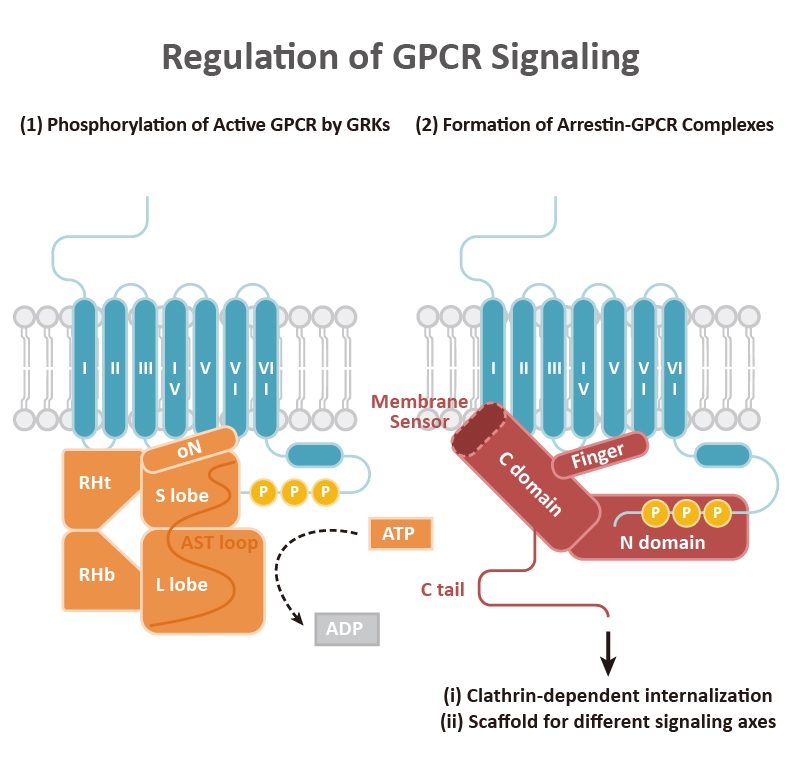
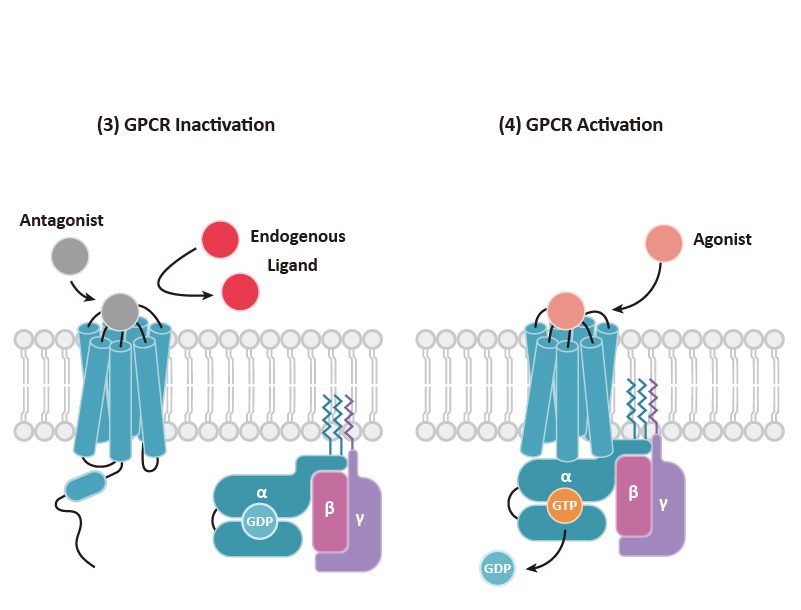
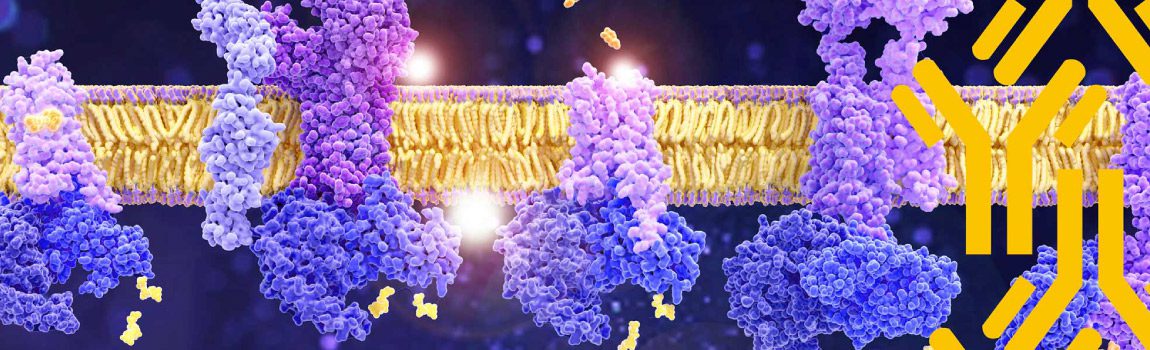
GPCRs play a crucial role in the regulation of tissue/cell physiology and homeostasis in the immune, nervous, endocrine, and cardiovascular systems, among others. They also function in a multitude of pathological processes, including cancer.
GPCRs in cancers
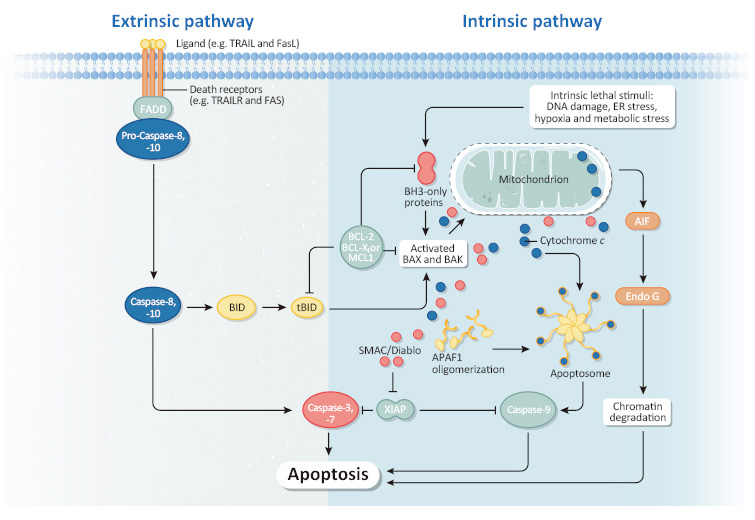
Many GPCRs serve as potential biomarkers for early cancer diagnosis. Furthermore, GPCRs are active in various aspects of cancer progression, including proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, migration, and invasion. Therefore, the pharmacological inhibition of GPCRs and their downstream targets presents a promising avenue for developing novel, mechanism-based strategies for cancer therapy.
GPCRs in the immune system
Inflammatory cells such as leukocytes, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells express more than one GPCR and sense a wide range of chemoattractants and chemokines. These receptors are crucial for the migration and infiltration of immune cells. Abnormal GPCR expression can lead to immune system dysfunction manifesting as inflammatory and autoimmune disease.
GPCRs in the nervous system
The nervous system utilizes membrane receptors to detect extracellular stimuli. By expressing GPCRs with diverse ligand-recognition capabilities, the nervous system can selectively filter and respond to specific signals. GPCRs are involved in chronic neurodegenerative diseases including but not limited to Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease.
GPCRs in homeostasis
GPCRs play a crucial role in maintaining metabolic balance by influencing key processes such as glucose homeostasis and insulin secretion, appetite, calcium sensing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Table 1. GPCRs related to different disorders
| Disorder |
GPCRs |
| Cancer |
Bradykinin receptor |
| Chemokine receptors |
| Endothelin receptors |
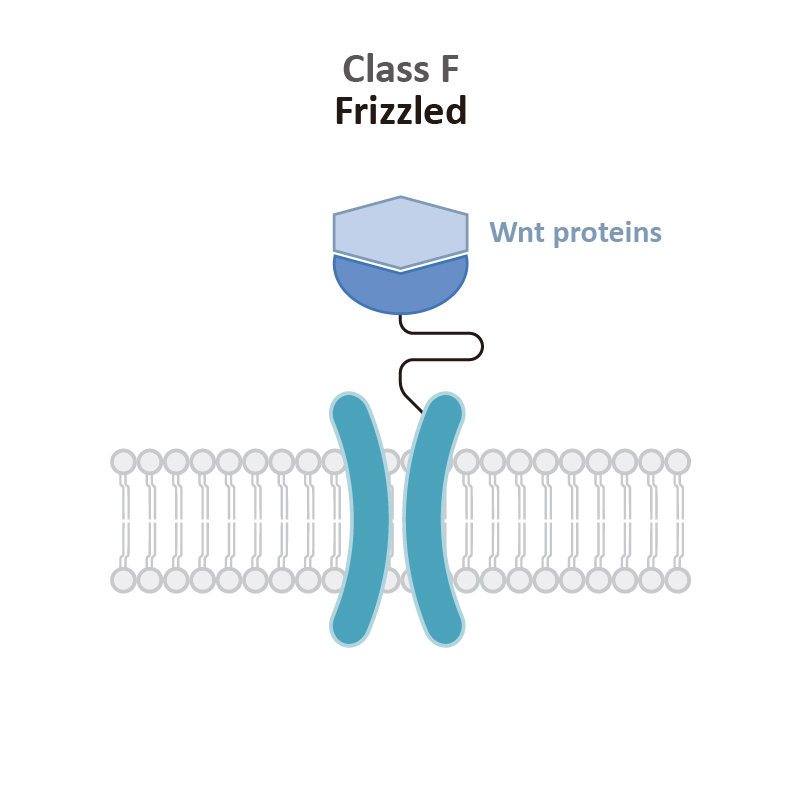
| Frizzled receptors |
| Protease-activated receptors Prostaglandin receptors |
| Immunological disorders |
Adenosine receptors |
| Anaphylatoxin receptors (C3aR, C5aR, and C5L2) |
| Cannabinoid receptors |
| Chemokine receptors |
| Histamine receptors |
| Neurokinin receptors |
| Prostaglandin receptors |
| Protease-activated receptors |


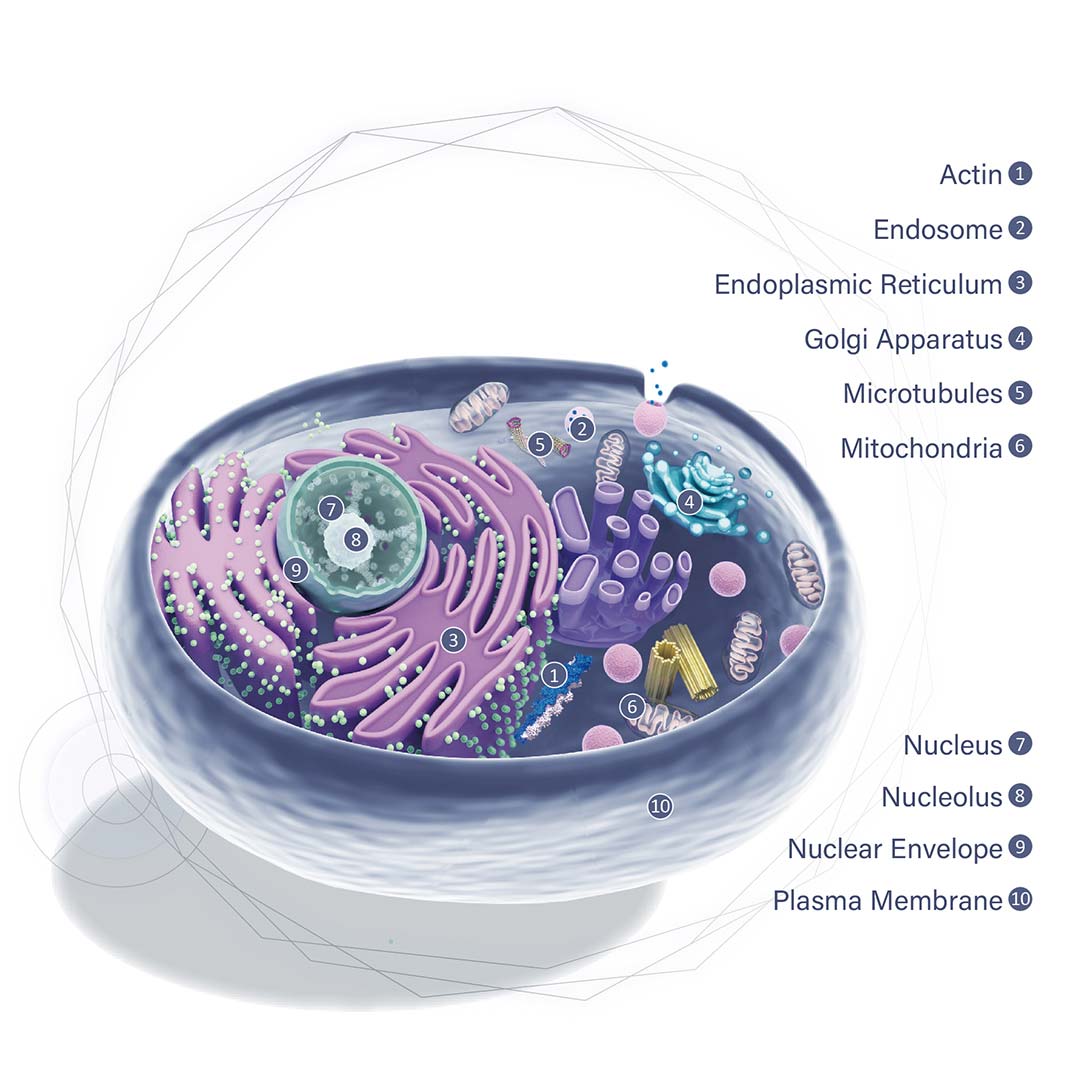
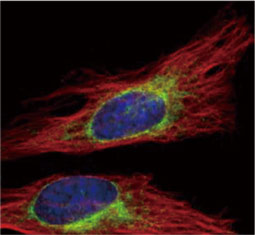
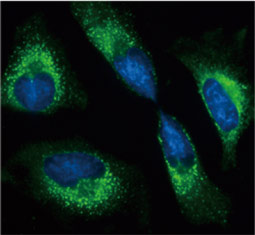
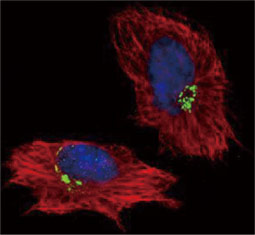
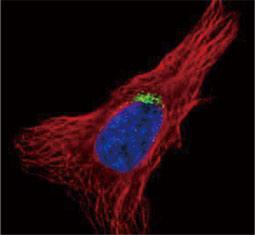
![CXCR2 antibody [HL2604] (GTX639056)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/CXCR2-antibody-HL2604-GTX639056.jpg)
![CXCR4 antibody [HL2424] (GTX638646)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/CXCR4-antibody-HL2424-GTX638646.jpg)
![Adenosine A1 Receptor antibody [HL2442] (GTX638758)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Adenosine-A1-Receptor-antibody-HL2442-GTX638758.jpg)
![Dopamine Receptor D2 antibody [HL1478] (GTX636952)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Dopamine-Receptor-D2-antibody-HL1478-GTX636952.jpg)
![Somatostatin receptor 3 antibody [HL2681] (GTX639345)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Somatostatin-receptor-3-antibody-HL2681-GTX639345.jpg)
![Dopamine Receptor D1 antibody [HL2680] (GTX639344)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Dopamine-Receptor-D1-antibody-HL2680-GTX639344.jpg)
![GLP1R antibody [HL2297] (GTX638352)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/GLP1R-antibody-HL2297-GTX638352.jpg)
![AGTR1 antibody [HL2524] (GTX638885)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/AGTR1-antibody-HL2524-GTX638885.jpg)

![Rhodopsin antibody [HL2668] (GTX639332)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Rhodopsin-antibody-HL2668-GTX639332.jpg)
![Rhodopsin antibody [HL2668] (GTX639332) 1](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Rhodopsin-antibody-HL2668-GTX639332-1.jpg)
![GLP1R antibody [HL2297] (GTX638352) 1](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/GLP1R-antibody-HL2297-GTX638352-1.jpg)
![GLP1R antibody [HL2297] (GTX638352) 2](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/GLP1R-antibody-HL2297-GTX638352-2.jpg)
![CD97 antibody [HL1925] (GTX637674)](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/CD97-antibody-HL1925-GTX637674.jpg)
![CD97 antibody [HL1925] (GTX637674) 1](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/CD97-antibody-HL1925-GTX637674-1.jpg)

![Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [HL2357] (GTX638563) 1](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Calcium-Sensing-Receptor-antibody-HL2357-GTX638563-1.jpg)
![Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [HL2357] (GTX638563) 2](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Calcium-Sensing-Receptor-antibody-HL2357-GTX638563-2.jpg)
![Frizzled 9 antibody [HL1675] (GTX637274) 1](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Frizzled-9-antibody-HL1675-GTX637274-1.jpg)
![Frizzled 9 antibody [HL1675] (GTX637274) 2](https://www.stratech.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Frizzled-9-antibody-HL1675-GTX637274-2.jpg)