Self-sampling has gained significant interest over the past decade, accelerated in recent years by the Covid-19 pandemic. Clinical self-sampling has been commonplace within infectious disease applications such as sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and HPV screening. Today, due to technological advancements, remote patient self-sampling is gaining significant recognition in many clinical applications.
Today, clinical diagnostics is largely based on blood, with the standard procedure being the patient travels to the health care facility to have a venous blood draw taken by a trained phlebotomist. The demand for protecting vulnerable patients on blood monitoring programs and improving patient outcomes has fuelled the development in novel, accurate remote self-sampling solutions.
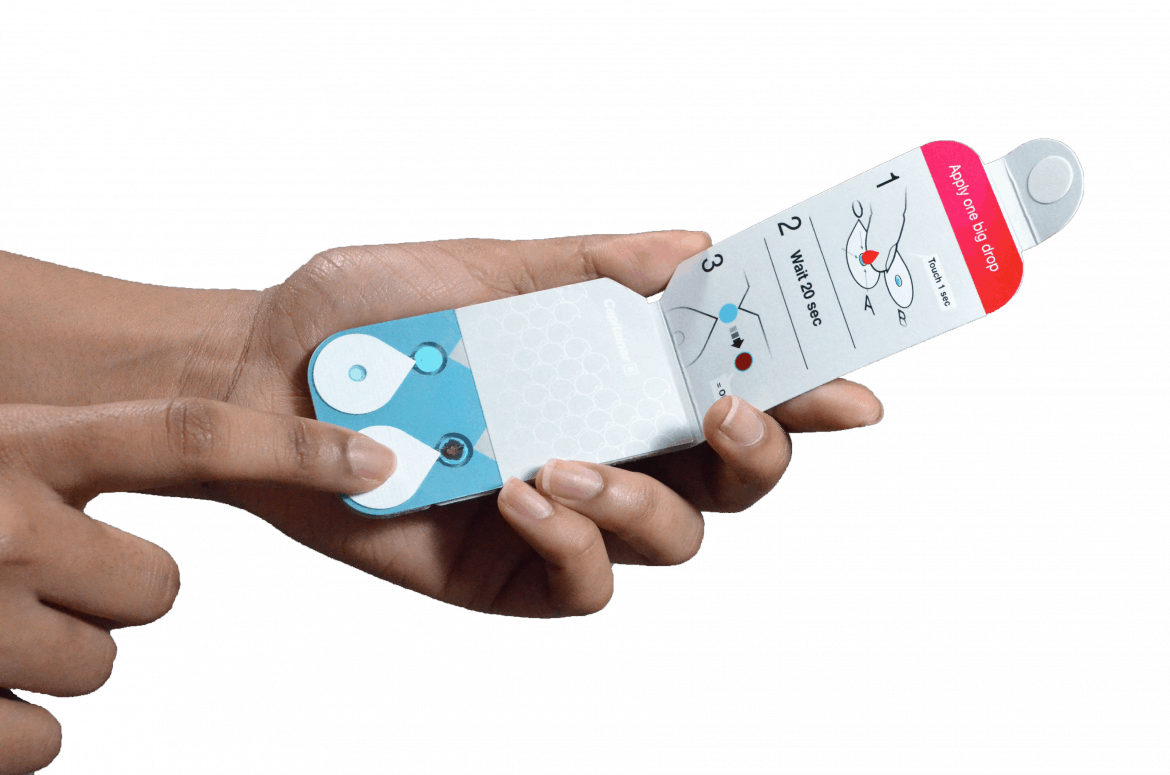
Capitainer has developed a solution based on a combination of new, advanced microfluidic technologies and traditional well established dried blood spot (DBS) techniques. The solution delivers a highly accurate volumetric sample for quantitative analytical results of the highest standard [1].
We see many demands on a sampling device for blood to be successfully implemented into clinical diagnostic pathways and have therefore built these features into our product. In this blog we would like to highlight three of them: