CAL2 enables reliable distinction of CALR mutated ET and PMF from PV and reactive bone marrow alterations.
MPNs – Myeloproliferative Neoplasms / ET – Essential Thrombocythaemia / PMF – Primary Myelofibrosis / PV – Polycythaemia Vera
MPNs – Myeloproliferative Neoplasms / ET – Essential Thrombocythaemia / PMF – Primary Myelofibrosis / PV – Polycythaemia Vera
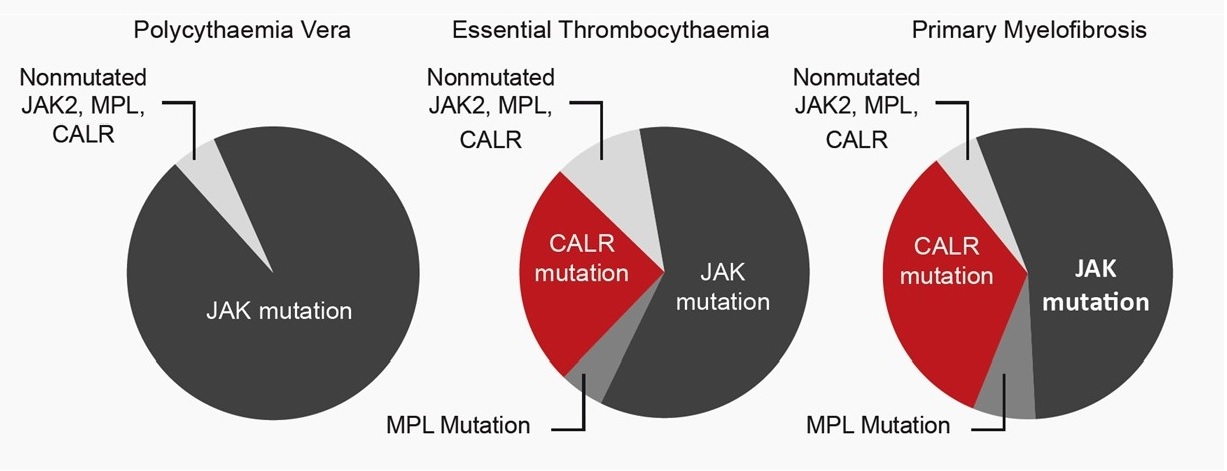
CALR mutations are detectable in 67% of ET and 88% of PMF cases with non-mutated JAK2 or MPL. It is mutually exclusive with mutations of JAK2 or MPL in MPNs: The detection of CALR mutations fills a diagnostic gap in ET and PMF patients harbouring non-mutated JAK2/MPL.
References:
CAL2 IHC in four MPN cases:
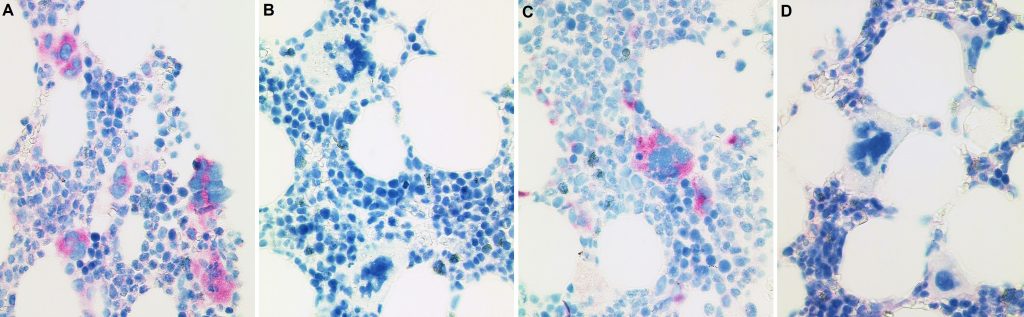
A and C: Selective staining of mutated CALR protein in megakaryocytes of essential thrombocythaemia (A) and early primary myelofibrosis (C).
B and D: Absent CAL2 staining in two essential thrombocythaemia cases with molecularly detected mutation in JAK2 (B) and MPL (D).
CAL2 IHC in four PMF cases:
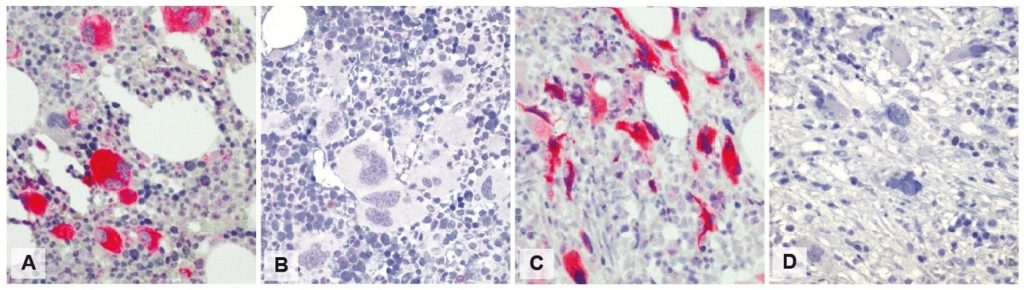
A and C: Selective staining of mutated CALR protein in megakaryocytes of two PMF cases, respectively in prefibrotic phase and in fibrotic phase, in which Sanger sequencing detected a CALR mutation.
B and D: Absent CAL2 staining in two PMF cases, respectively in prefibrotic and fibrotic phase, both without molecularly detected mutated CALR. The fibrotic stroma remains unstained (C and D).
CAL2 antibody immunohistochemistry (IHC) is suitable for
All different types of CALR mutations result in a novel C-terminus. This harbours a common epitope expressed in all different types of CALR mutations. The CAL2 antibody is directed against this common epitope. Therefore, it can be concluded that CAL2 antibody is able to detect all CALR mutations.
Please review the actual list of scientific publications for anti-CALRmut clone CAL2 on CiteAb.