Conventional dried blood spot testing (DBS) is a microsampling method that is widely used for qualitative or semi-quantitative bioanalyses, such as screening for the rare disorder phenylketonuria (PKU) in newborns. Capitainer®qDBS is the only microsampling device that ensures accurate and consistent blood volumes every single time. This greatly expands the possibilities for quantitative dried blood spot testing in various settings, including home sampling and remote sampling.
Altasciences, a contract research organisation working with pharmaceutical companies in drug development, recently tested Capitainer®qDBS for the quantification of a panel of 15 anti-epileptic drugs (AED), and found that the device delivered accurate and precise blood volumes, was straightforward to use, and was devoid of the limitations of conventional DBS.
The ups and downs of conventional DSB
In conventional DBS, finger-prick blood samples are spotted onto and dried on filter paper. DBS offers many advantages over venous blood sampling, including the possibility to perform remote and home sampling, since dried samples can easily be shipped to labs for a range of downstream analyses, e.g., DNA sequencing or analytical methods to measure metabolite or drug concentrations in the blood.
While conventional DBS has proven successful in qualitative analyses, its usefulness in quantitative microsampling procedures is hampered by natural variations in blood sampling volume as well as the hematocrit (Hct) effect, whereby the amount of haemoglobin in the blood influences blood viscosity.
Within DSB, it is common practice to sub-punch the filter to produce a disc of known size, which is assumed to harbour a fixed blood volume. Since the Hct effect influences how blood diffuses through the filter, conventional DBS may lead to varied testing outcomes, depending on where the filter paper is punched.
Altasciences finds that Capitainer®qDBS offers highly accurate and consistent blood microsampling
While qualitative results may be sufficient for genetic or other analyses that require a yes/no answer, blood volume accuracy and consistency is critical for quantitative applications, e.g., diagnostics that rely on measuring particular analytes, blood drug level testing, and monitoring patients for certain metabolites, proteins, or drugs before and during clinical trials.
In contrast to conventional DBS, the Capitainer®qDBS microsampling device is designed to prevent oversampling, ensuring accurate blood volumes of 10 µl every single time. Capitainer®qDBS also circumvents the Hct effect, because the integrated DBS disc is pre-cut prior to blood sampling to perfectly fit the wells of a standard 96-well plate, allowing the entire disc to be used for downstream analysis.
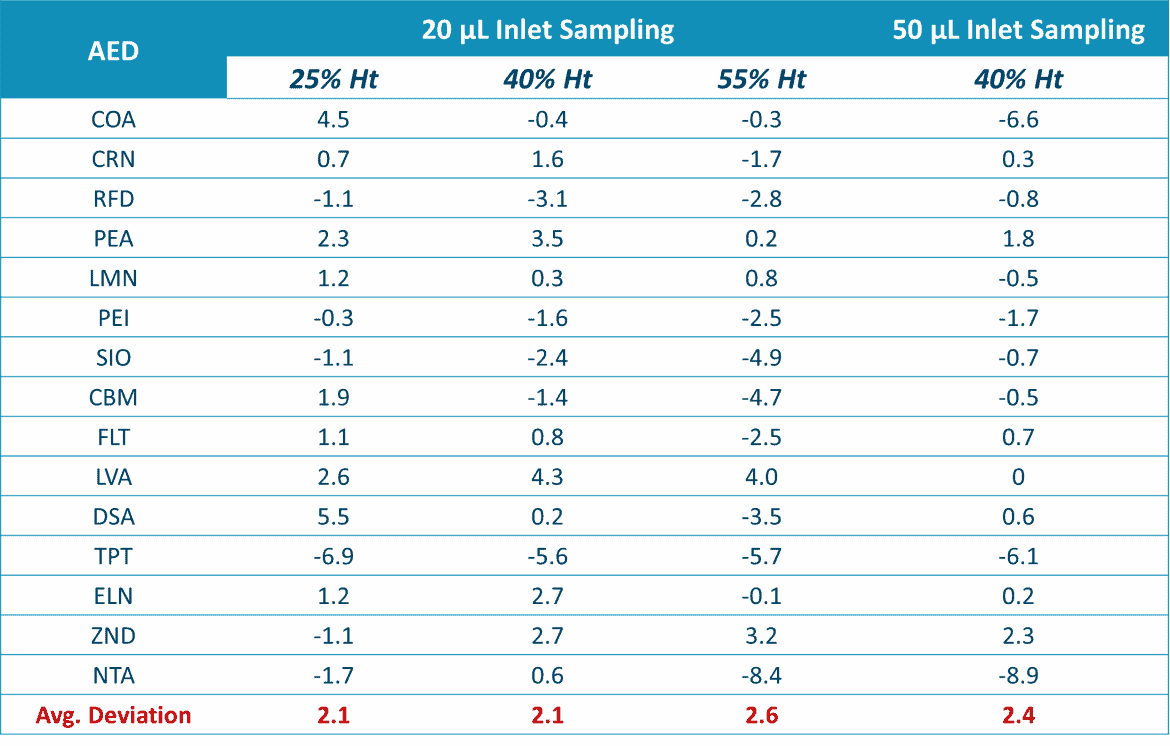
Altasciences evaluated Capitainer®qDBS for the quantification of 15 AEDs in whole blood. They assessed its ability to deliver accurate blood volumes to pre-cut cellulose discs and did not detect any oversampling with volumes between 20 µl and 50 µl. Moreover, they found no evidence of Hct effect, blood viscosity or bias with respect to analyte binding to the discs.