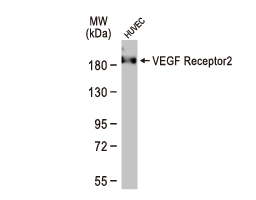
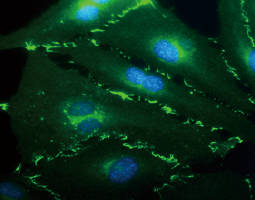
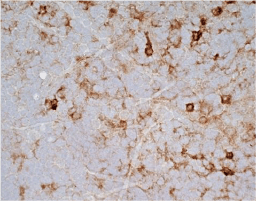
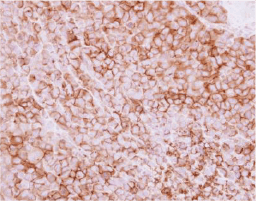
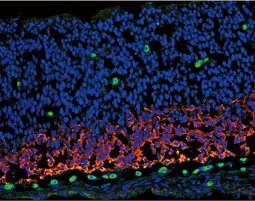
The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and circulatory system. It is responsible for delivery of oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to the body’s cells, as well as for carrying away carbon dioxide and waste products generated by those same cells. Lining the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vasculature are endothelial cells that together form a semi-selective barrier and are critical for transcellular transport of macromolecules, hemostasis, immune responses, angiogenesis, metabolism of circulating factors, and vascular tone. Endothelial cell dysfunction is a major reason that cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide.
Cardiovascular

The heart functions as a pump to drive a continuous column of blood through the vasculature. Heart dysfunction and disease can be due to coronary artery narrowing (atherosclerosis), valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathies affecting the myocardium, arrhythmias due to compromised conduction, and infectious or inflammatory processes (e.g. endocarditis, myocarditis, or pericarditis). The clinical and societal burden of heart and vascular disease makes cardiovascular biology research a top priority.
Highlighted Products

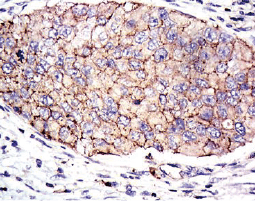
Separate from the lymphatic vessels, the systemic vasculature conducts blood to the body tissues and cells through arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. A system of venules and veins ultimately returns blood to the heart by way of the inferior and superior venae cavae, in addition to the pulmonary veins that empty directly into the left atrium. Disruption of vascular function can be due to atherosclerosis, thrombosis, autoimmune disease, metabolic disorders, or infection. In addition, various solid tumors can drive angiogenesis to support their access to oxygen and nutrients while also promoting metastasis.
Highlighted Products
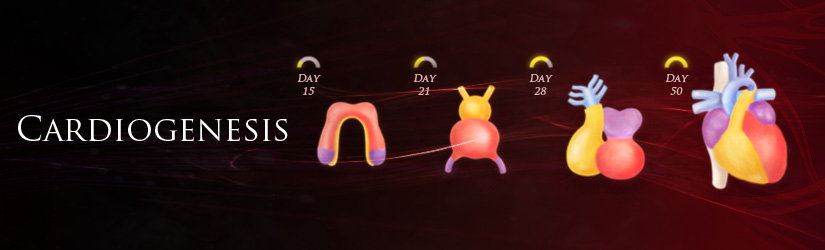
Cardiogenesis refers to the development of the heart, the first functional organ in the embryo. The linear heart tube is formed at three weeks gestation and begins beating. By seven weeks, the four chambers are established and the heart is connected to the pulmonary trunk and aorta. Cardiogenesis is a tightly regulated orchestration of differentiation and migration of at least three types of heart precursor cell. The study of cardiac biology aims to investigate the pathways involved in heart development to better understand and treat congenital heart conditions as well as ischemic heart disease. In addition, knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying embryonic cardiogenesis has provided invaluable insight into the design of cell-based therapies for adults. In conjunction with this, researchers have created protocols for the isolation and characterization of both cardiac progenitors and their definitive progeny.
Highlighted Products

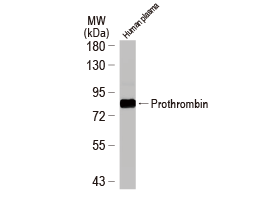
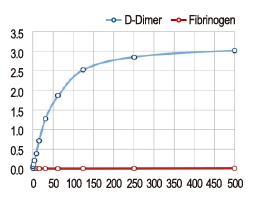
Thrombosis refers to clot formation within the vasculature that impedes the normal flow of blood. Clots can form in either arteries or veins. Arterial thrombi are often due to atherosclerosis, which is characterized by plaques that are highly thrombogenic when they rupture. Venous thrombi can result from vessel damage or disease, immobility, obesity, clotting disorders, certain medications, and other medical conditions. A particularly dangerous, and often lethal, result of thrombosis occurs when a clot breaks free and causes either an embolic stroke or a pulmonary embolism.
Highlighted Products
Atherosclerosis describes the thickening of arterial walls by the deposition of plaque, which can consist of calcium, fatty matter, cholesterol, cellular debris, or fibrin. It generally begins in youth and progresses with age. The danger from these plaques is two-fold. First, the narrowing of the arterial lumen by the thickened wall restricts blood flow to organs sensitive to ischemia, like the heart and brain. Second, if the plaque ruptures, a clot can form at the site of the damaged endothelium and either completely occlude the vessel, causing a thrombotic stroke or myocardial infarction, or break off and cause an embolic stroke.
Highlighted Products