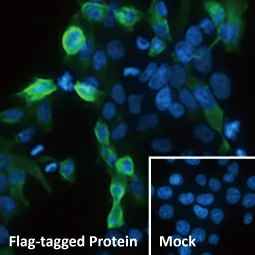
The 2020 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to “Harvey J Alter, Michael Houhgton and Charles M Rice“ for their discoveries of “Hepatitis C virus“.
Infectious Diseases

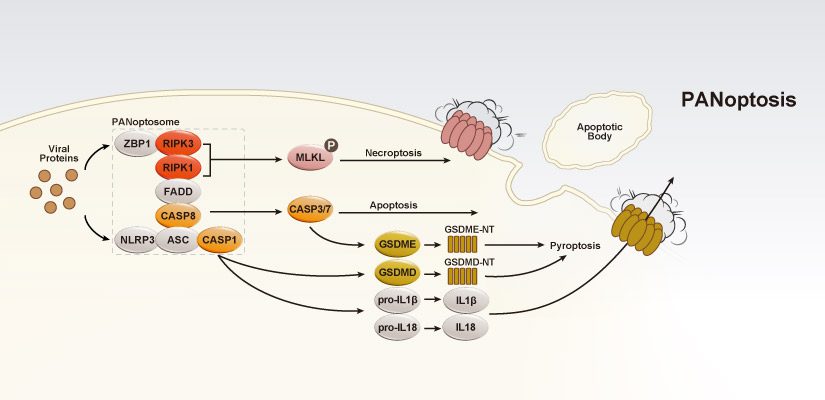
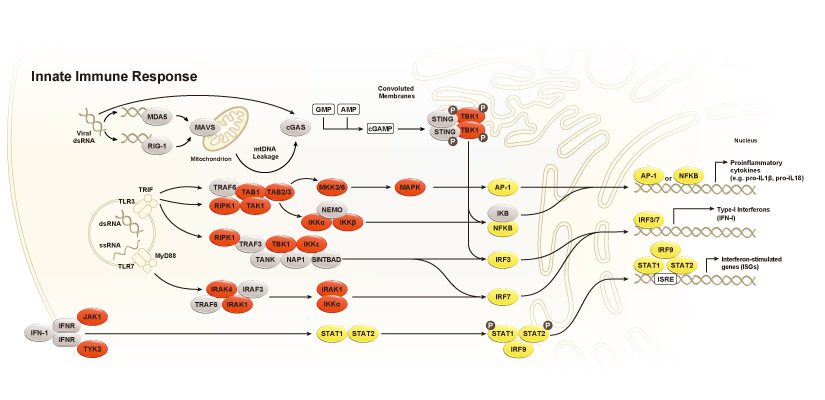
Viruses are small infectious agents that exist in the gray area between “living” and “nonliving” entities. In contrast to most bacteria, fungi, or parasites, viruses are completely dependent on the host cell for their replication, hijacking the cell’s biochemical machinery through the actions of viral genome-encoded factors. The fundamental structure of the viral particle includes the DNA or RNA genome within a protein coat, or capsid. This capsid is, for some viruses, enclosed within a lipid envelope usually derived from the host cell membrane. Attachment of a virus to a specific receptor on a host cell leads to internalization and frequently the initiation of a new round of viral replication.
There are more than 200 virus species that can infect humans, not including many others that affect humanity by targeting plants and animals used by people. Included in this viral pathogen list are the influenza viruses, dengue virus, Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), hepatitis viruses (e.g., HCV & HBV), enterovirus (EV71, EV68, and coxsackievirus) and Zika virus. GeneTex is proud to offer an extensive catalog of antibody reagents that can facilitate your research into these and other viruses.
Featured Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
ASFV p54 antibody [HL1289] (GTX636703)
![]()
ASFV p54 antibody [HL1289] (GTX636703)
![]()
Chikungunya Virus nsP2 antibody [HL1488] (GTX636962)
![]()
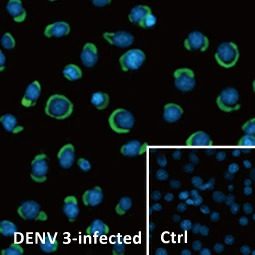
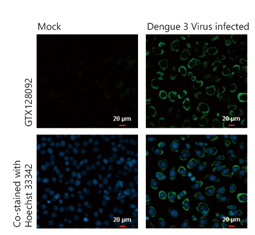
Dengue Virus prM protein antibody (GTX128092)
![]()
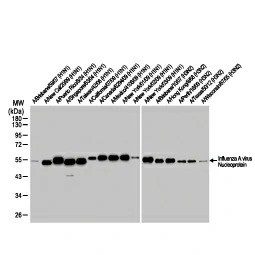
Influenza A Virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1103] (GTX636318)
![]()
![]()
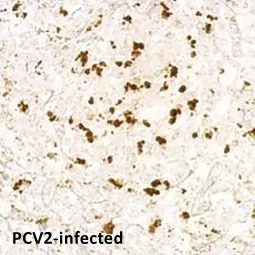
Porcine circovirus type 2 / PCV2 Capsid antibody (GTX128120)
![]()
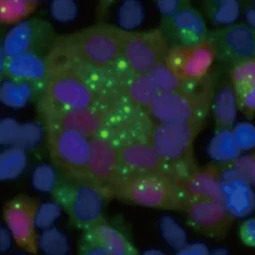
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1248] (GTX636650)
![]()
![]()
![]()
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1248] (GTX636650)
![]()
![]()
![]()
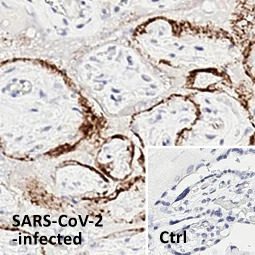
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Spike S1 antibody [HL6] (GTX635654)
![]()
![]()
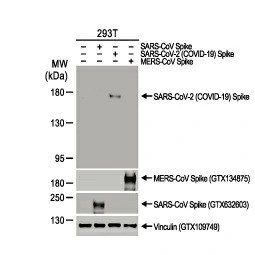
SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Spike S1 antibody [HL6] (GTX635654)
![]()
![]()
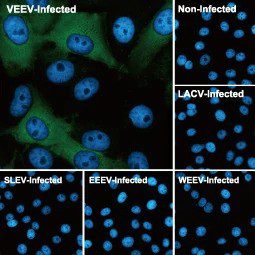
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP2 antibody [HL1919] (GTX637668)
![]()
![]()
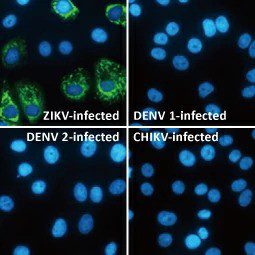
Zika Virus Envelope protein antibody (GTX133314)
![]()
![]()
GeneTex’s Comprehensive Product and Literature Catalog for Viral Infectious Disease Research

Figure 1. The Coxsackievirus (CV) virio
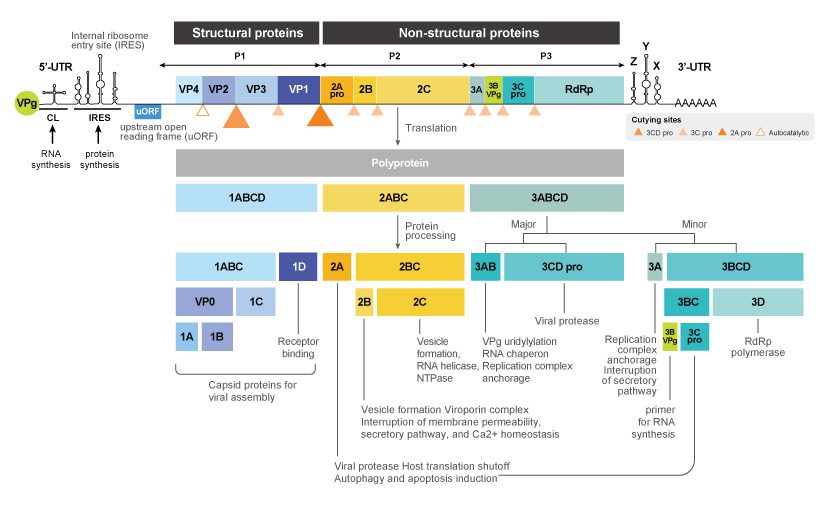
Figure 2. Coxsackievirus (CV) genomic organization
Featured Products
![]()

Coxsackievirus A6 VP2 antibody (GTX132348)

Coxsackievirus A6 VP3 antibody (GTX132689)
Coxsackie Adenovirus Receptor antibody (GTX118382)
| Product Name | Clonality | Applications | Cat. No | |
| Coxsackie Adenovirus Receptor antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, IP | GTX118382 | |
| Coxsackievirus A6 VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | GTX132346 | |
| Coxsackievirus A6 VP2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | GTX132348 | |
| Coxsackievirus A6 VP2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | GTX132347 | |
| Coxsackievirus A6 VP3 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | GTX132689 | |
| Coxsackievirus A6 VP3 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | GTX132688 |

| Dengue (DEN) is the most serious of the mosquito-borne viral diseases. It is caused by Dengue virus (DENV), from any of the four serotypes (DEN1-4). Patients develop long-term immunity to the initial infecting serotype. However, sequential infection by different serotypes leads to a greater risk of serious disease manifestations. From this observation emerged the hypothesis of antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) of infection, whereby previously acquired anti-DENV antibodies appear to facilitate both higher viremia and amplified release of inflammatory mediators in response to heterotypic DENV infection. This may explain the epidemiological findings that infants born to DEN-immune mothers are at higher risk of more severe clinical disease. Now Ng et al (1), using an elegant mouse model system, offer compelling evidence in support of the ADE hypothesis in the mother-offspring scenario. They found that DENV2-infected offspring born to DENV1-immune mothers displayed more serious disease and died sooner compared to DENV2-infected mice born to naïve mothers. Notably, the susceptibility to disease was age-dependent, recapitulating the epidemiological observations. Taken together, this ADE mouse model joins a growing list of animal models of infectious disease, and will provide promising opportunities to further dissect the underlying mechanisms of Dengue pathogenesis. |
| The Dengue virus (DEN) is of the genus Flavivirus and possesses a positive-strand RNA genome of approximately 10.6 kb that contains a single open-reading frame encoding for a polyprotein, which can be further cleaved by cellular and viral proteases into three structural proteins (capsid protein C, membrane protein M, envelope protein E), and seven non-structural proteins (NS1, NS2a, NS2b, NS3, NS4a, NS4b, NS5). |
| GeneTex proudly offers a comprehensive catalog of outstanding antibodies to DENV proteins. While most of these were created using recombinant antigens from DEN2, the majority are very likely to cross-react with the other serotypes. A few of the antibodies are more DEN2-specific. Please note our seven mouse monoclonal antibodies against the “E”, “NS1”, “NS3”, and “NS5” proteins that are validated for both ICC/IF and western blot (see below). |
Dengue Virus Protein Schematic Diagram |
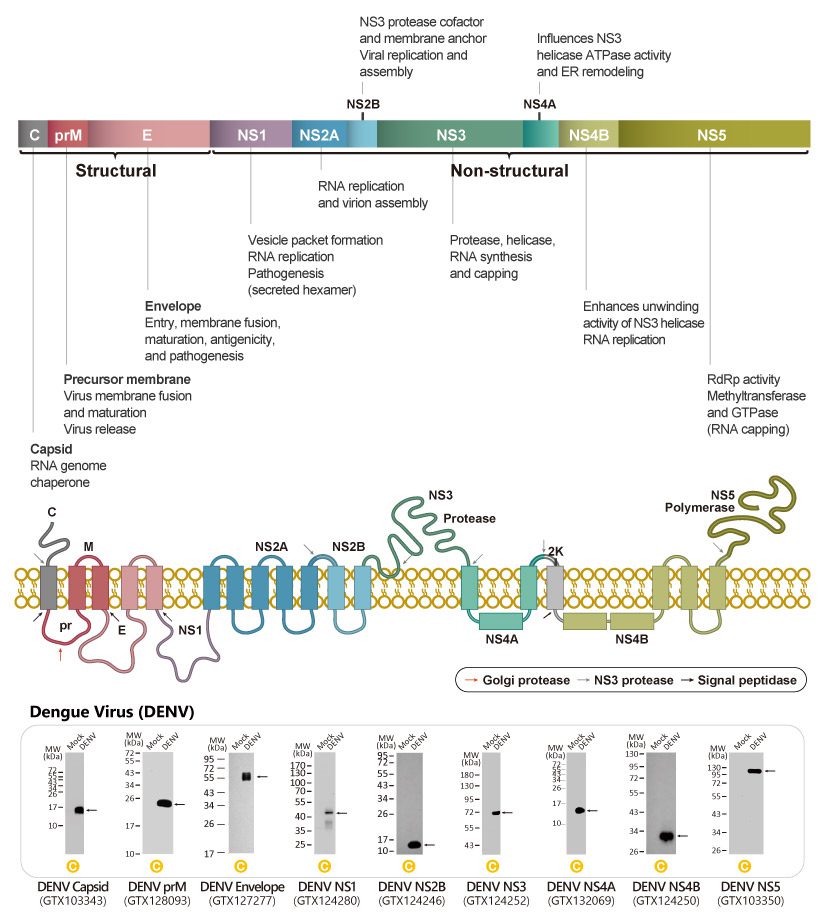
| WB analysis of virus-infected BHK21 cells. WB analysis with GeneTex dengue virus antibodies on virus-infected BHK21 cells. (A) mock. (B) virus infection. |
Featured Products
Dengue virus Capsid protein antibody
|
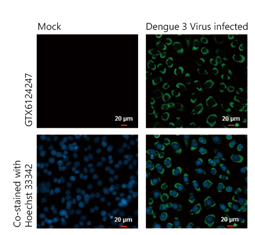
Dengue virus prM protein antibody
|
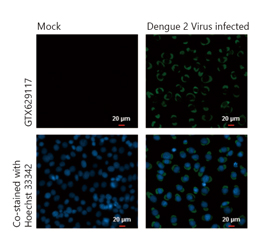
Dengue virus Envelope protein antibody
|
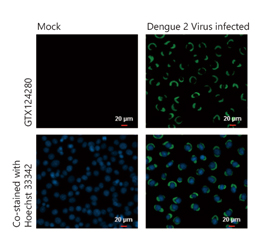
Dengue virus NS1 protein antibody
|
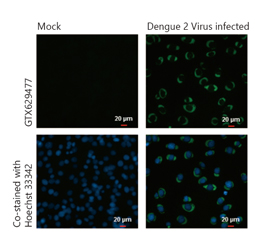
Dengue virus NS3 protein antibody
|
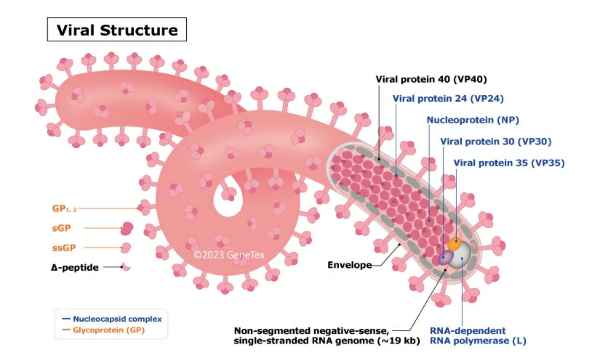
Figure 1. The EBOV virion
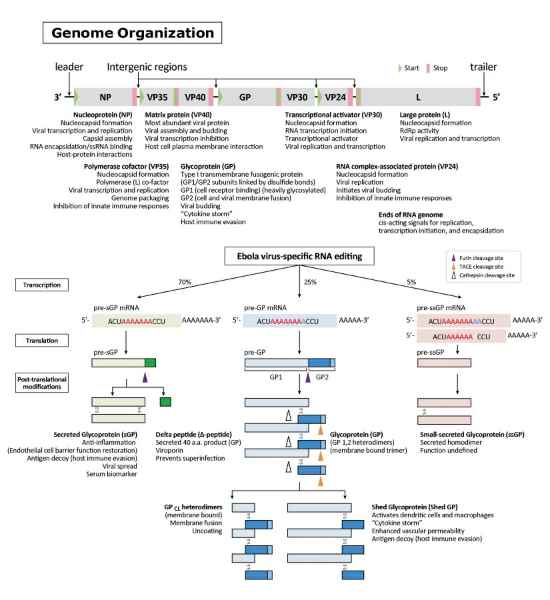
Figure 2. The EBOV genomic organization and EBOV-specific RNA editing
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
Ebola virus NP antibody (GTX134031)
![]()
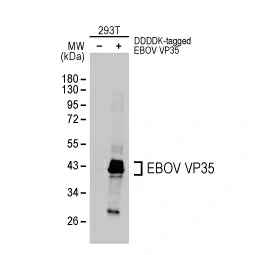
Ebola virus VP35 antibody (GTX134032)
![]()
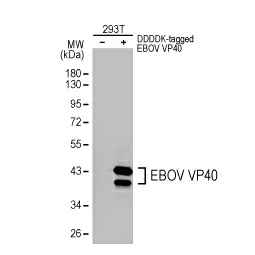
Ebola virus VP40 antibody (GTX134034)
![]()
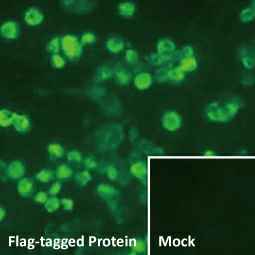
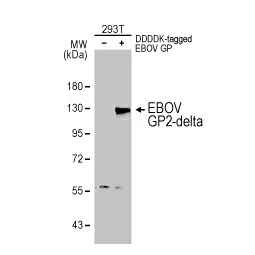
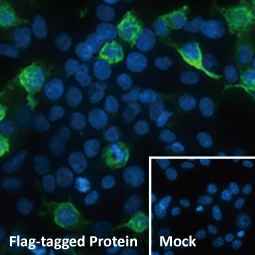
Ebola virus NP antibody (GTX134031)
![]()
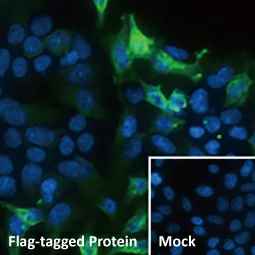
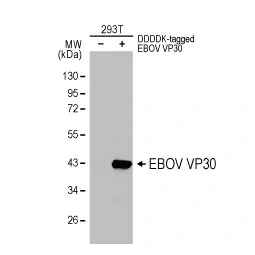
Ebola virus VP35 antibody (GTX134032)
![]()

Ebola virus VP40 antibody (GTX134034)
![]()
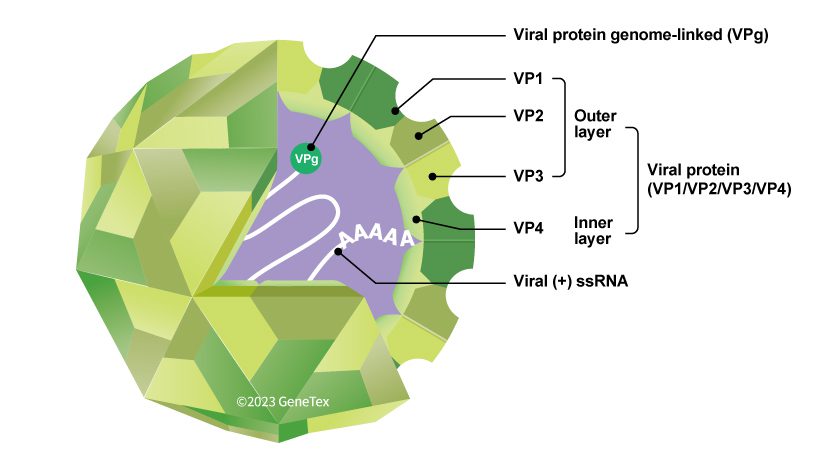
Figure 1. The EV-D68 virion
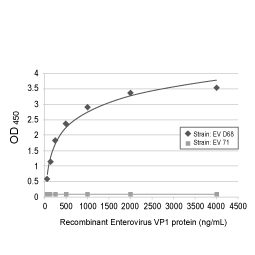
The Enterovirus genus (family Picornaviridae) encompasses 15 species, though only seven of these (i.e., Enterovirus A to D and Rhinovirus A to C) include viruses that infect humans. Each species contains various “types”, with the Enterovirus D species having five of which two (Enteroviruses D68 (EV-D68) and D70 (EV-D70)) infect only humans. EV-D68 can cause severe respiratory disease and is linked to the neurologic syndrome acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) that overwhelmingly (>90%) affects children (1, 2). Though first described in 1962, it is over the last one to two decades that there has been an increasing worldwide incidence of EV-D68 cases that tracks with AFM outbreaks. The EV-D68 genome has evolved rapidly and is now categorized into four clades, with mutations that appear to have broadened tissue tropism and virulence (including neurovirulence). Presently there are no available vaccines or antiviral agents for these pathogens.
Enterovirus D viruses are small and non-enveloped with a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome that is translated into a single polyprotein subsequently processed into 11 mature proteins. These include the four structural proteins VP1, VP2, VP3, and VP4 in addition to seven nonstructural proteins (i.e., 2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, 3B, 3C and 3D) (2). Further characterization of their functions and host-viral factor interactions are essential for a better understanding of Enterovirus D pathogenesis.
GeneTex continues to expand its infectious disease catalog with a growing portfolio of reagents for non-poliovirus Enterovirus (NPVE) research (including antibodies against Coxsackievirus A6, Enterovirus A71, and Enterovirus D68). This includes the new recombinant rabbit monoclonal Enterovirus D68 VP1 antibody [HL1997] (GTX637898) for the EV-D68 product line. Please see the highlighted product images and a complete EV-D68 antibody listing below.
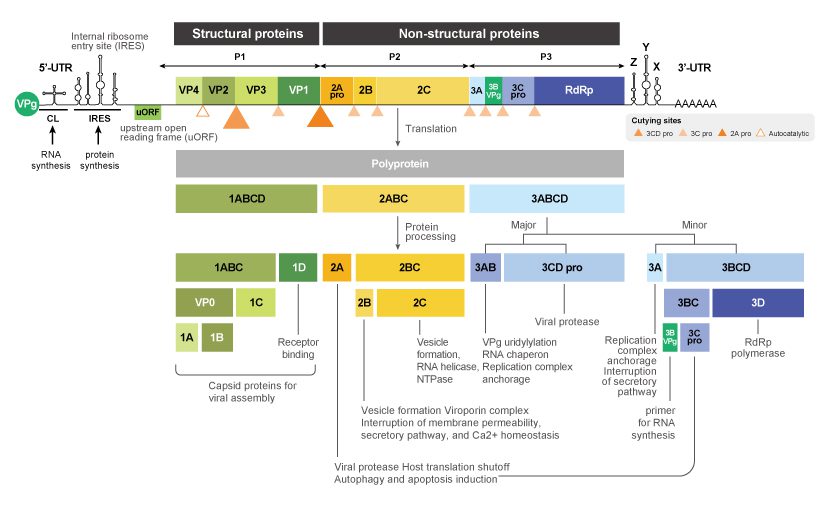
Figure 2. The EV-D68 genome codes for a single polyprotein that is processed into 11 mature proteins.
Featured Products
![]()
![]()
![]()
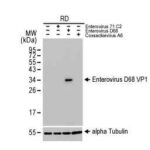
Enterovirus D68 VP1 antibody [HL1997] (GTX637898)
![]()
![]()
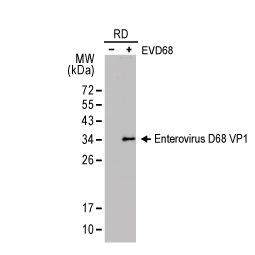
Enterovirus D68 VP1 antibody [GT11610] (GTX633688)
![]()
![]()
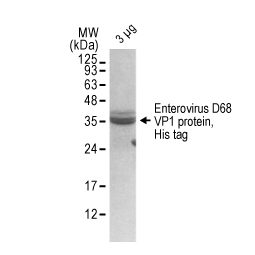
Enterovirus D68 VP1 protein, His tag (GTX138561-pro)

Enterovirus D68 VP3 antibody [GT1665] (GTX633706)
![]()
Enterovirus D68 2B antibody (GTX134419)
| Product Name | Clonality | Applications | Cat. No. | |
| Enterovirus D68 VP2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-Fr | GTX132314 | |
| Enterovirus D68 VP3 antibody [GT1665] | Ms mAb | WB | GTX633706 | |
| Enterovirus D68 VP3 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, IHC-P | GTX132315 | |
| Enterovirus D68 VP1 antibody [HL1997] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | GTX637898 | |
| Enterovirus D68 VP1 antibody [GT11610] | Rec Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA, IHC-P (cell pellet) | GTX633688 | |
| Enterovirus D68 VP1 antibody [GT1843] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, ELISA, Lateral Flow, IHC-P (cell pellet) | GTX633770 | |
| Enterovirus D68 VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, FACS | GTX132313 | |
| Enterovirus D68 VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | GTX132312 | |
| Enterovirus D68 2B antibody | Rb pAb | WB | GTX134419 |
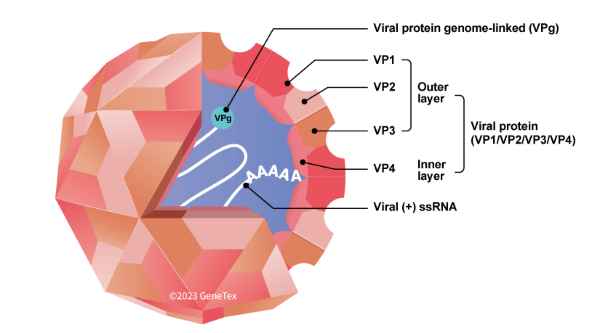
Figure 1. The EV71 virion
| Discovered in 1969, human enterovirus 71 (EV71) is the causative agent of hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) in young children, with a subset of patients developing more severe neurological disease that can result in death. Though epidemics have become more numerous since 1997, there are still no effective therapies or an established vaccine. Clearly, further research into the biology of this virus is of the utmost importance. |
| As a member of the genus Enterovirus in the family Picornaviridae, EV71 has a positive-stranded RNA genome coding for a 2,194 amino acid polyprotein, which is subsequently processed into four structural (VP1-VP4) and seven non-structural (2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, 3B, 3C, 3D) proteins. Identifying the specific functions of these proteins and their interactions with host factors will provide crucial information regarding EV71-associated neural pathogenesis and viral replication. |
| GeneTex is proud to offer an outstanding selection of antibodies for EV71 research. Please see the highlighted antibodies below. |
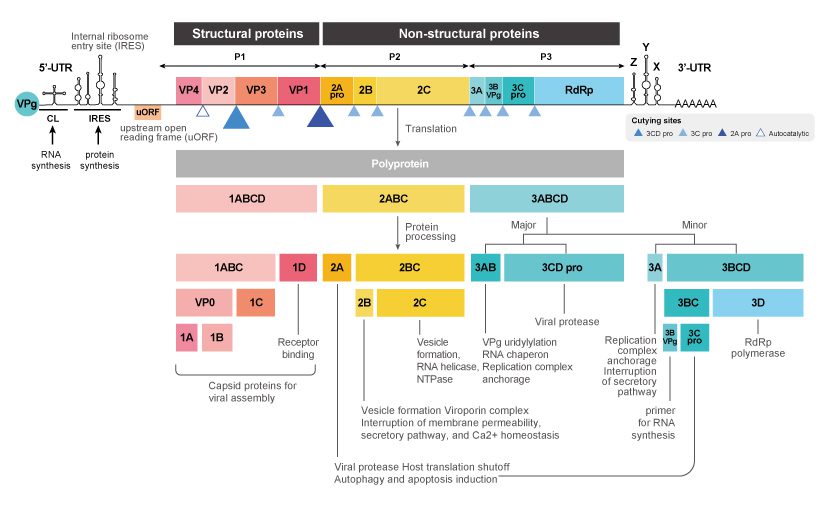
Figure 2. The EV71 genome codes for a single polyprotein that is processed into 11 mature proteins.
Featured Products
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
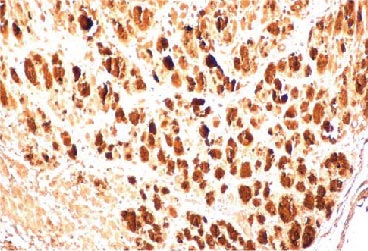
Enterovirus 71 3AB antibody (GTX132344)IHC-P analysis detecting expression of EV71 3AB protein in an EV71 infected mouse skeletal muscle tissue section. |
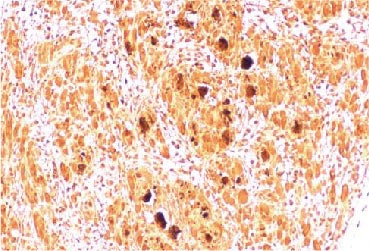
Enterovirus 71 2B antibody (GTX132343)IHC-P analysis detecting expression of EV71 2B protein in an EV71 infected mouse skeletal muscle tissue section. |
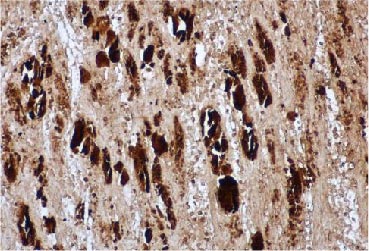
EV71 VP1 antibody (GTX132338)IHC-P analysis detecting expression of EV71 VP1 protein in an EV71 infected mouse skeletal muscle tissue section. |
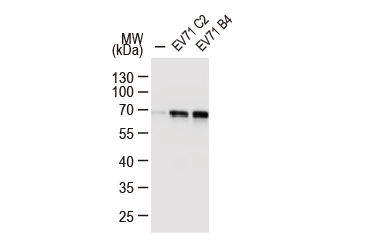
Enterovirus 71 antibody (GTX124261)WB analysis of EV71 proteins in RD cells infected with EV71 virus C2 or B4 strain. |
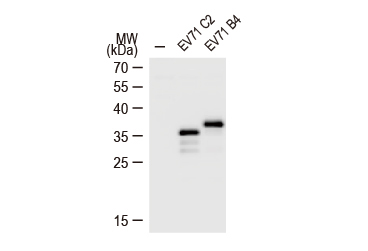
Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody (GTX132339)WB analysis of EV71 VP1 protein in RD cells infected with EV71 virus C2 or B4 strain. |
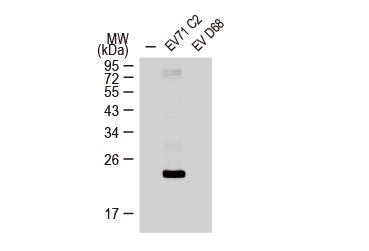
Enterovirus 71 3C antibody [B3] (GTX630191)WB analysis of EV71 3C protein in RD cells infected with EV71 or EV D68 virus. |
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host & Clonality | Applications | |
| GTX132340 | Enterovirus 71 VP2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P | |
| GTX132341 | Enterovirus 71 VP3 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX637687 | Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody [HL1928] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | |
| GTX637688 | Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody [HL1929] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | |
| GTX633390 | Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody [GT185] | Ms mAb | WB, ELISA | |
| GTX633583 | Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody [GT9512] | Ms mAb | WB, ELISA | |
| GTX132338 | Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P | |
| GTX132339 | Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P | |
| GTX132600 | Enterovirus 71 VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX132343 | Enterovirus 71 2B antibody | Rb pAb | WB, IHC-P | |
| GTX132354 | Enterovirus 71 2C antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX132344 | Enterovirus 71 3AB antibody | Rb pAb | WB, IHC-P | |
| GTX630191 | Enterovirus 71 3C antibody [B3] | Ms mAb | WB, FACS | |
| GTX132357 | Enterovirus 71 3C antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX630193 | Enterovirus 71 3D antibody [4] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IP | |
| GTX132355 | Enterovirus 71 3CD antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX132356 | Enterovirus 71 3CD antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX124261 | Enterovirus 71 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, ELISA |
Flavivirus Viral Structure
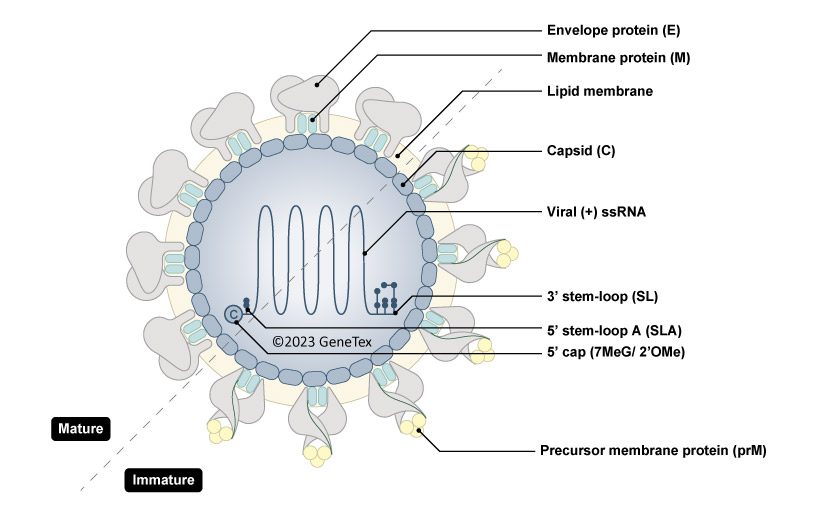
Flavivirus Protein Schematic Diagram
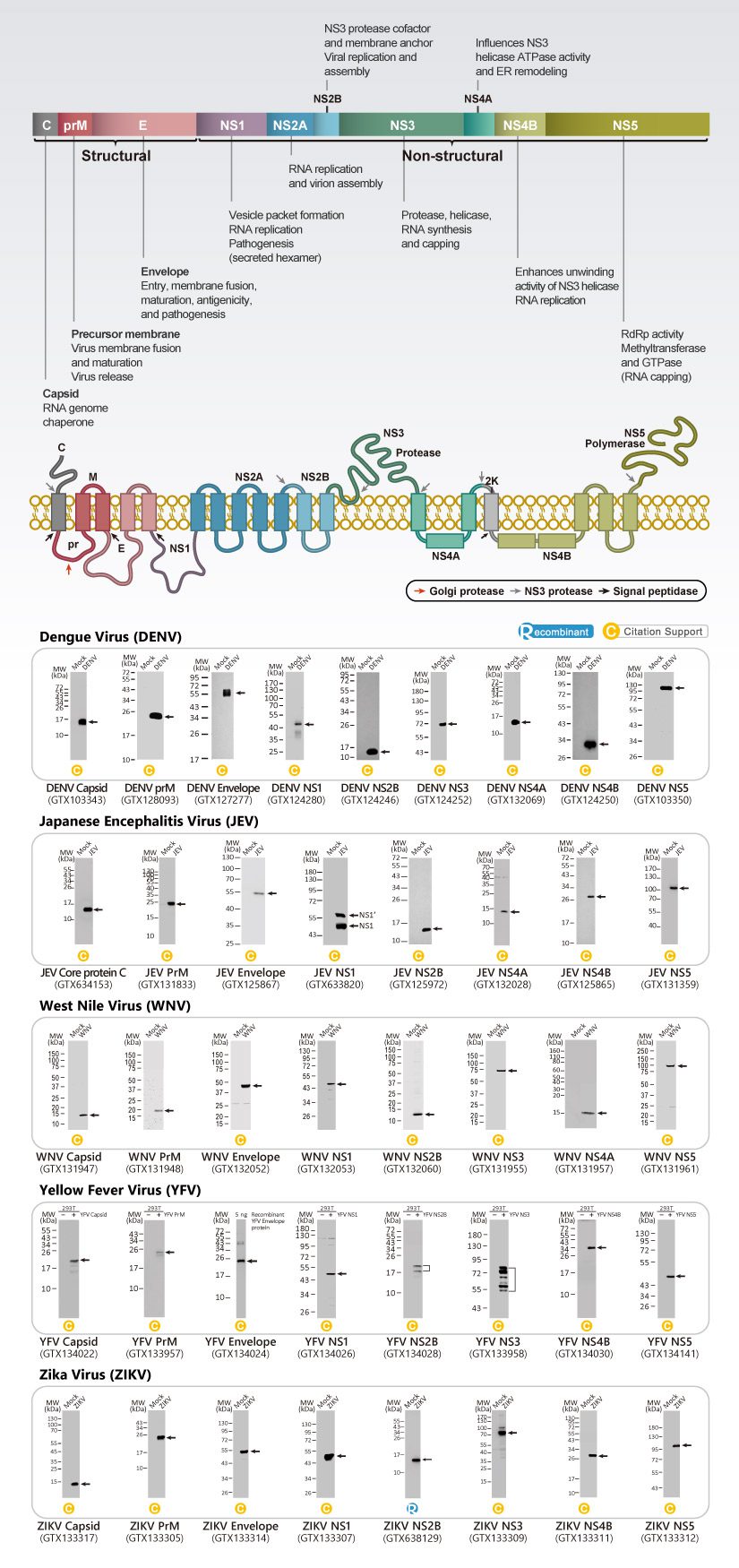
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX36855 | Hepatitis A virus VP3 antibody [1881] | Mouse | ICC/IF, ELISA, IHC | HAV |
| GTX36854 | Hepatitis A virus antibody [1885] | Mouse | ICC/IF, ELISA | HAV |
| GTX40741 | Hepatitis A virus Surface Antigen antibody [BGN/B5B3 (B5-B3)] | Mouse | ELISA, IRMA | HAV |
| GTX28254 | Hepatitis A virus antibody [MK-01] | Mouse | ELISA | HAV |
| GTX40269 | Hepatitis A virus antibody | Goat | ELISA | HAV |
| GTX30737 | Hepatitis A virus antibody | Goat | ELISA | HAV |

The 2020 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to “Harvey J Alter, Michael Houhgton and Charles M Rice“ for their discoveries of “Hepatitis C virus“.
| First identified in 1989, Hepatitis C virus (HCV) affects over 170 million people with almost 3% of the world population seropositive for anti-HCV antibodies. Chronic infection occurs in 80-85% of those acutely infected and can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and death. HCV belongs to the family Flaviviridae and has a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome that codes for a 3011 amino acid polyprotein. This polyprotein is subsequently processed by viral and cellular proteases into three structural proteins (core, E1, and E2) and seven non-structural proteins (p7, NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B). While genetic diversity makes HCV highly adaptable to challenges from the host immune system and antiviral drugs, research into HCV biology has revealed new targets (e.g., the NS5B polymerase and the NS3 protease) for specific antiviral therapies that create new hope for HCV-infected people. |
| GeneTex is proud to offer an outstanding selection of antibodies for HCV research. Please see the highlighted antibodies below. |

Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||

Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody (GTX131265)

Hepatitis C virus NS2 protein antibody (GTX131832)
![]()

Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody (GTX131276)
![]()

Hepatitis C Virus NS5A protein antibody (GTX131272)

Hepatitis C Virus NS5B protein antibody (GTX131273)
Structural
Core
| Product Name | Applications | Cat. No. |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody | WB | GTX131265 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [A1/3D1] | ELISA | GTX18700 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [B2] | WB, ELISA | GTX18728 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [1E5] (FITC) | IP, ELISA | GTX22584 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [1E5] (Rhodamine) | IP, ELISA | GTX22585 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [6A1] (FITC) | ICC/IF, IHC-Fr, ELISA | GTX40111 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [1868] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX40705 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [B317M] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, IHC, Sandwich ELISA | GTX41719 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [B306M] | ELISA | GTX41720 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [11-B3] | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-Fr, ELISA | GTX41722 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [B057M] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | GTX42536 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [B056M] | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | GTX42537 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [B055M] | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | GTX42538 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [H6-29] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, IHC | GTX64113 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [H6-29] (Biotin) | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, IHC | GTX64114 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen antibody [H6-29] (FITC) | WB, ICC/IF, IHC | GTX64115 |
Envelope
| Product Name | Applications | Cat. No. |
| Hepatitis C Virus E1 protein antibody [1879] | ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX36856 |
| Hepatitis C Virus E2 protein antibody | WB, ICC/IF, Blocking, EM | GTX103353 |
| Hepatitis C Virus E2 protein antibody [4F6/2] | WB, ICC/IF, IP, ELISA | GTX30856 |
| Hepatitis C Virus E2 protein antibody [6F6/I8] | ELISA, Purification | GTX30857 |
| Hepatitis C Virus E2 protein antibody | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX30878 |
| Hepatitis C virus E2 protein antibody [1876] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX40699 |
| Hepatitis C Virus E2 protein antibody [BDI167] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX40852 |
Non-structural
NS2
| Product Name | Applications | Cat. No. |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS2 protein antibody | WB | GTX131832 |
NS3
| Product Name | Applications | Cat. No. |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody | WB | GTX103356 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody | WB, IHC-P | GTX131269 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody | WB | GTX131276 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [20-8] | WB, ELISA, IHC | GTX18663 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [113] | WB, ELISA | GTX18664 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [281] | WB, ELISA | GTX18665 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [5] | WB, ELISA | GTX18666 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [328] | WB, ELISA | GTX18667 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [251] | WB, ELISA | GTX18668 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [242] | WB, ELISA | GTX18669 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [806] | WB, ELISA | GTX18671 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [70-13] | WB, ELISA | GTX18730 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX36540 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX41124 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [9-G2] | IHC-Fr, ELISA | GTX41696 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [BDI371] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX41717 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [V/1859] | ELISA, IHC | GTX78171 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS3 protein antibody [V/1828] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX81101 |
NS4
| Product Name | Applications | Cat. No. |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4 protein antibody [1G7] (Biotin) | WB, IHC-Fr, FACS, IP, ELISA | GTX22591 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4 protein antibody [1G7] (FITC) | WB, IHC-Fr, FACS, IP, ELISA | GTX22592 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4 protein antibody [1G7] (Rhodamine) | WB, IHC-Fr, FACS, IP, ELISA | GTX22593 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4 protein antibody | WB, ELISA, Conjugation | GTX40955 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4A protein antibody [5D4/10E7] | WB, IHC-P, ELISA | GTX19048 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4A protein antibody [497] | WB, ELISA | GTX19052 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4A protein antibody [4-F5] | WB, IHC-Fr, ELISA | GTX41689 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4A protein antibody [S4-13] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX64116 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4A protein antibody [S4-13] (Biotin) | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX64117 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4A protein antibody [S4-13] (FITC) | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX64118 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS4B protein antibody [2-H1] | WB, IHC-Fr, ELISA | GTX41684 |
NS5
| Product Name | Applications | Cat. No. |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5 protein antibody | WB, ELISA | GTX36547 |
| Hepatitis C virus NS5 protein antibody [BGN/1246/5G7] | WB, IHC-P, IHC-Fr, ELISA | GTX40671 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5 protein antibody [8926] | WB, ICC/IF | GTX64119 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5 protein antibody [8926] (FITC) | WB, ICC/IF | GTX64120 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5 protein antibody [8926] (Biotin) | WB, ICC/IF | GTX64121 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5A protein antibody | WB | GTX103358 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5A protein antibody | WB | GTX131272 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5A protein antibody [388] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX40342 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5A protein antibody [7-D4] | WB, IHC-Fr, ELISA | GTX41681 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5B protein antibody [NS5B-6] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX00713 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5B protein antibody [NS5B-6] (Biotin) | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX00846 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5B protein antibody [NS5B-6] (FITC) | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX00847 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5B protein antibody | WB | GTX131273 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5B protein antibody | WB | GTX131274 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5B protein antibody [1825] | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | GTX30873 |
| Hepatitis C Virus NS5B protein antibody [5B-12B7] | ICC/IF, IP, Neutralizing/Inhibition | GTX33940 |
Others
| Product Name | Applications | Cat. No. |
| Hepatitis C virus antibody [24-8] | WB, ELISA | GTX18662 |
| Hepatitis C virus antibody | WB, ELISA | GTX40404 |
| Hepatitis C virus antibody | WB | GTX70330 |
| Hepatitis C virus antibody | WB, IHC | GTX70331 |
| Hepatitis C Virus Core + NS3 + NS4 antibody | ELISA, Conjugation, IHC | GTX40324 |
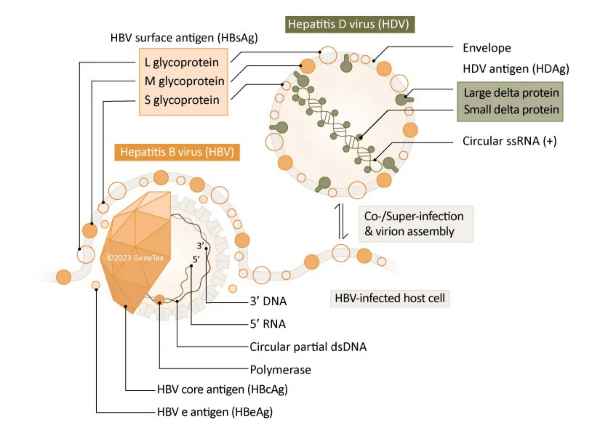
Figure 1. The HDV and HBV virions
First detected in 1977, Hepatitis Delta virus (HDV) is a major cause of cirrhosis (occurring in ~70-80% of chronic cases) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). At least 12 million people (and possibly significantly more) are chronically infected with both Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and HDV, putting them at increased risk of accelerated liver failure and HCC when compared to those patients carrying only HBV (1, 2). In addition, studies examining the oncogenicity of HDV itself, apart from its replicative dependence on HBV, have demonstrated that HDV-related HCC may be due to a mechanism (i.e., induction of genomic instability) distinct from that driving HBV-HCC (1). More research into HDV biology, HDV pathogenesis, and HDV hepatocarcinogenesis is essential, as the only recommended treatment (with limited success) is an extended course of peginterferon alfa (2).
HDV is a defective virus that can only infect individuals who are also infected with HBV, as it needs HBsAg in its envelope to enter hepatocytes (1, 2). It has the most compact genome known among animal viruses, consisting of a circular single-stranded RNA of perhaps 1.7 KB. The only protein encoded is the hepatitis delta antigen (HDAg), which exists as two isoforms: Large HDAg (L-HDAg (214 a.a.)) and Small HDAg (S-HDAg (195 a.a.)) (1). L-HDAg contains the S-HDAg sequence as well as a C-terminal isoprenylation motif required for linking the HDV ribonucleoprotein to HBsAg during viral particle assembly. S-HDAg is necessary for viral replication, while L-HDAg is inhibitory (1). HDV replicates only in the nucleus of hepatocytes and retasks the host RNA polymerase II to replicate its genome. Thus, HBsAg is the indispensable (and only) component needed from HBV for HDV replication, being crucial for HDV’s ability to infect hepatocytes as well as viral assembly and virion release (1, 2).
GeneTex continues its commitment to producing quality reagents for infectious disease research. For HDV research, GeneTex is proud to introduce new recombinant antibody products against the Large HDAg isoform (Hepatitis D virus Large delta protein antibody [HL1051] (GTX636026)) and both the Large and Small HDAg isoforms (Hepatitis D virus Large delta + Small delta protein antibody [HL1053] (GTX636028) and Hepatitis D virus Large delta + Small delta protein antibody [HL1055] (GTX636030)) to expand its catalog. Please see the highlighted product images below for more details.
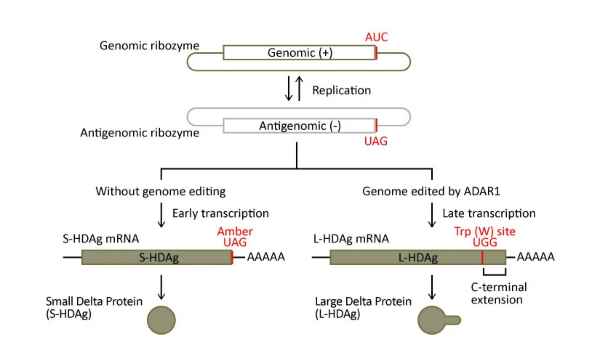
Figure 2. HDV HDAg transcription
Highlighted Products
![]()
![]()
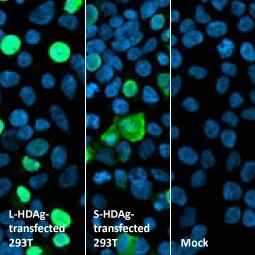
Hepatitis D virus Large delta + Small delta protein antibody [HL1055] (GTX636030)
![]()
Hepatitis D virus Large delta + Small delta protein antibody [HL1053] (GTX636028)
![]()
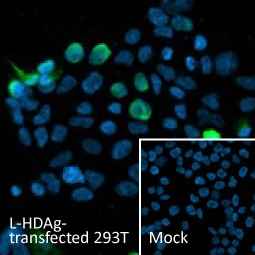
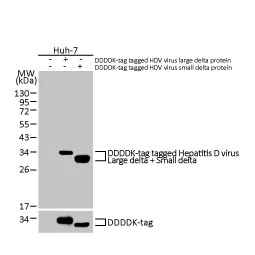
Hepatitis D virus Large delta protein antibody [HL1051] (GTX636026)
![]()
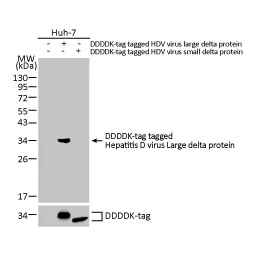
Hepatitis D virus Large delta protein antibody [HL1051] (GTX636026)
![]()
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications | |
| GTX636028 | Hepatitis D virus Large delta + Small delta protein antibody [HL1053] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX636030 | Hepatitis D virus Large delta + Small delta protein antibody [HL1055] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX135575 | Hepatitis D virus Large delta + Small delta antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX135576 | Hepatitis D virus Large delta + Small delta protein antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX636026 | Hepatitis D virus Large delta protein antibody [HL1051] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX135574 | Hepatitis D virus Large delta protein antibody | Rb pAb | WB |
| Cat. No. | Description | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX130852 | NMT1 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P | Hu, Ms, Rat |
| GTX40774 | HIV1 p24 antibody (Biotin) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64132 | HIV1 protease antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA, Neutralizing/Inhibition | HIV |
| GTX64128 | HIV1 p24 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX40278 | HIV1 p24 antibody [28E0] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-Fr, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64133 | HIV1 Reverse transcriptase antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX40080 | HIV1 p24 antibody [491] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX28327 | HIV protease antibody [1696] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64125 | HIV1 p15 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64127 | HIV1 p17 antibody | Guinea pig | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64129 | HIV1 p24 antibody | Guinea pig | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64124 | HIV1 Nef antibody | Guinea pig | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64126 | HIV1 p17 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX80390 | HIV1 P17 Gag antibody [17-1] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, FACS, IP | HIV |
| GTX64134 | HIV1 Reverse transcriptase antibody | Guinea pig | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64131 | HIV1 p55 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64123 | HIV1 Nef antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, Dot, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX64130 | HIV1 p24 antibody (Biotin) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF, IP, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX80729 | HIV1 p24 antibody [1941] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, IHC, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX82010 | HIV1 Rev antibody | Chicken | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | HIV |
| GTX80393 | HIV1 Vif antibody [319] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF | HIV |
| GTX57729 | NMT1 antibody [AT2C8] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF | HIV |
| GTX78443 | HIV protease antibody [1696] (Azide Free) | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Functional Assay | HIV |
| GTX36524 | HIV1 virions antibody (HRP) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, IHC | HIV |
| GTX36848 | HIV1 p24 antibody [1941] (FITC) | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, IHC | HIV |
| GTX41618 | HIV 1/2 p24 antibody [B1217M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX36486 | HIV1 gp41 antibody (HRP) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA, IHC | HIV |
| GTX80730 | HIV1 p24 antibody [1946] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX41582 | HIV1 p24 antibody [BDI690] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX36496 | HIV1 p24 antibody (HRP) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA, IHC | HIV |
| GTX36495 | HIV1 gp120 antibody (HRP) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA, IHC | HIV |
| GTX80391 | HIV1 integrase antibody [IN-2] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, IP | HIV |
| GTX36845 | HIV1 p24 antibody [1949] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX40569 | HIV1 p24 antibody (FITC) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | HIV |
| GTX41179 | HIV1 gp120 antibody | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX40452 | HIV2 gp36 antibody [BDI411] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX41590 | HIV1 p24 antibody [BDI479] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX80392 | HIV2 Nef antibody [4B5] | Rat | Monoclonal | WB, IP | HIV |
| GTX19054 | HIV1 p24 antibody [473] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX36419 | HIV1 gp120 antibody (Biotin) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX36847 | HIV1 p24 antibody [1947] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX19975 | HIV1 gp41 antibody [5A1] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX41616 | HIV p24 antibody [B281M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX41585 | HIV1 p24 antibody [BDI489] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX36846 | HIV1 p24 antibody [1948] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX80731 | HIV1 p17 antibody [1981] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX28246 | HIV1 p24 antibody [ND1] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX41607 | HIV p24 antibody [B910M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX41620 | HIV 1/2 p24 antibody [B1216M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX40105 | HIV1 gp120 antibody (Biotin) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX41583 | HIV1 p24 antibody [BDI499] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HIV |
| GTX18168 | HIV1 gp120 antibody [8.A.001] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HIV |
| GTX13412 | HIV2 gp39 antibody [HIV2gp39] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA | HIV |
| GTX13933 | HIV1 p24 antibody [HIV1gp24] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA | HIV |
| GTX40890 | HIV1 gp41 antibody | Goat | Polyclonal | WB | HIV |
| GTX17460 | HIV1 tat antibody | Chicken | Polyclonal | WB | HIV |
| GTX40823 | HIV1 antibody (Biotin) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB | HIV |
| GTX41604 | HIV1 gp41 antibody [191] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB | HIV |
| GTX13411 | HIV1 gp120 antibody [NYRHIV1gp120] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA | HIV |
| GTX36410 | HIV1 gp41 antibody (Biotin) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB | HIV |
| GTX36600 | HIV1 virions antibody | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF | HIV |
| GTX80728 | HIV1 gp41 antibody [1911] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB | HIV |
| GTX19961 | HIV1 p24 antibody | Goat | Polyclonal | WB | HIV |
| GTX36372 | HIV1 virions antibody (FITC) | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF | HIV |
| GTX36448 | HIV1 virions antibody (Biotin) | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF | HIV |
| GTX41608 | HIV p24 antibody [B891M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | HIV |
| Cat. No. | Description | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX637546 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody [HL1821] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | HPV16 |
| GTX638883 | Human Papillomavirus type 18 E7 antibody [HL2522] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Lateral Flow | HPV18 |
| GTX637228 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody [HL1647] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | HPV16 |
| GTX132686 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E6 antibody | Rabbit | Monoclonal | WB | HPV16 |
| GTX634337 | Human Papillomavirus type 18 E7 antibody [GT881] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow | HPV18 |
| GTX133411 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | HPV16 |
| GTX133412 | Human Papillomavirus type 18 E7 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | HPV18 |
| GTX04630 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E6 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IHC-P, FACS | HPV16 |
| GTX132687 | Human Papillomavirus type 18 E6 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | HPV |
| GTX133373 | Human Papillomavirus type 18 E2 antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | HPV18 |
| GTX60410 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody [6F3] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, IHC-P, ELISA | HPV16 |
| GTX73652 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 L1 antibody [CamVir 1] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, IP | HPV |
| GTX20070 | Human Papillomavirus type 16/18 E6 antibody | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, IHC-P, IP | HPV |
| GTX40864 | Human Papillomavirus type 16/18 E7 antibody [718-15] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HPV |
| GTX41516 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody [B716M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HPV |
| GTX39477 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody [716-D1] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HPV |
| GTX41484 | Human Papillomavirus type 18 E7 antibody [718-67] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HPV |
| GTX41556 | Human Papillomavirus type 11 E7 antibody [B021M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HPV |
| GTX41519 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody [B616M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HPV |
| GTX03724 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody [716-332cc] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HPV |
| GTX41163 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E7 antibody [716-325] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | HPV |
| GTX02771 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 L1 antibody [HPV16/2058R] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | IHC-P | HPV16 |
| GTX17185 | Human Papillomavirus type 16 E2 antibody | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | HPV |
GeneTex has supported the world’s leading researchers for over 25 years with our quality antibodies. Our products continue to be referenced in leading publications and we are proud to be able to contribute to the research community.
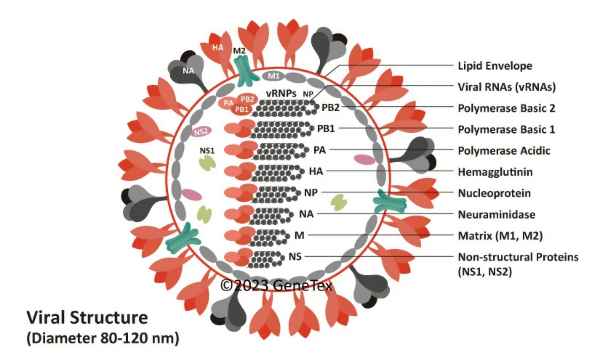
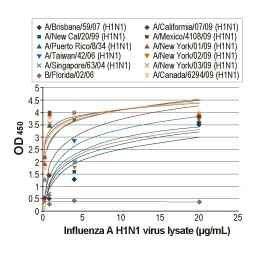
There are three types of influenza virus: Types A, B, and C. The influenza A and B viruses are the ones most associated with serious human infections,while the Type C cases are clinically much milder. The main antigenic determinants of influenza A and B viruses are the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) transmembrane glycoproteins. Based on the antigenicity of these glycoproteins, influenza A viruses are further subdivided into sixteen “H” (H1-H16) and nine “N” (N1-N9) subtypes.The influenza A virus genome consists of eight separate RNA segments that encode the proteins (i.e., PB1, PB2, PA, HA, NA, NP, M1, M2, NS1, and NS2) essential for host infection, viral genome replication, and virus particle packaging.
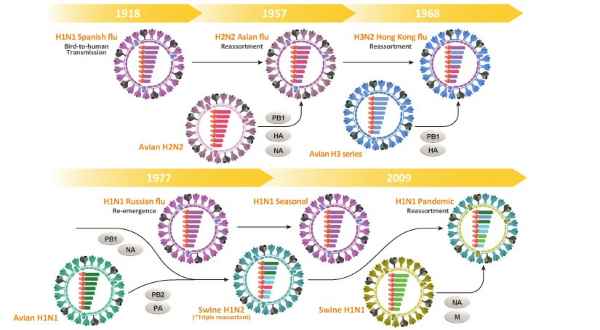
Figure 2. Antigenic shift and drift of influenza A virus
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
Influenza A Viral Proteins
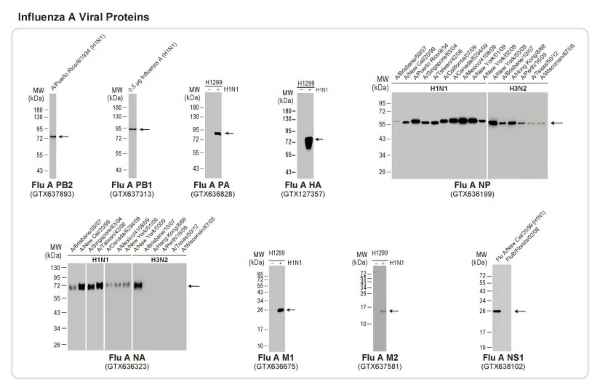
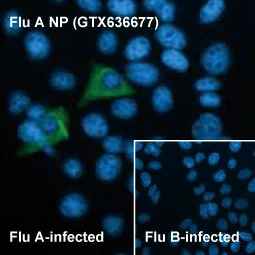
Influenza virus A NP
More Influenza virus A NP
| Flu A | Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications | |
| PB2 | GTX637893 | Influenza A virus PB2 protein antibody [HL1992] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| PB2 | GTX125926 | Influenza A virus PB2 protein antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| PB1 | GTX637313 | Influenza A virus PB1 protein antibody [HL1714] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| PB1 | GTX125923 | Influenza A virus PB1 protein antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| PA | GTX636828 | Influenza A virus PA protein antibody [HL1388] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| PA | GTX118991 | Influenza A virus PA protein antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| HA | GTX637034 | Influenza A virus H10N3 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody [HL1559] | Rec Rb mAb | ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| HA | GTX629750 | Influenza A virus H1N1 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody [GT223] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| HA | GTX127357 | Influenza A virus H1N1 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, ELISA | |
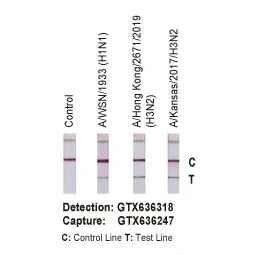
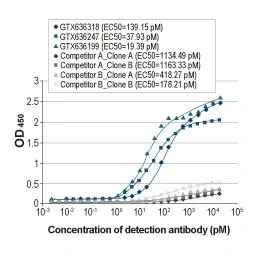
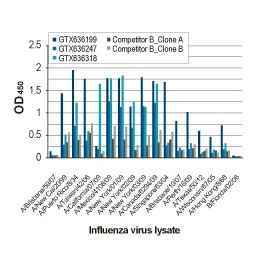
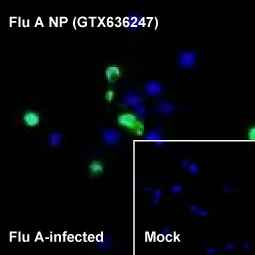
| NP | GTX636247 | Influenza A virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1089] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| NP | GTX636318 | Influenza A virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1103] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| NP | GTX636199 | Influenza A virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1078] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | |
| NP | GTX637790 | Influenza A virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1953] | Rec Rb mAb | Lateral Flow | |
| NP | GTX629633 | Influenza A virus Nucleoprotein antibody [GT1236] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, IHC-Fr, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | |
| NP | GTX629544 | Influenza A virus Nucleoprotein antibody [GT778] | Ms mAb | WB | |
| NP | GTX125989 | Influenza A virus Nucleoprotein antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, IP, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | |
| NA | GTX636323 | Influenza A virus H1N1 NA (Neuraminidase) antibody [HL1108] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| NA | GTX629696 | Influenza A virus H1N1 NA (Neuraminidase) antibody [GT288] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| NA | GTX125974 | Influenza A virus H1N1 NA (Neuraminidase) antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| M1 | GTX636675 | Influenza A virus M1 (matrix protein) antibody [HL1273] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| M1 | GTX125928 | Influenza A virus M1 (matrix protein) antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-Fr | |
| M2 | GTX637581 | Influenza A virus M2 (matrix protein) antibody [HL1856] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| M2 | GTX125951 | Influenza A virus M2 (matrix protein) antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| NS1 | GTX638102 | Influenza A virus NS1 (nonstructural protein) antibody [HL2130] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| NS1 | GTX633685 | Influenza A virus NS1 (nonstructural protein) antibody [GT1653] | Ms mAb | WB | |
| NS1 | GTX125990 | Influenza A virus NS1 (nonstructural protein) antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P | |
| NS2 | GTX125953 | Influenza A virus NS2 / NEP antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF |
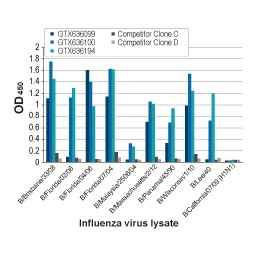
Influenza B Viral Proteins
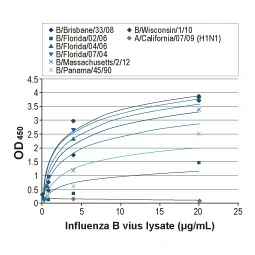
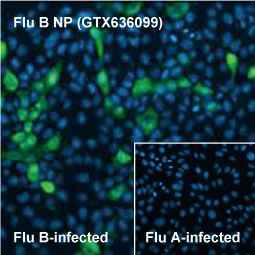
Influenza virus B NP
Avian and Swine Influenza A Viral Proteins
| Avian Flu A | Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications (Final) | |
| HA | GTX632358 | Avian Influenza A virus H5N1 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody [1D10] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| HA | GTX127299 | Avian Influenza A virus H5N3 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| HA | GTX637025 | Avian Influenza A virus H5N8 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody [HL1550] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| HA | GTX127303 | Avian Influenza A virus H7N7 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| HA | GTX127305 | Avian Influenza A virus H9N2 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| NA | GTX127984 | Avian Influenza A virus H5N1 NA (Neuraminidase) antibody | Rb pAb | WB |
| Swine Flu A | Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications (Final) | |
| HA | GTX636762 | Swine Influenza A virus G4 EA H1N1 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody [HL1342] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| HA | GTX135762 | Swine Influenza A virus G4 EA H1N1 HA (Hemagglutinin) antibody | Rb pAb | WB |
More Influenza virus B NP
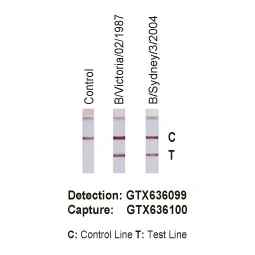
| Flu B | Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications | |
| HA | GTX638212 | Influenza B virus Hemagglutinin (HA) antibody [HL2208] | Rec Rb mAb | WB | |
| HA | GTX128542 | Influenza B virus Hemagglutinin (HA) antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | |
| NP | GTX636099 | Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1068] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | |
| NP | GTX636100 | Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1069] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | |
| NP | GTX629882 | Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein antibody [GT371] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | |
| NP | GTX128538 | Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | |
| NP | GTX128539 | Influenza B virus Nucleoprotein antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | |
| NA | GTX636950 | Influenza B virus Neuraminidase (NA) antibody [HL1476] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| NA | GTX128540 | Influenza B virus Neuraminidase (NA) antibody | Rb pAb | ICC/IF | |
| M | GTX128537 | Influenza B virus M (matrix protein) antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF |
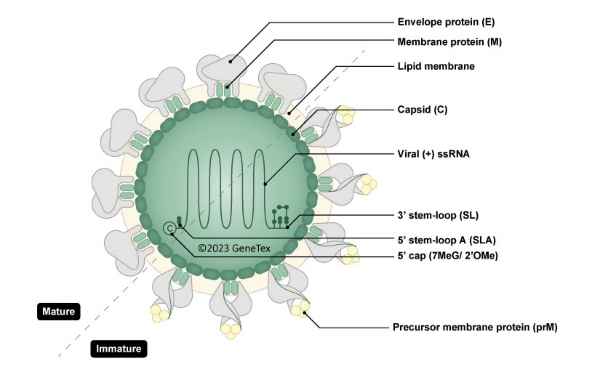
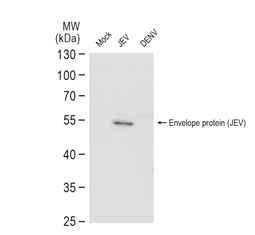
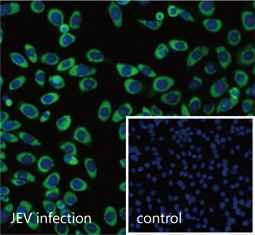
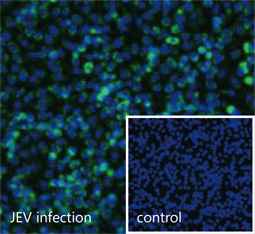
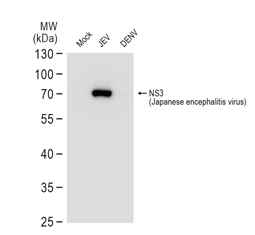
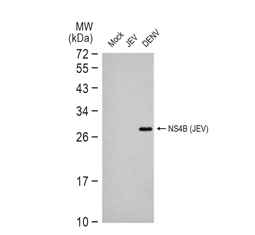
| Japanese encephalitis is a very serious infectious disease caused by Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), which belongs to the family Flaviviridae and is maintained in a zoonotic cycle involving the Culex species of mosquitoes and vertebrate hosts. Endemic to most of Asia and to certain regions of the western Pacific, JEV frequently causes severe neurologic sequelae or death in infected humans. This enveloped virus possesses a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome packaged in a spherical nucleocapsid. The genome contains a single open reading frame that encodes for a polyprotein, which is further cleaved into three structural (C, prM, E) and seven non-structural proteins (NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5). |
| GeneTex offers an outstanding selection of antibodies to support your JEV research. Please see highlighted products below or click here to view our latest products. |
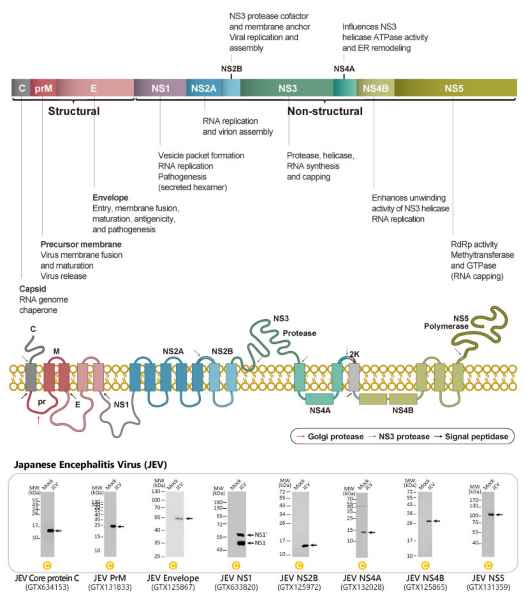
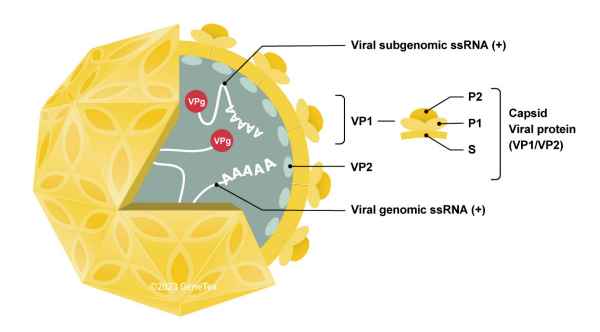
Figure 1. The Norovirus (NoV) virion
Human noroviruses (HuNoV) (previously referred to as the Norwalk Virus (NV) or Norwalk-like viruses) are the overwhelming (>95%) cause of epidemic non-bacterial gastroenteritis in the world, accounting for more than 200,000 deaths annually and significant morbidity (1). NoVs spread primarily through the fecal-oral route, which facilitates their spread through children under five years of age, the elderly, the immunocompromised, and tourists. The viral-induced self-limited gastroenteritis generally involves abdominal cramping, watery diarrhea, and vomiting. Though there is at least one vaccine candidate in development, there are no specific antivirals for HuNoVs and thorough handwashing procedures remain the best preventative strategy.
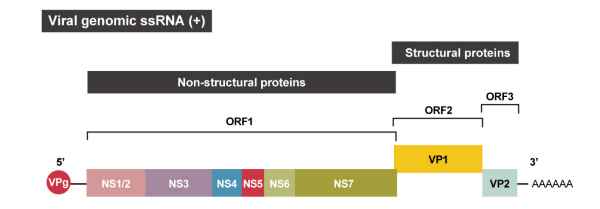
HuNoVs belong to the genus Norovirus of the family Caliciviridae. They are non-enveloped viruses containing a positive-sense, single-stranded genomic RNA of ~7.5-7.7 kb (Figures 1-2). Three open-reading frames (ORFs) encode the six non-structural proteins (NS1/2 to NS7), the main capsid protein VP1, and the minor capsid protein VP2, respectively. There are currently ten genogroups (GI–GX) (further subdivided into 49 genotypes) of NoV specified by the sequences of VP1 and the NS7 polymerase, though only GI (to which NV belongs), GII, and GIV cause acute gastroenteritis in humans (1, 2). The GII.4 genotype is associated with a more severe clinical course, and has spun off six pandemic strains. GII.17 is another highly infectious genotype that has been recently detected. Owing to antigenic shift and drift, new variants with more potent invasive capacity and resistance continue to emerge.
GeneTex is proud to add two new genotype-specific antibodies against HuNoV VP1 to its expanding portfolio of NoV research reagents. These are both recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies: Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL1672] (GTX637271) (GII.4-specific) and Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] (GTX638181) (GII.17-specific). Please see the highlighted product images and a complete NoV antibody listing below.
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
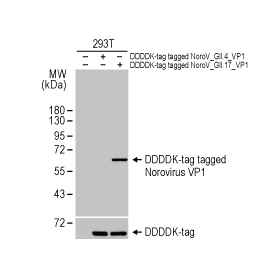
Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] (GTX638181) (GII.17-specific)
![]()
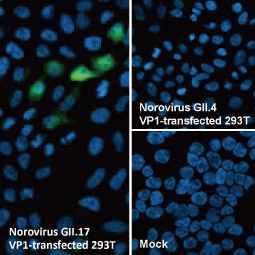
Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] (GTX638181) (GII.17-specific)
![]()
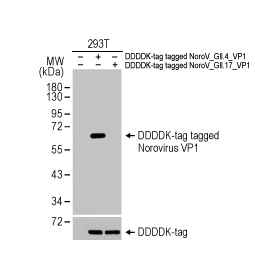
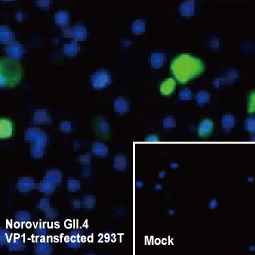
Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL1672] (GTX637271) (GII.4-specific)
![]()
Norovirus VP1 antibody (GTX134381) (GII.4-specific)
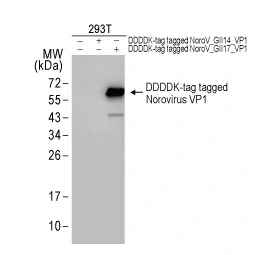
Norovirus VP1 antibody (GTX134382) (GII.17-specific)
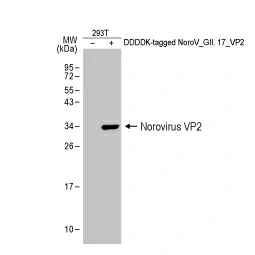
Norovirus VP2 antibody (GTX134386)
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications | |
| GTX637271 | Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL1672] | Rec Rb mAb | WB | |
| GTX638181 | Norovirus VP1 antibody [HL2177] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX134381 | Norovirus VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| GTX134382 | Norovirus VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX134380 | Norovirus VP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX134386 | Norovirus VP2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX134383 | Norovirus VP2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB |

The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), previously known as 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), is a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that causes the potentially lethal COVID-19 respiratory tract infection. This new virus belongs to the genus Betacoronavirus, which also includes SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.
GeneTex is proud to offer an extensive line of research antibodies and proteins to support the study of SARS-CoV-2, several of which were validated using virus-infected cell lysates. Please see the highlighted products below or click the button to see more product information.
| Highlighted Products | |||||
|
|
|||||
Antibodies
Spike antibody [1A9] (GTX632604) |
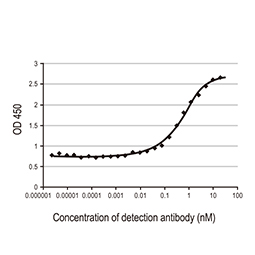
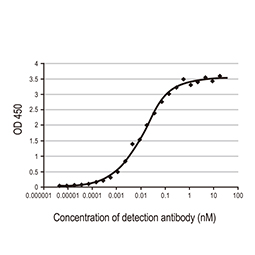
Spike S1 antibody [HL6] (EC50: 0.552 nM) (GTX635654) |
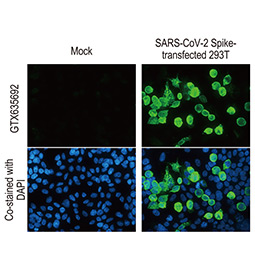
Spike RBD antibody [HL257] (GTX635692) |
Nucleocapsid antibody [HL5511] (EC50: 0.014 nM) (GTX635689)
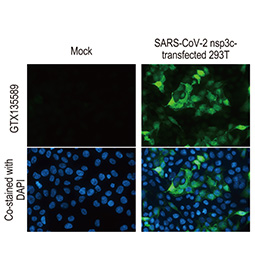
PLpro (nsp3) antibody (GTX135589)

RdRp (nsp12) antibody (GTX135467)
Proteins
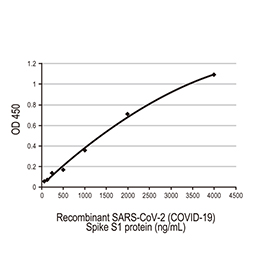
Spike S1 protein, His and Avi tag (active) (GTX01548-pro)
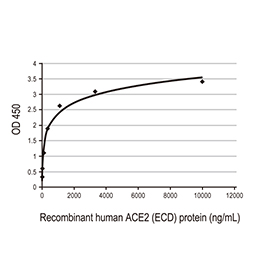
Spike RBD protein, His tag (active) (GTX01546-pro)
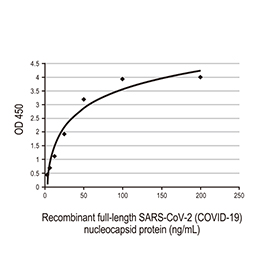
Nucleocapsid protein, His tag (GTX135592-pro)
ELISA Pairs
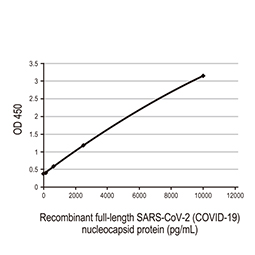
Nucleocapsid ELISA Pair [HL5511 / HL448] (GTX500045)
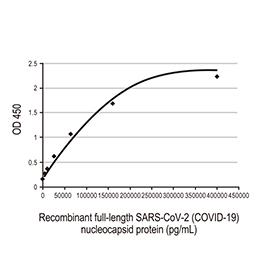
Nucleocapsid ELISA Pair [HL5410 / HL455-MS] (GTX500042)
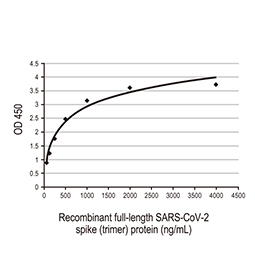
Spike ELISA Pair [1A9 / HL6] (GTX500040)
The first case of COVID-19 was detected in December, 2019 in Wuhan, China, and has now been declared a pandemic (1). With SARS-CoV-2 now reaching pandemic status, researchers and clinicians have been working furiously to learn more about the virus’s biology and pathogenesis as well as how to treat the more clinically aggressive COVID-19 cases.
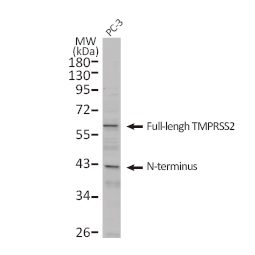
In their study published very recently in Cell, Hoffmann et al. confirm findings reported by Zhou et al. that angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is the cellular receptor for SARS-CoV-2, as it is for SARS-CoV (2, 3). In addition, they identify the serine protease TMPRSS2 as a critical factor in the priming of the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein, an essential step for viral entry into host cells through fusion of the viral and cellular membranes. The authors also demonstrate that the serine protease inhibitor camostat mesylate, an agent that has already seen clinical application as a treatment for chronic pancreatitis in Japan, is able to interfere with SARS-CoV-2 infection of lung cells.
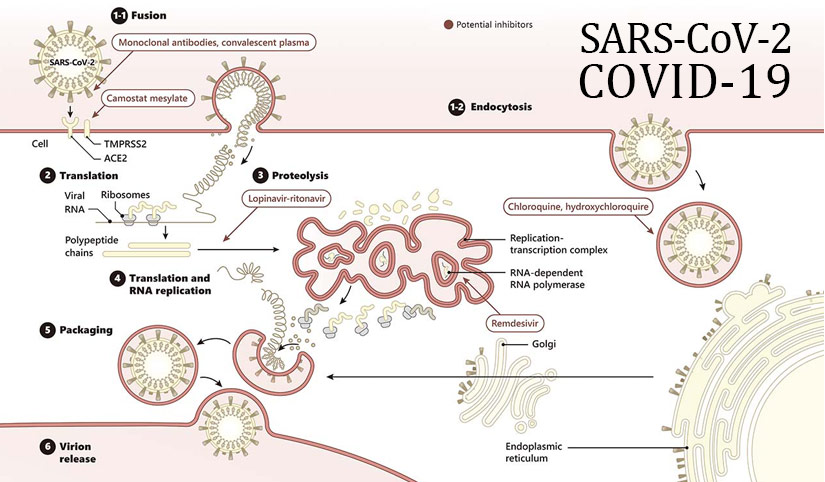
To further expedite the identification of agents with activity against SARS-CoV-2, the WHO’s SOLIDARITY study will assess the potential utility of four different classes of clinically known drugs or drug combinations against the virus (4). The four arms include the viral polymerase inhibitor remdesivir, the anti-malarial agents chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, the HIV protease inhibitors lopinavir and ritonavir, and lopinavir/ritonavir with interferon-beta. This study, which is one of many ongoing trials that are reviewing more than a dozen possible therapies, is stripped down to accelerate data acquisition and be accessible to physicians everywhere. The central focus of many of these trials is to evaluate existing agents with acceptable safety profiles (e.g., the serine protease inhibitor camostat mesylate) that are amenable to repurposing for use against SARS-CoV-2. In addition, compounds previously found to have activity against SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, or other viruses are being reexamined, as is the use of convalescent plasma from recovered COVID-19 patients and monoclonal antibodies targeting viral components (5). The singular determination to fight this virus as a world community is now widely appreciated as the only path to eventual success.
References:
- Nature News. 11 March 2020.
- Nature 579, 270-273 (2020).
- Cell 181, 1-10 (2020).
- Science 367(6485), 1412-1413 (2020).
- Science 2020 Apr 3. pii: eabb7269.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX632603 | SARS-CoV Spike (SΔ3) antibody [7G12] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, IP | SARS-CoV |
| GTX36802 | SARS-CoV Nucleoprotein antibody [3851] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | SARS-CoV |
| GTX83199 | SARS-CoV M antibody [2H2C4] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | SARS-CoV |
| GTX36801 | SARS-CoV Nucleoprotein antibody [3861] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | SARS- |
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX134868 | MERS-CoV Nucleoprotein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA | MERS-CoV |
| GTX134870 | MERS-CoV ORF4b antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | MERS-CoV |
| GTX134869 | MERS-CoV ORF4a antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | MERS-CoV |
| GTX135382 | MERS-CoV Envelope protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | MERS-CoV |
| GTX135653-pro | MERS-CoV Nucleocapsid protein, DDDDK tag | ELISA | |||
| GTX134875 | MERS-CoV Spike (S1) antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | MERS-CoV |
| GTX134864 | MERS-CoV Spike (S1) antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | MERS-CoV |
| GTX134866 | MERS-CoV M protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | MERS-CoV |
| GTX135381 | MERS-CoV Spike (S2) antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | MERS-CoV |
| GTX135370 | MERS-CoV Envelope protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | MERS-CoV |
| GTX134880 | MERS-CoV ORF4a antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | MERS-CoV |
| GTX535667 | MERS-CoV Spike overexpression 293T whole cell lysate | WB |
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX131955 | West Nile virus NS3 protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | WNV |
| GTX131961 | West Nile virus NS5 protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IHC-P | WNV |
| GTX131947 | West Nile virus Capsid protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | WNV |
| GTX132060 | West Nile virus NS2B protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | WNV |
| GTX132052 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | WNV |
| GTX131948 | West Nile virus prM protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | WNV |
| GTX132053 | West Nile virus NS1 protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | WNV |
| GTX131957 | West Nile virus NS4A protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | WNV |
| GTX138916-pro | West Nile virus NS1 protein, His tag | WNV | |||
| GTX633919 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [GT3029] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF | WNV |
| GTX85509 | West Nile virus Capsid protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX36805 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [3671] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX36811 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [3631] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX36806 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [3661] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX36810 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [3641] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX36807 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [3655] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX38694 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [B851M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX38693 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [B857M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX38695 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [B849M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX38697 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody [B847M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | WNV |
| GTX85512 | West Nile virus Matrix antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ELISA | WNV |
| GTX85506 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ELISA | WNV |
| GTX85507 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ELISA | WNV |
| GTX85511 | West Nile virus Matrix antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ELISA | WNV |
| GTX85508 | West Nile virus Envelope antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ELISA | WNV |
| GTX85510 | West Nile virus Capsid protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ELISA | WNV |
| GTX85508-PEP | West Nile virus Envelope Peptide | Neutralizing/Inhibition | |||
| GTX85509-PEP | West Nile virus Capsid peptide | Neutralizing/Inhibition | |||
| GTX85512-PEP | West Nile virus Matrix Peptide | Neutralizing/Inhibition | |||
| GTX85511-PEP | West Nile virus Matrix Peptide | Neutralizing/Inhibition | |||
| GTX85507-PEP | West Nile virus Envelope Peptide | Neutralizing/Inhibition | |||
| GTX85510-PEP | West Nile virus Capsid peptide | Neutralizing/Inhibition | |||
| GTX85506-PEP | West Nile virus Envelope Peptide | Neutralizing/Inhibition |

Yellow fever, caused by the mosquito-transmitted yellow fever virus (YFV), is a potentially fatal disease that has plagued humans for centuries. The 17D vaccine, raised against an attenuated strain of YFV, has been available for more than 80 years and provides excellent protection. Nevertheless, significant vulnerability in the world population persists even with vaccination and vector control programs, as exemplified by recent outbreaks in Africa and South America. In addition, the existence of the vaccine may have slowed the impetus to identify therapeutic antivirals to treat symptomatic cases of yellow fever in unvaccinated people. Thus, research into YFV biology and candidate agents that disrupt the viral life cycle remain a world public health priority.
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
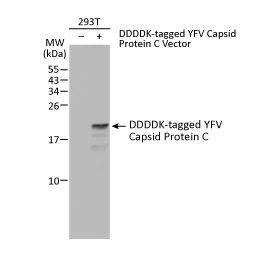
YFV Capsid Protein C antibody (GTX134022)
![]()

YFV NS4B Protein antibody (GTX134030)
![]()
YFV NS5 Protein antibody (GTX134141)
![]()
In their recent Antiviral Research study, Gao et al. describe the development of antibody-based assays to facilitate high-throughput discovery of anti-YFV agents. To do this, the researchers first performed an exhaustive analysis on a series of research antibodies from GeneTex that target the three structural and five of the nonstructural proteins encoded by the YFV genome. They used the antibodies for both biochemical and cell biology assays to explore YFV polyprotein processing, replication complex organization, and viral RNA synthesis. The anti-NS4B antibody (GTX134030) was then incorporated into in-cell western and high-content imaging assays that revealed a synergistic antiviral effect of the compounds BDAA and Sofosbuvir, which target NS4B and the NS5 RNA polymerase, respectively. These findings demonstrate how antibody-based assays can not only expedite screening for antiviral agents against YFV, but also provide insight into the mechanistic basis of their inhibitory actions.
GeneTex is a leader in the production of reliable reagents for the study of an array of viral pathogens, including flaviviruses, influenza viruses, enteroviruses, and coronaviruses (i.e., MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2), among others. The GeneTex team’s top priority is to create reagents that perform well in the hands of researchers. We are particularly gratified by the impressive results generated by Gao et al. using our YFV antibodies.
References:
Product Highlights |
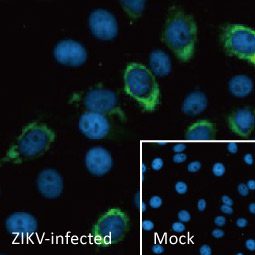
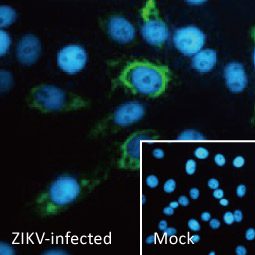
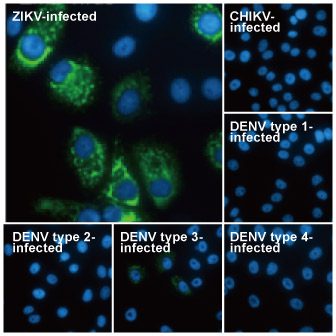
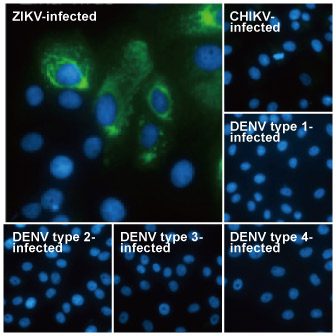
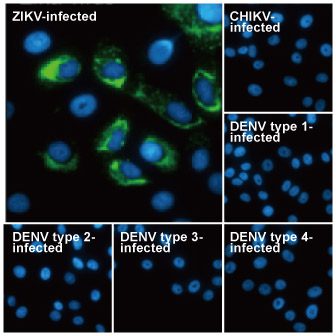
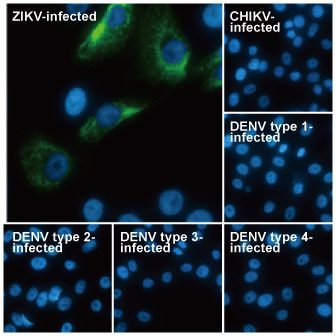
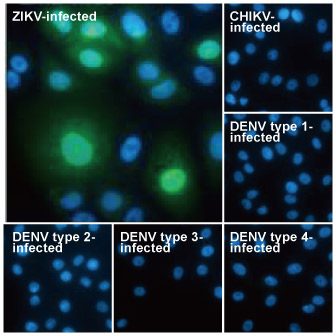
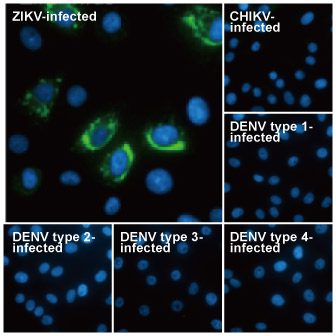
| ✔ Validated by WB on lysate from Zika virus-infected cells. ✔ Appear to distinguish between Zika, Dengue, and Chikungunya virus via IFA. ✔ An extensive line of research antibodies against different Zika virus proteins. |
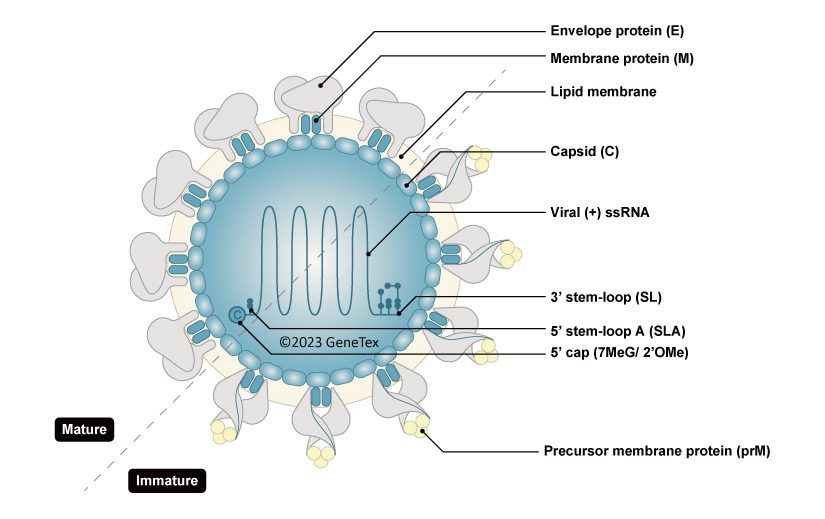
| Zika virus (ZIKV) exploded into international prominence in 2015. This mosquito-borne flavivirus had its first reported outbreak in 2007, followed by a larger event in 2013 in French Polynesia and the present outbreak in Brazil. Nearly 70 countries and territories have documented ZIKV transmission since 2007. |
| While about 80% of ZIKV infections are asymptomatic, the virus can cause influenza-like symptoms and other clinical manifestations including conjunctivitis. Infection has been linked to cases of neurological disease, including Guillain-Barre syndrome. Most concerning is the increasingly robust evidence associating ZIKV with microcephaly (and other neurodevelopmental problems) in newborns from infected mothers. ZIKV infection is diagnosed by serological, cytokine profiling, and RT-PCR testing. The serological assays can be cumbersome and can fail to clearly identify ZIKV in the presence of Dengue or other flaviviruses, so RT-PCR is the most reliable method to specifically detect the virus. However, antibodies targeting different protein components of ZIKV would be immensely useful to facilitate both basic research and as potential diagnostic reagents. |
| GeneTex is proud to offer an extensive line of research antibodies to support the study of Zika virus. Please see the highlighted products below or click the button to view the full list of GeneTex antibodies against Zika virus proteins. |
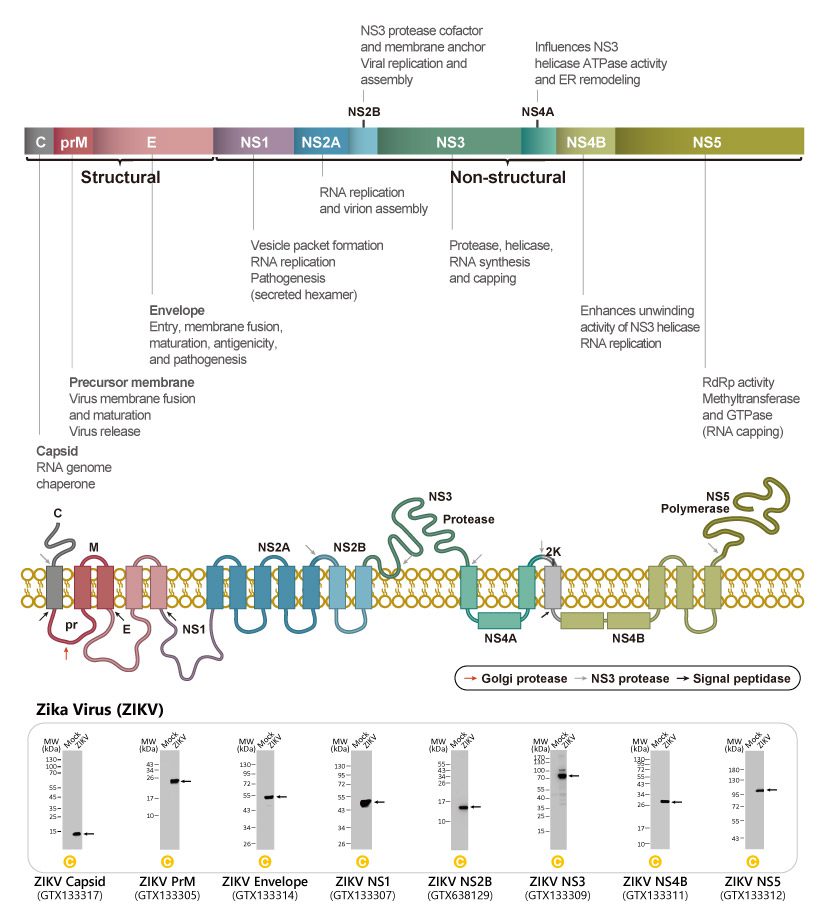
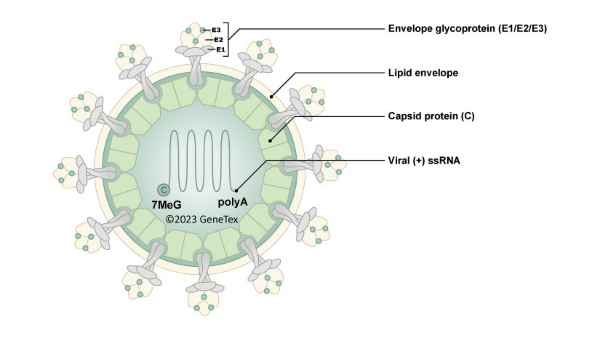
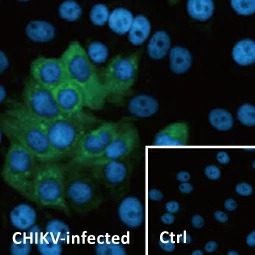
Figure 1. The CHIKV virion
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is an alphavirus in the Togaviridae family. The enveloped capsid core contains a ~12 kb single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome that encodes four nonstructural and five structural proteins. CHIKV has both sylvatic (in Asia and Africa involving non-human primates and forest-localized mosquitoes) and urban (with transmission to and between humans mediated by infected Aedes aegypti and albopictus mosquitoes) lifecycles. In fact, among the alphaviruses, it is the most prevalent one transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes (1). There are four major geographically described CHIKV lineages, including the East Central South Africa (ECSA), the West Africa (WA), the Asian, and the more recent Indian Ocean lineages. CHIKV is now found in over 60 countries in Asia, Africa, the Americas, and Europe, with additional spread inevitable as trade globalization and climate change expand the ranges of Aedes mosquitoes.
The word “Chikungunya” is derived from a Kimakonde root verb with several meanings, with perhaps the most illustrative being “to walk bent over”. CHIKV infection causes an acute fever with myalgia and polyarthralgia that can become chronic and debilitating. Thus, despite the fact that fatalities are comparatively rare (occurring primarily in patients with comorbidities, co-infections, or certain genetic features), it nevertheless can have calamitous effects on quality of life. There are no antiviral therapeutics for this virus, so treatment is largely supportive and preventative strategies involving vector control are paramount. Due to the possibility that it could cause a pandemic, CHIKV is a priority for vaccine development.
GeneTex continues its commitment to producing quality reagents for infectious disease research with an expanding portfolio of reagents for arbovirus research (including antibodies against Zika virus, Dengue virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus, among many others). For CHIKV research, GeneTex is proud to introduce new recombinant antibody products (e.g., Chikungunya virus E1 antibody [HL2069] (GTX637973) and Chikungunya virus nsP2 antibody [HL1488] (GTX636962)) to expand its already near-comprehensive line of CHIKV protein antibodies. Please see the highlighted product images and a complete CHIKV antibody listing below.
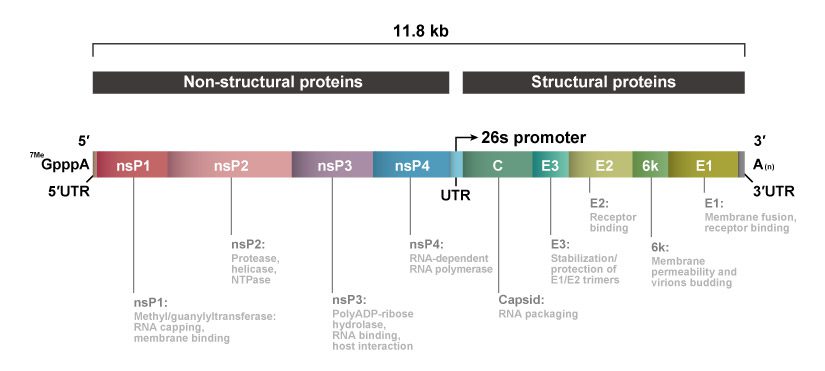
Figure 2. CHIKV genomic organization
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
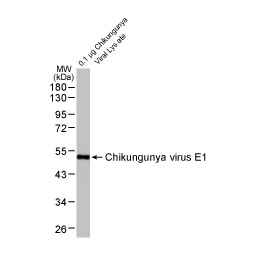
Chikungunya virus E1 antibody [HL2069] (GTX637973)
![]()
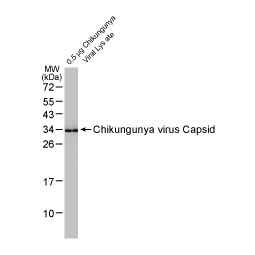
Chikungunya virus Capsid antibody (GTX135183)
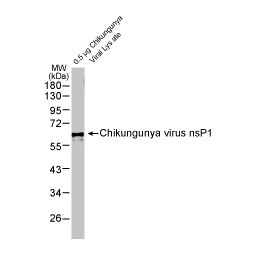
Chikungunya virus nsP1 antibody (GTX135191)
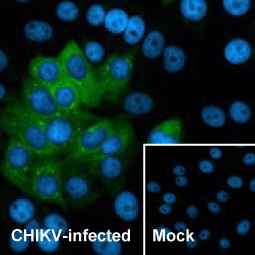
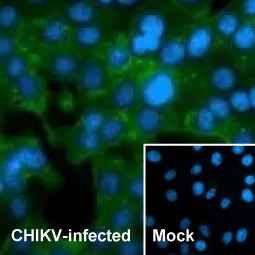
Chikungunya virus nsP2 antibody [HL1488] (GTX636962)
![]()
Chikungunya virus nsP3 antibody (GTX135189)
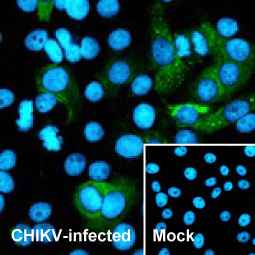
Chikungunya virus nsP4 antibody (GTX135190)
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications | |
| GTX135191 | Chikungunya virus nsP1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX636897 | Chikungunya virus nsP2 antibody [HL1431] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX636898 | Chikungunya virus nsP2 antibody [HL1432] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX636962 | Chikungunya virus nsP2 antibody [HL1488] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| GTX135188 | Chikungunya virus nsP2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| GTX135189 | Chikungunya virus nsP3 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| GTX135190 | Chikungunya virus nsP4 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX135183 | Chikungunya virus Capsid antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX637973 | Chikungunya virus E1 antibody [HL2069] | Rec Rb mAb | WB | |
| GTX135187 | Chikungunya virus E1 antibody | Rb pAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX135184 | Chikungunya virus E3 antibody | Rb pAb | WB |
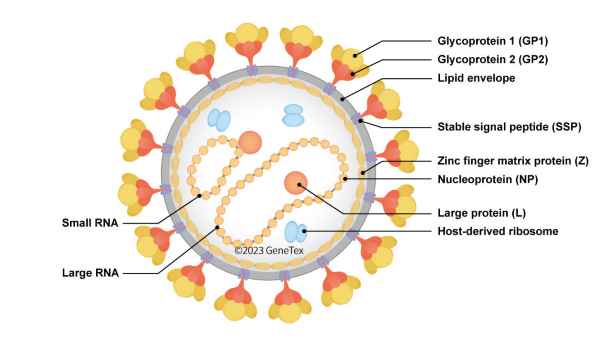
Figure 1. The LASV virion
Lassa virus (LASV) is the etiologic agent of Lassa fever, a viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF) with a high case fatality rate (between 20-70%) associated primarily with countries in West Africa. Belonging to the Mammarenavirus genus of the Old World Arenaviridae family, LASV is endemic to rodent (most notably Mastomys natalensis) populations in these regions and is characterized by frequent spillovers to humans through exposures (inhalation or contact) to infected feces, aerosolized urine or contaminated dust, or during preparation/consumption of infected rodents as food. Human-to-human transmission has also been described. Though ~80% of human infections are mild or asymptomatic, perhaps 20% lead to Lassa fever with 40% of those having a very severe clinical course with orifice and mucosal hemorrhage, circulatory shock, and multi-organ failure (1). With at least seven lineages found in West Africa, there is presently no LASV vaccine. Ribavirin has shown some clinical benefit, yet therapy is primarily supportive.
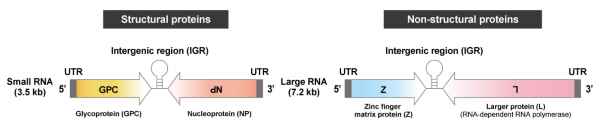
LASV is an enveloped virus with a genome consisting of two ambisense, single-stranded RNA segments (Large (L) and Small (S)) that each code for two proteins, with all four proteins being multifunctional. The ambisense RNAs give rise to early translation of the nucleoprotein (NP) and large (L) protein (RNA-dependent RNA polymerase) components followed by later translation of the glycoprotein complex (GPC) proteins (GP1 and GP2) as well as the zinc-binding protein (Z, matrix protein) (1). Interestingly, LASV particles also contain host ribosomes.
LASV is attracting more global attention due to the continuing geographical spread of its rodent reservoirs, increasing outbreak frequency, its importation to other continents, significant potential for weaponization, and the genesis of new lineages in West Africa. Reliable point-of-care diagnostics, targeted therapies, thoughtful vaccine(s) development, and effective rodent control strategies are among the essential approaches to control LASV-related morbidity and mortality.
GeneTex continues its commitment to manufacturing quality reagents for infectious disease research with new recombinant monoclonal antibodies against the LASV NP protein (e.g., Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1392] (GTX636832) and Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1390] (GTX636830)) to expand its current LASV reagent catalog. Additional products for detection of other LASV proteins will be forthcoming. Please see the highlighted product images and a complete LASV antibody listing below.
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
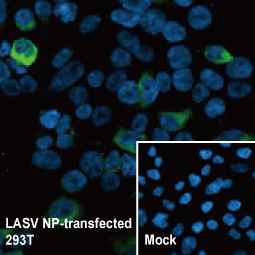
Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1392] (GTX636832)
![]()

Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1390] (GTX636830)
![]()
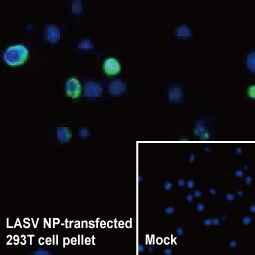
Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody (GTX134873)
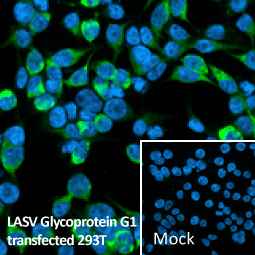
Lassa virus Glycoprotein G1 antibody [HL2536]
(GTX638905)
![]()
![]()
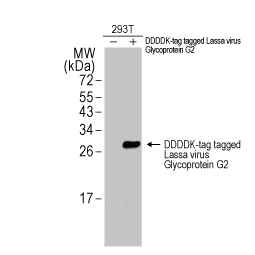
Lassa virus Glycoprotein G2 antibody (GTX134883)
![]()

Lassa virus RING finger protein Z antibody (GTX134874)
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications | |
| GTX638905 | Lassa virus Glycoprotein G1 antibody [HL2536] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX134883 | Lassa virus Glycoprotein G2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX134872 | Lassa virus Glycoprotein G2 antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX636830 | Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1390] | Rec Rb mAb | WB | |
| GTX636832 | Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1392] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF | |
| GTX134873 | Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody | Rb pAb | WB, IHC-P (cell pellet) | |
| GTX134884 | Lassa virus Nucleoprotein antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX134885 | Lassa virus RING finger protein Z antibody | Rb pAb | WB | |
| GTX134874 | Lassa virus RING finger protein Z antibody | Rb pAb | WB |
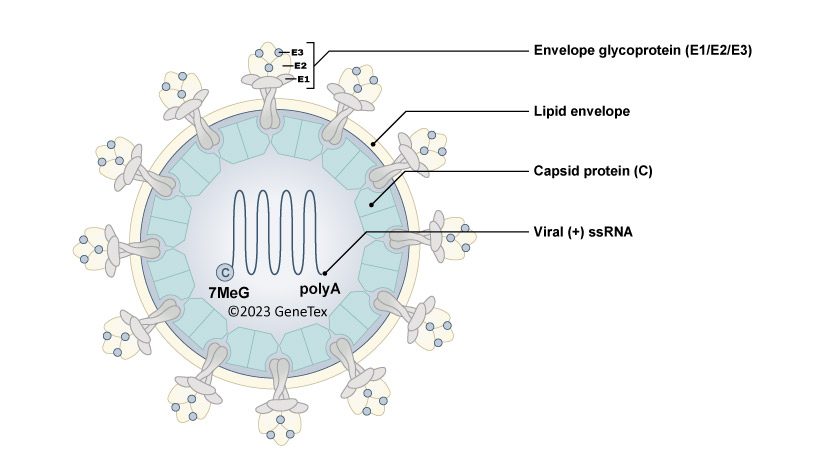
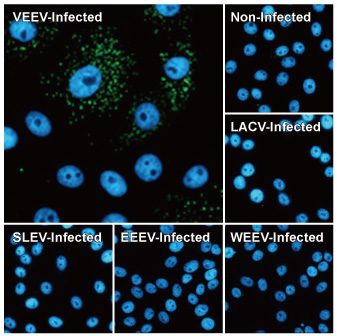
Figure 1. The VEEV virion
Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus (VEEV) is one of the three major encephalitic alphaviruses (the others being Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus (EEEV) and Western Equine Encephalitis Virus (WEEV)) that can cause severe illness in humans. VEEV infects both equids and humans in a geographical distribution that includes Mexico to northern South America. As an arbovirus, VEEV is primarily transmitted by hematophagous insects, including mosquitoes, and most frequently causes a mild flu-like syndrome in humans. However, neurologic complications can occur in nearly 15% of cases, with case fatality rates that can be almost 10%. Presently, there is no available vaccine for widespread use and no medical treatment but supportive care. The potential for VEEV and other alphaviruses to be weaponized remains a significant concern (1).
VEEV is an enveloped virus with a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome that codes for four nonstructural (nsP1-nsP4) and six structural proteins (1). As part of its efforts to generate the most comprehensive line of reagents for infectious disease research, GeneTex is proud to offer new recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies against the VEEV nonstructural proteins (see “Highlighted Products” below). These antibodies are exciting additions to GeneTex’s expanding portfolio of reagents for arbovirus research (which includes antibodies against Zika virus, Chikungunya virus, Dengue virus, and Japanese encephalitis virus, among others). Please see the highlighted product images and a complete VEEV antibody listing below.
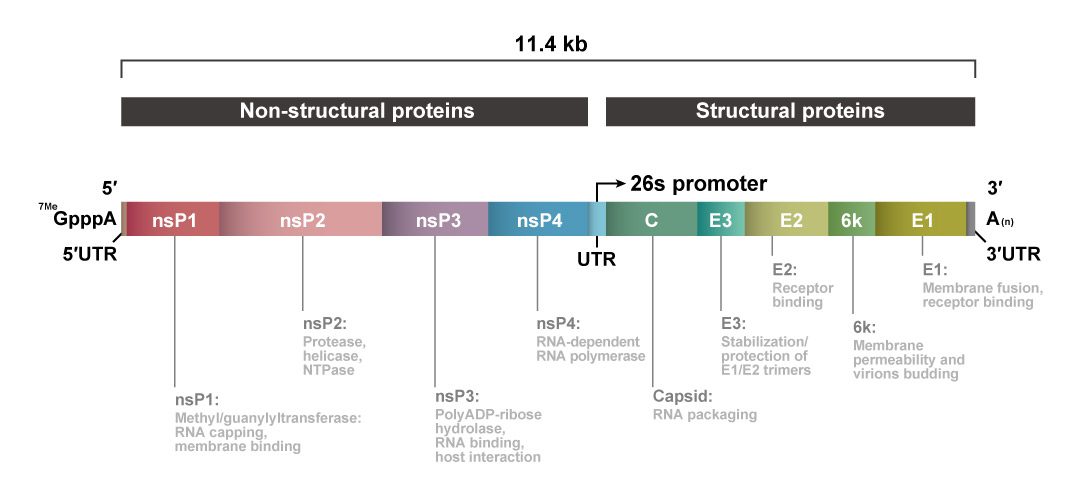
Figure 2. The VEEV genomic organization
Highlighted Products
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP1 antibody [HL1472] (GTX636946)
![]()
![]()
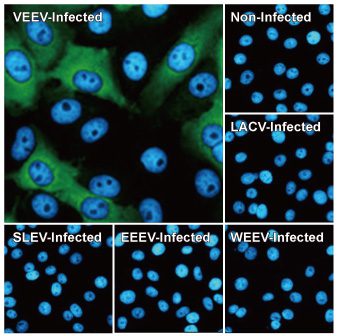
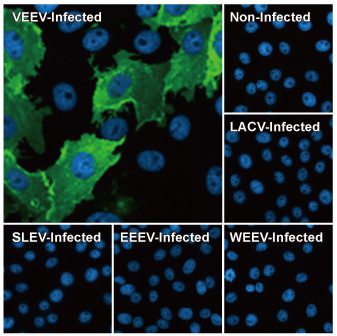
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP2 antibody [HL1919] (GTX637668)
![]()
![]()
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP3 antibody [HL1502] (GTX636976)
![]()
![]()
Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP4 antibody [HL1741] (GTX637389)
![]()
![]()
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Clonality | Applications |
| GTX636946 | Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP1 antibody [HL1472] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) |
| GTX637072 | Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP1 antibody [HL1593] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, IHC-P (cell pellet) |
| GTX637668 | Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP2 antibody [HL1919] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF |
| GTX636976 | Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP3 antibody [HL1502] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P (cell pellet) |
| GTX636978 | Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP3 antibody [HL1504] | Rec Rb mAb | WB |
| GTX637389 | Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus nsP4 antibody [HL1741] | Rec Rb mAb | WB, ICC/IF |
Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is an underdiagnosed, often lethal respiratory pathogen affecting infants and children as well as the elderly, immunocompromised, and long-term care facility populations. Infection, which occurs through aerosolized droplets and close contact, is essentially universal within the first two years of life and reinfection is common in both children and adults. Though often thought to be clinically less severe than influenza, RSV is linked to perhaps 250,000 adult, and 60,000 pediatric, deaths per year.
RSV is a filamentous/spherical, enveloped, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus of the Pneumoviridae family. Its 15.2 kb genome encodes eleven proteins from ten genes (1). Though the two major RSV antigenic subgroups, designated “A” and “B”, display differences in multiple proteins, the primary antigenic determinant is the “G” attachment glycoprotein. Interestingly, it is the “prefusion” form of the “F” fusion protein that has proven to be the most successful immunogenic RSV factor (via its “theta” site) in terms of eliciting neutralizing antibodies and generating promising vaccine trials against both RSV Type A and Type B (2). Several monoclonal antibody therapies directed against prefusion F are in development to augment the one available RSV monoclonal antibody therapy (palivizumab) that is indicated for high-risk infants, though it targets postfusion F and has both cost and administration issues.
There are a number of approaches to diagnose RSV. However, the most reliable method presently is RT-PCR performed on nasopharyngeal swab samples. Antigen testing for rapid point-of-care diagnosis would greatly facilitate diagnosis as well as potentially more effective early intervention. For this reason, and to support additional research into basic RSV biology, GeneTex is developing recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibodies against various RSV proteins, focusing first on the RSV nucleoprotein (indicated as NP below). The initial series of NP antibodies have superior binding affinity and are validated for ELISA, sandwich ELISA (sELISA), and lateral flow assay (LFA) (see below and individual datasheets). In addition, several of them perform well in western blot, immunoprecipitation, and immunocytochemistry.
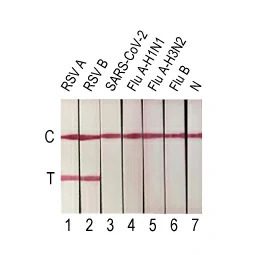
Recommended RSV Antibody Pairs for Lateral Flow Assay

Comparison of GeneTex’s Recombinant RSV Antibodies with other Market-leading Clones
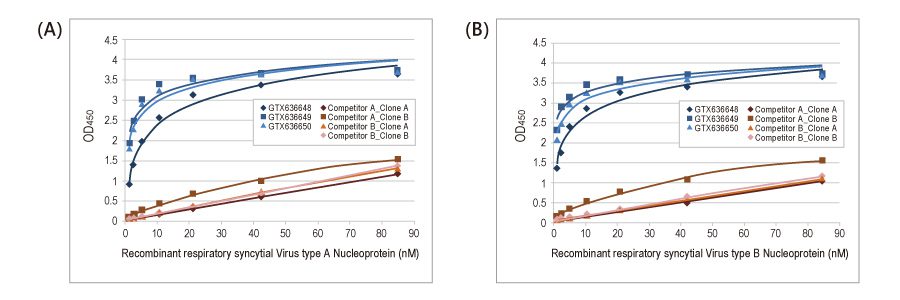
Recommended RSV Antibody Pairs for Sandwich ELISA
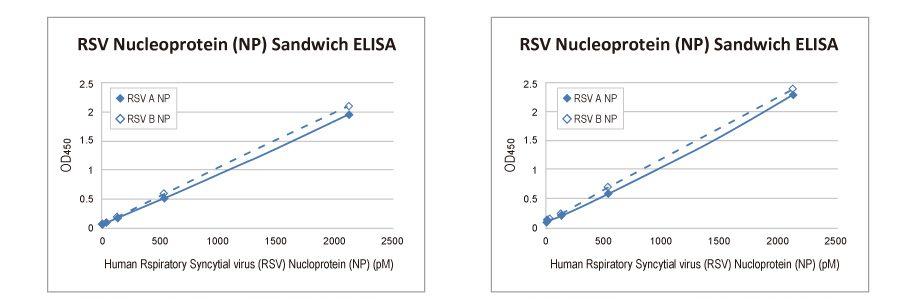
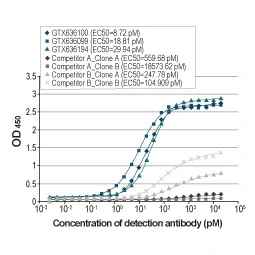
Superior Binding Affinities of Recombinant RSV Antibodies
![]()
![]()
| Cat. No. | Clone | EC50 RSV A NP (GTX136751-pro) | EC50 RSV B NP (GTX136931-pro) | |
| GTX636648 | HL1246 | 13.6 pM | 15.4 pM | |
| GTX636649 | HL1247 | 3.8 pM | 15.9 pM | |
| GTX636650 | HL1248 | 8.9 pM | 10.1 pM | |
| GTX636705 | HL1291 | 10.7 pM | 19.0 pM | |
| GTX636709 | HL1295 | 19.8 pM | 105.4 pM | |
| GTX636710 | HL1296 | 29.0 pM | 170.8 pM | |
| GTX636711* | HL1297 | 16.7 pM | 2854.8 pM |
* GTX636711 is specific for RSV A NP.
RSV Nucleoprotein Recombinant Proteins
![]()
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Expression System | Applications | |
| |
GTX136751-pro | Respiratory Syncytial Virus type A Nucleoprotein, DDDDK tag | HEK293 | WB, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA |
| |
GTX136931-pro | Respiratory Syncytial Virus type B Nucleoprotein, DDDDK tag | HEK293 | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA |
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
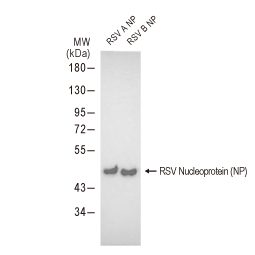
Respiratory Syncytial Virus type A Nucleoprotein, DDDDK tag
(GTX136751-pro)
Respiratory Syncytial Virus type B
Nucleoprotein, DDDDK tag
(GTX136931-pro)
Respiratory Syncytial Virus Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1248] (GTX636650)
![]()
![]()
![]()
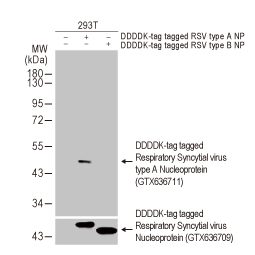
Respiratory Syncytial Virus type A Nucleoprotein antibody [HL1297] (GTX636711)
![]()
![]()
References:
(1) Nat Rev Microbiol. 2019 Apr;17(4):233-245.
(2) Pathogens. 2022 Nov 11;11(11):1324.
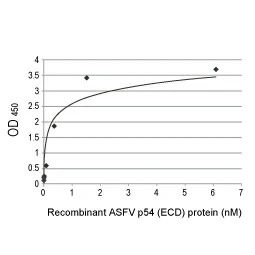
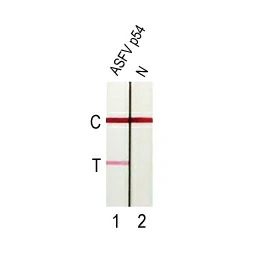
African Swine Fever Virus: An ongoing threat to the global swine industry
African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) is a deadly (95-100% mortality rate) and highly contagious pathogen that primarily infects domestic and wild pigs. Originating in Sub-Saharan Africa, African Swine Fever (ASF) has been reported in more than 50 countries across Africa, Europe, and Asia and has extended into the Caribbean. Although it cannot infect humans, it has had serious economic impact on the swine industry with almost 25% of the global pig population dying of ASF from 2018-2019.
Transmission of ASF occurs through direct contact with infected pigs as well as exposure to their blood, body fluids, feces, and carcasses. Thus far, no effective treatment or efficacious vaccine has been developed. The currently implemented measures to slow the spread of ASF rely heavily on early detection, on-farm biosecurity measures, culling of herds, and movement control. All of these require reliable diagnostic assays to facilitate early warning, prompt intervention, and monitoring of transmission.
Current diagnostic methodologies include conventional and real-time PCR for detecting viral DNA, ELISA and lateral flow tests for detecting ASFV antigens or antibodies, and the more definitive but time-consuming virus isolation and hemadsorption (HAD).
GeneTex offers an expanding catalog of high-quality validated for various applications, including western blot (WB), ICC/IF, IHC-P, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA and Lateral Flow. Please see the highlighted products below
| ✔ Validated for multiple applications: WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA |
| ✔ Validated Sandwich ELISA Pairs |
| ✔ Validated Lateral Flow Pairs |
| ✔ Mouse and Rabbit Monoclonal Antibodies |
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
ASFV p54 antibody [HL1287] (GTX636701) 
ASFV p54 antibody [HL1289] (GTX636703)
Highlighted Antibody Products
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host & Clonality | Applications | |
| GTX636700 | ASFV p54 antibody [HL1286] | Rb mAb | WB, Sandwich ELISA | |
| GTX636701 | ASFV p54 antibody [HL1287] | Rb mAb | WB, Sandwich ELISA, Lateral Flow | |
| GTX636703 | ASFV p54 antibody [HL1289] | Rb mAb | WB, Sandwich ELISA, Lateral Flow | |
| GTX636563 | ASFV p54 antibody [HL1219] | Rb mAb | WB, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | |
| GTX635690 | ASFV p54 antibody [GT853] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA | |
| GTX635691 | ASFV p54 antibody [GT1075] | Ms mAb | WB, ICC/IF, IHC-P, ELISA, Lateral Flow, Sandwich ELISA |
Selected Recombinant Proteins
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Expression System |
| GTX135175-pro | ASFV p54 (ECD) protein, His Tag | E. Coli |
| GTX137950-pro | ASFV p54 (ECD) protein, His Tag | HEK293 cells |
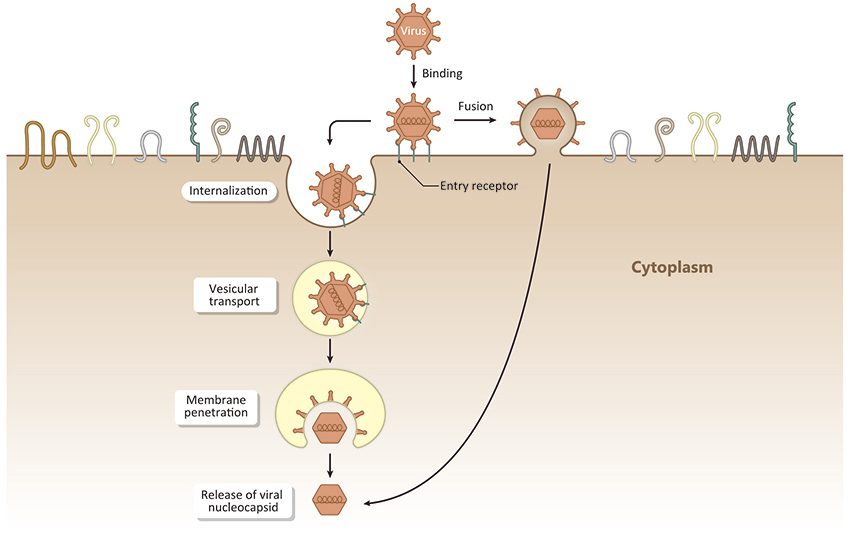
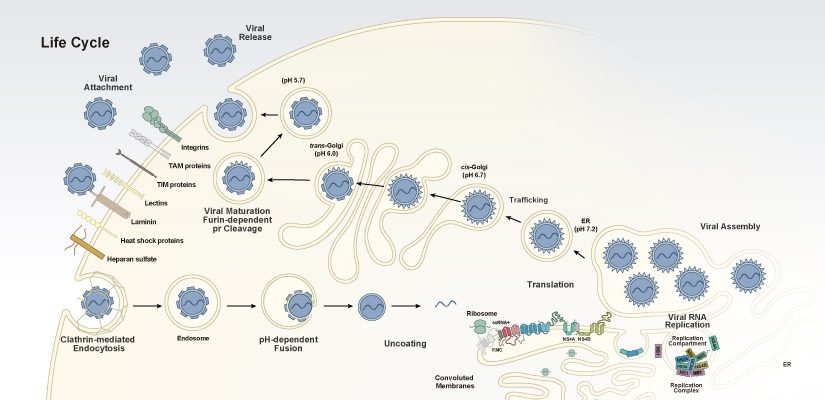
Infection by animal viruses is initiated by viral binding to host cells. Delineation of the mechanisms mediating subsequent viral entry is an area of intense research, as there is considerable complexity and variability among different viruses. Nevertheless, a general framework for this process, particularly for some enveloped viruses, involves the following steps: (1) viral attachment to host cell receptors, (2) cell signaling pathway activation, (3) endocytosis, (4) penetration of cellular membranes and intracellular trafficking, and (5) viral genome uncoating. The viral genome is then available for expression, replication, packaging and release to infect other cells. Understanding the molecular events underlying virus/host cell interactions during entry is of paramount importance for the potential identification of targets for pharmacologic intervention.
GeneTex is proud to offer an outstanding selection of antibodies to study virus attachment, internalization and penetration for infectious disease research. These antibodies are validated for various applications to facilitate your efforts in this exciting field. Please see the highlighted products below
Highlighted Products |
|||||
|
|
|||||
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX40096 | Candida albicans antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Immunoelectrophoresis, IHC | C. albicans |
| GTX36577 | Candida albicans antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Immunoelectrophoresis, IHC | C. albicans |
| GTX40028 | Candida albicans antibody (HRP) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Immunoelectrophoresis, IHC | C. albicans |
| GTX40005 | Candida albicans antibody (Biotin) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Immunoelectrophoresis, IHC | C. albicans |
| GTX41164 | Candida albicans antibody (FITC) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Immunoelectrophoresis, IHC | C. albicans |
| GTX44278 | Candida albicans antibody [B341M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA | C. albicans |
| GTX42559 | Candida albicans antibody [231/439] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA | C. albicans |
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX637947 | PRRS virus Nucleocapsid protein antibody [HL2046] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PRRSV |
| GTX640149 | PRRS virus GP5 protein antibody [HL2872] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | WB | PRRSV |
| GTX638953 | PRRS virus M protein antibody [HL2575] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | WB | PRRSV |
| GTX639073 | PRRS virus M protein antibody [HL2619] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | WB | PRRSV |
| GTX637650 | PRRS virus Nucleocapsid protein antibody [HL1901] | Rabbit | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PRRSV |
| GTX129270 | PRRS virus Nucleocapsid protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PRRSV |
| GTX129062 | PRRS virus GP5 protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PRRSV |
| GTX129063 | PRRS virus M protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PRRSV |
| GTX135352 | PRRS virus Nucleocapsid protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PRRSV |
| GTX135353 | PRRS virus Nucleocapsid protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PRRSV |
| GTX135351 | PRRS virus Nucleocapsid protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PRRSV |
| GTX129272 | PRRS virus GP3 protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | PRRSV |
| GTX133700 | PRRS virus Nsp4 protein antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | PRRSV |
| GTX133695 | PRRS virus Nsp1 alpha antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | PRRSV |
| GTX133696 | PRRS virus Nsp1 beta antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | PRRSV |
| GTX634651 | VetSignal – PRRS virus M protein antibody [GT1911] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB | PRRSV |
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX128121 | Porcine circovirus type 2 / PCV2 Capsid antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IHC-P | PCV2 |
| GTX128120 | Porcine circovirus type 2 / PCV2 Capsid antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IHC-P, IHC | PCV2 |
| GTX133638 | Porcine circovirus type 2 / PCV2 replicase antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PCV2 |
| GTX634210 | Porcine circovirus type 2 / PCV2 Capsid antibody [GT863] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, IHC-P | PCV2 |
| GTX634211 | Porcine circovirus type 2 / PCV2 Capsid antibody [GT972] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PCV2 |
| GTX634172 | Porcine circovirus type 2 / PCV2 Capsid antibody [GT1641] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF | PCV2 |
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Host | Clonality | Applications | Reactivity |
| GTX40856 | E. coli antibody (FITC) | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, FACS, ELISA | E. coli, Bacteria |
| GTX00863 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (SLT-1 + SLT-2) subunit A antibody [vero-01] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Lateral Flow | C. jejuni, E. coli, S. aureus, S. Enteritidis |
| GTX13626 | E. coli antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli, Bacteria |
| GTX40001 | Lipid A LPS antibody | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF | E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, S. sonnei, Y. entercolitica, S. Enteritidis, E. hermannii, K. aerogenes |
| GTX64150 | RecA antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF, IP, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX41231 | E. coli LPS antibody [GNE13-337.5 (2D7/1)] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, IP, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX64191 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (SLT-1 + SLT-2) antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX48847 | L-Asparaginase antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA, IHC | E. coli |
| GTX48707 | Lac I antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, ELISA | E. coli, S. sonnei |
| GTX64136 | LexA antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP, ChIP assay, IHC | E. coli |
| GTX64108 | DNA Polymerase I (E coli) antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP | E. coli |
| GTX64109 | E. coli LT toxin antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, IP | E. coli |
| GTX36484 | E. coli antibody (HRP) | Goat | Polyclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA, IHC | E. coli |
| GTX49173 | DsbA antibody [1A2-D4-G10] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB | E. coli |
| GTX40640 | E. coli antibody (Biotin) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ELISA, Functional Assay | E. coli |
| GTX64162 | RuvA antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX36923 | E. coli O157 antibody [1026] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX43110 | E. coli O157 antibody [B837M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX36927 | E. coli O157 antibody [1022] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX43048 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (SLT-1 + SLT-2) antibody [Mixed] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Neutralizing/Inhibition | E. coli |
| GTX43249 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (SLT-2) subunit B antibody [286-12212] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Neutralizing/Inhibition | E. coli |
| GTX43055 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (SLT-1 + SLT-2) antibody [286-13310] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Neutralizing/Inhibition | E. coli |
| GTX36925 | E. coli O157 antibody [1024] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX41226 | E. coli Labile Toxin A antibody [20/480] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX43112 | E. coli O157 antibody [B835M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX43106 | E. coli O157 antibody [B839M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX43111 | E. coli O157 antibody [B836M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX36924 | E. coli O157 antibody [1025] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX43109 | E. coli O157 antibody [B838M] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX36926 | E. coli O157 antibody [1023] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA, Sandwich ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX64164 | RuvC antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | E. coli |
| GTX64163 | RuvB antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | E. coli |
| GTX64186 | UmuD antibody | Rabbit | Polyclonal | WB | E. coli |
| GTX54513 | CNF1 + CNF2 antibody [JC4] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Functional Assay | |
| GTX80808 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (STX-2) subunit A antibody [7585] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Neutralizing/Inhibition | Bacteria |
| GTX80805 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (STX-1) subunit B antibody [7583] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Neutralizing/Inhibition | Bacteria |
| GTX40976 | E. coli O157 antibody [3011] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX43105 | E. coli O157 antibody [BDI160] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX36919 | E. coli O157 antibody [1061] (FITC) | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX36920 | E. coli O157 antibody [1061] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX54512 | CNF1 antibody [NG8] | Mouse | Monoclonal | WB, ELISA, Functional Assay | |
| GTX41248 | E. coli O15 antibody [15/443] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX41110 | E. coli antibody (HRP) | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX36374 | E. coli antibody (FITC) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX38706 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (SLT-2, STX-2) subunit A antibody [557] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Neutralizing/Inhibition | E. coli |
| GTX41230 | E. coli K88A antibody [1050/66] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ICC/IF, ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX66885-pro | TRXB protein (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66889-pro | SodA protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66891-pro | Malate dehydrogenase protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66893-pro | Glk protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66883-pro | SlyD protein (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66888-pro | SurA protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66892-pro | GldA protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66895-pro | Idnk protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66896-pro | Carbonic anhydrase protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66897-pro | AmpC protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66887-pro | Uridine phosphorypase protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66890-pro | Gor protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX66894-pro | Idha protein, His tag (active) | Functional Assay | |||
| GTX04515 | Lipid A LPS antibody [26-5] | Mouse | Monoclonal | Immunoassay | Bacteria |
| GTX36332 | E. coli antibody (FITC) | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF | E. coli |
| GTX13623 | E. coli K99 pilus antibody [6911] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX40765 | E. coli antibody (Biotin) | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF | E. coli |
| GTX43248 | E. coli antibody [110] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX40521 | E. coli antibody | Goat | Polyclonal | ICC/IF | E. coli |
| GTX02558 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (SLT-2) subunit B antibody [7582] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA, Neutralizing/Inhibition | |
| GTX13622 | E. coli antibody [1011] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA | E. coli |
| GTX57493-pro | E. coli gldA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57490-pro | E. coli lldD protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57491-pro | E. coli SecB protein | ||||
| GTX57495-pro | E. coli melA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57466-pro | E. coli NFNB protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57485-pro | E. coli mutY protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57464-pro | E. coli FuR protein | ||||
| GTX57478-pro | E. coli rnhA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57460-pro | E. coli DnaK protein | ||||
| GTX57482-pro | E. coli nth protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57489-pro | E. coli glpE protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57486-pro | E. coli mug protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57470-pro | E. coli glsA1 protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57474-pro | E. coli mutM protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57461-pro | E. coli DnaJ protein | ||||
| GTX57500-pro | E. coli deoC protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57479-pro | E. coli phrB protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57499-pro | E. coli ppa protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57481-pro | E. coli GrpE protein | ||||
| GTX57480-pro | E. coli ung protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57492-pro | E. coli glpK protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57469-pro | E. coli pykF protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57462-pro | E. coli Carbonic Anhydrase protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57498-pro | E. coli msrA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57487-pro | E. coli nanA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57467-pro | E. coli TPX protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57476-pro | E. coli glk protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57513-pro | E. coli NusA protein | ||||
| GTX57477-pro | E. coli grxB protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57497-pro | E. coli groL protein | ||||
| GTX57471-pro | E. coli ansA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57472-pro | E. coli IdhA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57488-pro | E. coli map protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57475-pro | E. coli ackA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57496-pro | E. coli GroES protein | ||||
| GTX57465-pro | E. coli ndk protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57494-pro | E. coli CoaA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57468-pro | E. coli idnk protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57473-pro | E. coli hchA protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57483-pro | E. coli msrB protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX57484-pro | E. coli cysH protein, His tag | ||||
| GTX02559 | Verotoxin / Shiga toxin (SLT-2) subunit B antibody [7587] | Mouse | Monoclonal | ELISA |