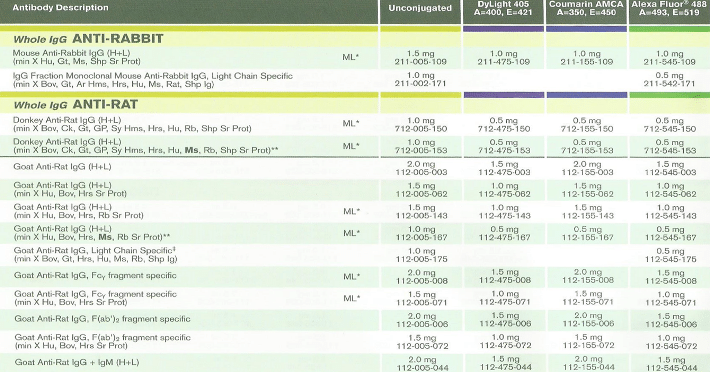
Minimised cross reactivity antibodies:
- Most multiple-labelling experiments require minimised cross reactivity antibodies.
- Tested by ELISA and/or adsorbed against the IgG and serum proteins of other species.
- Use when immunoglobulins from other species may lead to interfering cross-reactivities.
- Anti-Mouse IgG (min X Rat and other species) and Anti-Rat IgG (min X Mouse IgG and other species) have diminished epitope recognition.
Pitfalls!!!
-
 Warning: Antibodies against one species may cross-react with a number of other species.
Warning: Antibodies against one species may cross-react with a number of other species. - Warning: Bovine serum albumin (BSA) and dry milk may contain IgG which reacts with anti-bovine IgG, anti-goat IgG, anti-horse IgG, and anti-sheep IgG antibodies.
Example of the use of minimum cross reactivity secondaries
Mouse tissue antigen A |
Mouse tissue antigen B |
Mouse tissue antigen C |
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1:
4-5% Normal Donkey Serum
Step 2:
Goat Anti-Mouse antigen A
Step 3:
Probe 1-conjugated
Donkey Anti-Goat IgG
(H+L) (min X Ck, GP, Sy Hms, Hrs, Hu, Ms, Rb, Rat Serum Proteins)
|
Step 4: 4-5% Normal Donkey SerumStep 5: Rabbit Anti-Mouse antigen BStep 6: Probe 2-conjugated Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (min X Bov, Ck, Gt, GP, Sy Hms, Hrs, Hu, Ms, Rat, Shp Serum Proteins) |
Step 7: 4-5% Normal Donkey SerumStep 8: Rat Anti-Mouse antigen CStep 9: Probe 3-conjugated Donkey Anti-Rat IgG (H+L) (min X Bov, Ck, Gt, GP, Sy Hms, Hrs, Hu, Ms, Rb, Shp Serum Proteins) |
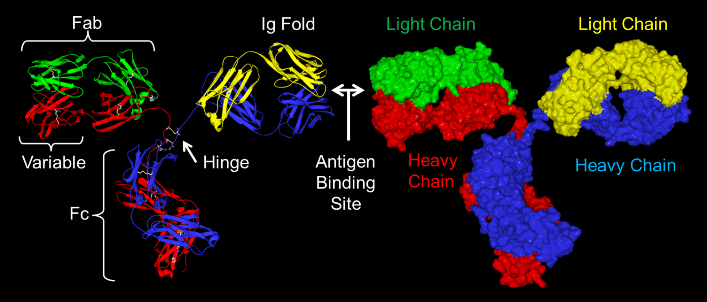
Blocking and Double Labelling with Fab Fragments
- Fab fragments of affinity-purified, secondary antibodies are used to sterically cover the surface of immunoglobulins for…
- Double labelling primary antibodies from the same host species,
- To block endogenous immunoglobulins on cell or tissue sections.
- As a means to label primary antibodies in solution without compromising activity.
Why monovalent Fab fragments?
- Whole IgG molecules and F(ab’)2 fragments of IgG have two antigen binding sites.
- After binding to its primary antibody most secondary antibodies will still have one open binding site, which can capture a different second primary antibody from the same species.
- Overlapping labelling of the two antigens will occur.
- Not necessary when primary antibodies from the same host species are different classes of immunoglobulins, such as IgG and IgM.
- Not necessary when primary antibodies from the same host species are different subclasses of IgG, e.g. Mouse IgG1 and Mouse IgG2a.
- Class-specific / Subclass-specific antibodies can be used.
Possible protocols for double labelling using Fab fragments
- Empirical optimisation will be necessary.
- Block with appropriate 4-5% normal serum between certain steps to reduce background.
- In experiments with multiple layers, a fixative step may be needed.
 Warning: Antibodies against one species may cross-react with a number of other species.
Warning: Antibodies against one species may cross-react with a number of other species.