in the heart, muscle, and kidneys but at much lower levels. In healthy subjects, serum ALT levels are relatively low. However, when cells are damaged, such as during acute and chronic hepatitis, obstructive jaundice, carcinoma of liver, myocardial infarction, ALT leaks into the blood stream causing a significant increase in serum ALT levels. Therefore, determination of serum ALT levels has great clinical and diagnostic significance.