Cusabio COVID-19
Research Solutions for Coronavirus – Cusabio
Cusabio COVID-19 RUO Detection Kits (IgG/IgM and qPCR based)
On 26 November 2021, WHO designated the variant B.1.1.529 -the newest COVID-19 “variant of concern” , named Omicron.
Why are scientists worried about it?
Omicron (B.1.1.529) was first detected in Southern Africa. Omicron’s rapid rise in South Africa is what worries researchers most. Cases have also been reported in Botswana, but also in Israel, Belgium, the U.K., even Hong Kong. So far, the virus has been detected in more than 30 countries and at least 9 states. The COVID-19 Omicron variant has already made its way across the globe.
What scientists know so far?
The B.1.1.529 variant carries more than 30 mutations in the Spike protein, which is has an unprecedented number of mutations compared to Delta. It’s critically important to understand whether these mutations allow the Omicron variant to escape from neutralizing antibodies. It is not yet clear about the Transmissibility and Severity of disease.
Does Omicron boast faster transmission and stronger resistance to established immunity? Omicron is a big unknown.
Omicron (B.1.1.529) Reagents: CUSABIO are Starting to Take Pre-Orders!
At present, epidemiologists, Laboratorians and researchers worldwide are conducting studies to better understand many aspects of Omicron. To support the study of Omicron variants, CUSABIO is developing Omicron Variants related products. We’re starting to take Pre-orders now. Pre-orders will allow you to guarantee immediate shipment on release. Here is the collection for the most popular SARS-CoV-2 Omicron products. Please Contact Us for Pre-Orders.
| Code | Product Name | Target Antigen | Source | Region and Mutations |
| CSB-YP3325GMY(M18) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) Omicron Variant | Nucleoprotein | Yeast | 1-419aa(P13L, Δ31-33, R203K, G204R) |
| CSB-EP3325GMY(M18) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) Omicron Variant | Nucleoprotein | E-Coli | 1-419aa(P13L, Δ31-33, R203K, G204R) |
| CSB-BP3325GMY(M18) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) Omicron Variant | Nucleoprotein | Baculovirus | 1-419aa(P13L, Δ31-33, R203K, G204R) |
| CSB-MP3325GMY(M18) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) Omicron Variant | Nucleoprotein | Mammalian | 1-419aa(P13L, Δ31-33, R203K, G204R) |
| CSB-YP3324GMY9(M) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) Omicron Variant | Spike glycoprotein | Yeast | 13-303aa(A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, ΔN211, L212I, ins214EPE) |
| CSB-EP3324GMY9(M) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) Omicron Variant | Spike glycoprotein | E-Coli | 13-303aa(A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, ΔN211, L212I, ins214EPE) |
| CSB-BP3324GMY9(M) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) Omicron Variant | Spike glycoprotein | Baculovirus | 13-303aa(A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, ΔN211, L212I, ins214EPE) |
| CSB-MP3324GMY9(M) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) Omicron Variant | Spike glycoprotein | Mammalian | 13-303aa(A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, ΔN211, L212I, ins214EPE) |
| CSB-YP3324GMY1(M14) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S)(B.1.1.529) Partial | Spike glycoprotein | Yeast | 319-541aa(G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| CSB-EP3324GMY1(M14) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S)(B.1.1.529) Partial | Spike glycoprotein | E-Coli | 319-541aa(G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| CSB-BP3324GMY1(M14) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S)(B.1.1.529) Partial | Spike glycoprotein | Baculovirus | 319-541aa(G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| CSB-MP3324GMY1(M14) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S)(B.1.1.529) Partial | Spike glycoprotein | Mammalian | 319-541aa(G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| CSB-EP3324GMY1(M14)-B | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S)(B.1.1.529) Partial | Spike glycoprotein | E-Coli | 319-541aa(G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| CSB-MP3324GMY1(M14)-B | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S)(B.1.1.529) Partial | Spike glycoprotein | Mammalian | 319-541aa(G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| CSB-YP3324GMY(M7) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) Omicron, Partial | Spike glycoprotein | Yeast | 16-685aa(A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, Δ211, L212I, ins214-215EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H); |
| CSB-EP3324GMY(M7) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) Omicron, Partial | Spike glycoprotein | E-Coli | 16-685aa(A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, Δ211, L212I, ins214-215EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H); |
| CSB-BP3324GMY(M7) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) Omicron, Partial | Spike glycoprotein | Baculovirus | 16-685aa(A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, Δ211, L212I, ins214-215EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H); |
| CSB-MP3324GMY(M7) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) Omicron, Partial | Spike glycoprotein | Mammalian | 16-685aa(A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D, Δ143-145, Δ211, L212I, ins214-215EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H); |
| Product Name | Code | Sample Types | Assay Principle |
| SARS-CoV-2 N IgG Antibody ELISA Kit | CSB-EL3325HU | serum, plasma | Qualitative |
| SARS-CoV-2 N ELISA Kit | CSB-EL33251 | serum, plasma, swabs | Quantitative |
| Human SARS-CoV-2 S RBD Ab (IgG) ELISA Kit | CSB-EL33241HU | serum, plasma | Qualitative |
| Human SARS-CoV-2 S RBD Ab (IgM) ELISA Kit | CSB-EL33242HU | serum, plasma | Qualitative |
| Human SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody ELISA Kit | CSB-EL33243HU | serum, plasma | Qualitative |
| Human SARS-CoV-2 N/S1 Ab (IgG) ELISA Kit | CSB-EL3326HU | serum, plasma | Qualitative |
| SARS-CoV-2 S1 RBD ELISA Kit | CSB-EL33244 | serum, plasma, swabs | Quantitative |
| Target Name | Product Name | Code | Species | Source | Tag Info |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) | CSB-EP3325GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | E.coli | N-terminal His-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) | CSB-YP3325GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | Yeast | N-terminal His-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) | CSB-BP3325GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | Baculovirus | N-terminal His-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) | CSB-MP3325GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | N-terminal His-tagged |
| S | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial | CSB-YP3324GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | Yeast | N-terminal His-tagged |
| S | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial | CSB-BP3324GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | Baculovirus | N-terminal His-tagged |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY1 | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | C-terminal 6xHis-mFc-tagged |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY1b1 | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial | CSB-YP3324GMY1 | SARS-CoV-2 | Yeast | N-terminal 6xHis-sumostar-tagged |
| S (S1) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial | CSB-YP3324GMYa4 | SARS-CoV-2 | Yeast | N-terminal 6xHis-sumostar-tagged |
| S (S1) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Flag-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N),partial | CSB-EP3325GMY1 | SARS-CoV-2 | E.coli | |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N),Biotinylated | CSB-EP3325GMY-B | SARS-CoV-2 | E.coli | |
| NSP3 | Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Non-structural protein 3(nsp3),partial | CSB-EP3398GND | SARS-CoV-2 | E.coli | |
| NSP5 | Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 3C-like proteinase(NSP5) | CSB-EP3389GND | SARS-CoV-2 | E.coli | |
| Nsp9 | Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Non-structural protein 9(nsp9) | CSB-MP3388GND | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | |
| Nsp9 | Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Non-structural protein 9(nsp9) | CSB-EP3388GND | SARS-CoV-2 | E.coli | |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) (V367F), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M1) | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) (W436R), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M2) | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) (G476S), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M4) | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) (N501Y), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M6) | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) (V483A), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M5) | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | |
| S (RBD) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial,Biotinylated | CSB-MP3324GMY1-B | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | |
| S (S1) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S), partial | CSB-YP3324GMYa4 | SARS-CoV-2 | Yeast | |
| S (S1) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) (D614G), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY(M1) | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell | |
| S (S1) | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S)(N501Y,P681H), partial | CSB-MP3324GMY(M2) | SARS-CoV-2 | Mammalian cell |
| Product Name | Code | Reactivity Species | Tested Applications |
| N Antibody | CSB-RA33255A0GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| N Antibody | CSB-RA33255A1GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA, WB, GICA |
| N Antibody, Biotin conjugated | CSB-RA33255D1GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| N Antibody, FITC conjugated | CSB-RA33255C1GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| N Antibody, HRP conjugated | CSB-RA33255B1GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| S Antibody | CSB-RA33245A0GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| S Antibody | CSB-RA33245A1GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA, GICA, Neutralization |
| Spike RBD Nanobody | CSB-RA33245A2GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA, GICA, Neutralization |
| S Antibody, Biotin conjugated | CSB-RA33245D1GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| S Antibody, FITC conjugated | CSB-RA33245C1GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| S Antibody, HRP conjugated | CSB-RA33245B1GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| N Antibody | CSB-RA33255A2GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 RBD Nanobody, Biotin conjugated | CSB-RA33245D2GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 RBD Nanobody, FITC conjugated | CSB-RA33245C2GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 RBD Nanobody, HRP conjugated | CSB-RA33245B2GMY | SARS-CoV-2 | ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody Pair 1 | CSB-EAP33245 | SARS-CoV-2 | S-ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 N Antibody Pair 1 | CSB-EAP33255A1 | SARS-CoV-2 | S-ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 N Antibody Pair 2 | CSB-EAP33255A2 | SARS-CoV-2 | S-ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 N Antibody Pair 3 | CSB-EAP33255A3 | SARS-CoV-2 | S-ELISA |
| SARS-CoV-2 N Antibody Pair 4 | CSB-EAP33255A4 | SARS-CoV-2 | S-ELISA |
| Product Name | Code | Tested Applications | Raised in |
| S Monoclonal Antibody | CSB-MA33245A0m | GICA | Mouse |
| S Monoclonal Antibody | CSB-MA33245A1m | GICA | Mouse |
| S Monoclonal Antibody | CSB-MA33245A2m | GICA | Mouse |
| S Antibody | CSB-PA33245YA01GMY | GICA | Rabbit |
| S Antibody | CSB-PA33245YA11GMY | GICA | Rabbit |
| N Antibody | CSB-PA33254A0Rb | GICA | Rabbit |
| N Antibody | CSB-MA33255A0m | GICA | Mouse |
| N Antibody | CSB-MA33255A1m | GICA | Mouse |
| N Antibody | CSB-MA33255A2m | GICA | Mouse |
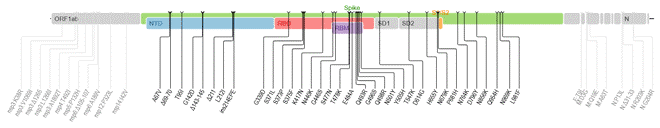
Partial popular mutants from SARS-CoV-2 Variants
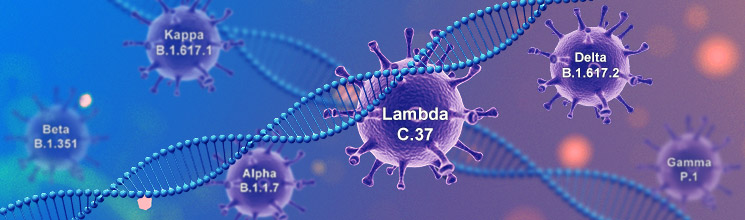
The COVID19 epidemic that broke out at the end of 2019 is still raging around the world. The cause of this epidemic, the SARS-CoV-2, has an astonishing speed of mutation. It took just over a year to use nearly 1/2 of the Greek alphabet, and developed from Alpha to Lambda.
At the end of December 2020, the SARS-CoV-2 variant Alpha was discovered in the United Kingdom, and the epidemic in the United Kingdom suddenly got out of control. Then, South Africa discovered Beta, India discovered Delta, and Peru discovered Lambda.
Aiming at the main variants of the SARS-CoV-2 in the world, CUSABIO has developed and produced a series of high-quality mutant antigens with various tag. Most of these mutant antigens have been validated in bioactivity.
SARS-CoV-2 Lambda | C.37 (South America)
| Target | Product Name | Code | Source | Mutation | Tag Info |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (R203K,G204R) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M12) | E.coli | R203K, G204R | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
SARS-CoV-2 Delta | B.1.617.2 (India)
| Target | Product Name | Code | Source | Mutation | Tag Info |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (D63G,R203M,D377Y) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M14) | E.coli | D63G, R203M, D377Y | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
SARS-CoV-2 Kappa | B.1.617.1 (India)
| Target | Product Name | Code | Source | Mutation | Tag Info |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (R203M,D377Y) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M13) | E.coli | R203M, D377Y | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
SARS-CoV-2 Alpha | B.1.1.7 (U.K)
| Target | Product Name | Code | Source | Mutation | Tag Info |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (D3L,R203K,G204R,S235F) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M1) | E.coli | D3L, R203K, G204R, S235F | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (R203K,G204R) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M12) | E.coli | R203K, G204R | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| S1 | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (D614G),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY(M1) | Mammalian cell | D614G | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (N501Y),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M6) | Mammalian cell | N501Y | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (N501Y),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M6)k2 | Mammalian cell | N501Y | C-terminal 6xHis-mFC-tagged |
SARS-CoV-2 Beta | B.1.351 (South Africa)
| Target | Product Name | Code | Source | Mutation | Tag Info |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (D3L,R203K,G204R,S235F) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M1) | E.coli | D3L, R203K, G204R, S235F | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (R203K,G204R) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M12) | E.coli | R203K, G204R | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| S1 | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (D614G),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY(M1) | Mammalian cell | D614G | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (N501Y),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M6) | Mammalian cell | N501Y | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (N501Y),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M6)k2 | Mammalian cell | N501Y | C-terminal 6xHis-mFC-ta |
SARS-CoV-2 Gamma | P.1 (Brazil)
| Target | Product Name | Code | Source | Mutation | Tag Info |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (P80R) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M3) | E.coli | P80R | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| S1 | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (D614G),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY(M1) | Mammalian cell | D614G | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (N501Y),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M6) | Mammalian cell | N501Y | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (N501Y),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M6)k2 | Mammalian cell | N501Y | C-terminal 6xHis-mFC-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S)(E484K),partial | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M8) | Mammalian cell | E484K | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) (E484K), partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M8)h8 | Mammalian cell | E484K | C-terminal mFC-tagged |
Other SARS-CoV-2 Variants
| Target | Product Name | Code | Source | Mutation | Tag Info |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (P13L) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M4) | E.coli | P13L | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (D103Y) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M5) | E.coli | D103Y | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (L230F) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M9) | E.coli | L230F | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (I292T) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M10) | E.coli | I292T | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (Q384H) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M11) | E.coli | Q384H | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Nucleoprotein (N) (S202N) (Active) | CSB-EP3325GMY(M8) | E.coli | S202N | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (V367F),partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M1) | Mammalian cell | V367F | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (W436R), partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M2) | Mammalian cell | W436R | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| S1-RBD | Recombinant Human Novel Coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S) (G476S), partial (Active) | CSB-MP3324GMY1(M4) | Mammalian cell | G476S | C-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
Partial Validated Data
● Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein (N)(R203K,G204R) (Active) (CSB-EP3325GMY(M12))
-SDS.jpg)
Its purity is greater than 96% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-AC1.jpg)
Its binding ability measured by functional ELISA with N Mouse Monoclonal Antibody at 2 μg/ml, of which EC50 is 6.775-13.04 ng/ml.
-AC2.jpg)
Its binding ability measured by functional ELISA with N Recombinant Antibody at 2 μg/ml, of which EC50 is 4.664-8.256 ng/ml.
● Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein (N)(D63G,R203M,D377Y) (Active) (CSB-EP3325GMY(M14))
-SDS.jpg)
Its purity is greater than 85.7% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-AC1.jpg)
Its binding ability measured by functional ELISA with N Mouse Monoclonal Antibody at 2 μg/ml, of which EC50 is 3.834 – 5.294 ng/ml.
-AC2.jpg)
Its binding ability measured by functional ELISA with N Recombinant Antibody at 2 μg/ml, of which EC50 is 1.304 – 1.875 ng/ml ng/ml.
● Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein(S) (E484K), partial (Active) (CSB-MP3324GMY1(M8)h8)
h8-SDS.jpg)
Its purity is greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
h8-AC1.jpg)
Its binding ability measured by functional ELISA with human ACE2 at 2 μg/ml, the EC50 is 6.597-8.187 ng/ml.
h8-AC2.jpg)
Its binding ability measured by functional ELISA with Biotin-S Antibody at 2 μg/ml, the EC50 is 118.7 ng/ml.
Coronavirus Related Products
| Target Name | Product Name | Code | Species | Source | Tag Info |
| HE | Recombinant Bovine coronavirus Hemagglutinin-esterase(HE) | CSB-YP323648BJK | BCoV | Yeast | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| N | Recombinant Bovine coronavirus Nucleoprotein(N) | CSB-EP320768BJK | BCoV | E.coli | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| Orf1ab | Recombinant Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus Orf1ab,partial | CSB-EP320768BJK | MERS-CoV | E.coli | Tag-Free |
| S | Recombinant Human coronavirus OC43 Spike glycoprotein(S) ,partial | CSB-EP336163HIY | HCoV-OC43 | E.coli | N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO-tagged |
| S | Recombinant Human coronavirus OC43 Spike glycoprotein(S) ,partial | CSB-YP336163HIY | HCoV-OC43 | Yeast | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| S | Recombinant Bovine coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) ,partial | CSB-EP333052BJO | BCoV | E.coli | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| S | Recombinant Bovine coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S),partial | CSB-EP322803BJK | BCoV | E.coli | N-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| SARS-COV-RBD | Recombinant Human SARS coronavirus Spike glycoprotein(S) ,partial | CSB-MP348663HQE | SARS-CoV | Mammalian cell |
| Product Name | Code | Species Reactivity | Tested Applications |
| S Antibody | CSB-PA333052LA01BJO | Bovine coronavirus | ELISA |
| S Antibody | CSB-PA322803LA01BJK | Bovine coronavirus | ELISA, WB |
| S Antibody | CSB-PA336163EA01HIY | Human coronavirus OC43 | ELISA |
Coronavirus-Host Interactome Targets Products
| Product Name | Code | Sample Types | Detection Range |
| Human ACE2 ELISA Kit | CSB-E04489h | serum, plasma, cell culture supernates | 0.156 ng/mL-10 ng/mL |
| Human APN ELISA kit | CSB-EL001827HU | serum, plasma, tissue homogenates | 31.25 pg/mL-2000 pg/mL |
| Human CD147 ELISA Kit | CSB-E12994h | serum, plasma | 12.5 pg/mL-800 pg/mL |
| Human CTSB ELISA kit | CSB-E13450h | serum, plasma, tissue homogenates | 0.312 ng/mL-20 ng/mL |
| Human NRP1 ELISA kit | CSB-EL016091HU | serum, plasma, tissue homogenates | 6.25 pg/mL-400 pg/mL |
| Product Name | Code | Species Reactivity | Tested Applications |
| ACE2 Antibody | CSB-PA866317LA01HU | Human | ELISA, IHC, IF |
| ACE2 Antibody | CSB-PA001150GA01HU | Human, Mouse, Rat | ELISA,WB |
| APN Antibody | CSB-PA001827LA01HU | Human, Mouse | ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| APN Antibody | CSB-PA001827GA01HU | Human,Mouse,Rat | ELISA,WB |
| CD147 antibody | CSB-PA11759A0Rb | Human | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| CTSB Antibody | CSB-PA06974A0Rb | Human, Mouse | ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| DPP4 Antibody | CSB-PA06229A0Rb | Human, Rat | ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
| DPP4 Antibody | CSB-PA007139GA01HU | Human,Mouse,Rat | ELISA,WB,IHC |
| TMPRSS2 Antibody | CSB-PA971239 | Human | ELISA,WB |
| NRP1 Antibody | CSB-PA016091ESR1HU | Human | ELISA, IHC |
| Target Name | Product Name | Code | Species | Source | Tag Info |
| ACE2 | Recombinant Human Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2(ACE2),partial | CSB-AP005671HU | Human | Mammalian cell | C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| CD147 | Recombinant Human Basigin(BSG),partial | CSB-RP117574h | Human | E.coli | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| CTSB | Recombinant Human Cathepsin B(CTSB),partial (Active) | CSB-AP005381HU | Human | Mammalian cell | C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| CTSB | Recombinant Human Cathepsin B(CTSB),partial | CSB-EP006185HU1 | Human | E.coli | N-terminal GST-tagged |
| DPP4 | Recombinant Human Dipeptidyl peptidase 4(DPP4) | CSB-CF007139HU | Human | in vitro E.coli expression system | N-terminal 10xHis-tagged |
| TMPRSS2 | Recombinant Human Transmembrane protease serine 2(TMPRSS2),partial | CSB-EP023924HU | Human | E.coli | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| TMPRSS2 | Recombinant Human Transmembrane protease serine 2(TMPRSS2),partial | CSB-YP023924HU | Human | Yeast | N-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| ACE2 | Recombinant Human Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2(ACE2),partial | CSB-MP866317HU | Human | Mammalian cell | |
| CD147 | Recombinant Human Basigin(BSG),partial | CSB-MP002831HU | Human | Mammalian cell | |
| CD147 | Recombinant Human Basigin(BSG),partial | CSB-MP002831HUf3 | Human | Mammalian cell | |
| NUP98 | Recombinant Human Nuclear pore complex protein Nup98-Nup96(NUP98) ,partial | CSB-MP016209HU | Human | Mammalian cell |
2019 Novel Coronavirus
Based on the fact that the number of infected people in China has increased and outbreaks have occurred in many countries. On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization announced that the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) was listed as Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). At this point, the SARS-CoV-2 disease (COVID-19) disease is not only a battle in China, but also a global battle. So what exactly is the SARS-CoV-2? How does it spread? Where does SARS-CoV-2 come from? And how to treat it? Don’t worry, we will illustrate these questions one by one.
What is The Coronavirus?
Before introducing the SARS-CoV-2, let us understand what is a coronavirus. Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that can cause respiratory illnesses such as the common cold. Almost everyone gets infected with coronaviruses at least once in their life, but symptoms are typically mild to moderate. Most coronaviruses are not dangerous, but some are. Those that cause Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) or severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) can be deadly.
As the Figure 1 shows, coronaviruses are viruses that are spherical, have protrusions, and are crown-like. They are collectively referred to as coronaviruses. The virus has a diameter of 75 to 160 nanometers, and the virus genome is a continuous linear single-stranded RNA, and the molecular weight is usually (5.5 to 6.1) x106.
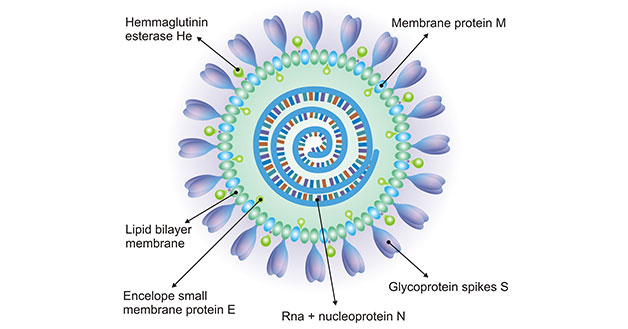
The coronavirus genome encodes a spike protein (S), an envelope protein, a membrane protein, and a nucleoprotein in this order. Among them, spike protein is the most important surface membrane protein of coronavirus.
What is The SARS-CoV-2?
The SARS-CoV-2 was discovered because of Wuhan Viral Pneumonia cases in 2019, and was named by the World Health Organization on January 12, 2020. It belongs to the beta genera of the Coronaviridae family in 2003, together with SARS coronavirus (SARS CoV) in 2003 and MERS coronavirus (MERS CoV) in 2012. The alignment between SARS-CoV-2 and 2002 SARS CoV has about 70% sequence similarity and 40% sequence similarity with MERS CoV. There is currently no specific treatment, but many symptoms can be managed, and need to be treated according to the clinical situation of the patient.
CUSABIO paid close attention to the progression of SARS-CoV-2. Once obtaining the virus gene sequence information, we quickly developed and produced SARS-CoV-2 related products. Targets include the Spike protein (S), N protein (N) and ACE2. Moreover, we also provide several products about coronavirus to meet the needs of scientific research.
How does SARS-CoV-2 Spread?
The virus is reportedly spreading from person-to-person in many parts of China and in some other countries by interacting with ACE2 from mucous membrane of eye, mouth and nose. On Jan. 30, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) identified the first case of person-to-person spread in the United States.
In terms of how one would catch the virus, the CDC says that human coronaviruses are most commonly spread between an infected person and others via:
- The air (from viral particles from a cough or sneeze);
- Close personal contact (touching or shaking hands);
- An object or surface with viral particles on it (then touching your mouth, nose or eyes before washing your hands);
- And rarely from fecal contamination.
What are The Symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 Infection?
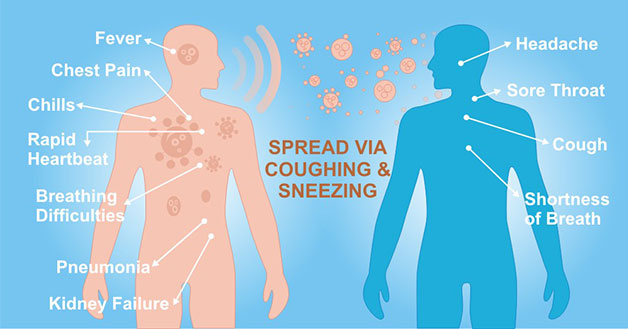
As the Figure 2 shows, the typical symptoms of the SARS-CoV-2 infection include:
- Main symptoms are fever, fatigue, and dry cough;
- Nasal congestion, runny nose and other upper respiratory symptoms are rare;
- Approximately half of the patients experienced dyspnea after one week, and the severe cases progressed rapidly to acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, difficult to correct metabolic acidosis, and coagulopathy.
It is worth noting that in the course of severe and critically ill patients, there can be moderate to low fever, even without obvious fever. Some patients have mild onset symptoms and no fever. They usually recover after 1 week. Most patients have a good prognosis, and a few patients are critically ill and even die.
Where Does SARS-CoV-2 Come From?
Currently, the origin of SARS-CoV-2 also isn’t clear. But experts suppose that the origin still is wildlife like the other coronaviruses. Coronaviruses originate in animals-like camels, civets and bats-and are usually not transmissible to humans. But occasionally a coronavirus mutates and can pass from animals to humans and then from human to human, as such the case with the SARS epidemic in the early 2000s. China’s National Health Commission confirmed that 15 health care workers have become infected, indicating that the virus can spread from human to human.
Writing here, you may confuse that should I be concerned about pets (such as dog and cat) carring SARS-CoV-2? Exactly, there is no evidence suggested coronavirus in dogs and other pets. But, CDC recommends that people traveling to China avoid animals both live and dead.
How to Treat 2019 Novel Coronavirus?
In terms of SARS-CoV-2 treatment, there are no specific treatments for coronavirus infections and most people will recover on their own. So treatment involves rest and medication to relieve symptoms. A humidifier or hot shower can help to relieve a sore throat and cough. If you are mildly sick, you should drink a lot of fluids and rest.
Although there is no vaccine for the new coronavirus, researchers at the U.S. National Institutes of Health confirmed they were in preliminary stages of developing one. Officials plan to launch a phase 1 clinical trial of a potential vaccine within the next three months. Moreover, researchers are also working on gathering samples of the virus to design a therapy that will train patients’ immune cells to detect and destroy the virus.
How to Protect Yourself From Coronavirus?
Although there are no specific treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection, we can take these measures to prevent us from it:
- Wash your hands: wet your hands with clean, running water and apply soap.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze, then throw the tissue and wash your hands. If you do not have a tissue to hand, cough or sneeze into your elbow rather than your hands.
- Face masks offer some protection as they block liquid droplets.
- Seek early medical help if you have a fever, cough and difficulty breathing, and share your travel history with healthcare providers.
- If you have returned from an affected area in the last two weeks, stay indoors and avoid contact with other people for 14 days. This means not going to work, school or public areas.