Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions involved in maintaining the living state of cells and the organism. These chemical reactions are organized into metabolic pathways and can be divided into two categories: catabolism, the breakdown of organic molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids and proteins with the release of energy, and anabolism, the synthesis of complex molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids from simpler compounds that generally requires energy. Metabolic pathways are evolutionarily highly conserved between species. Disorders of these processes may result from nutritional deficiencies, disease in metabolic organs such as the liver and pancreas, or genetic mutations. The human and economic impact of conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and osteoporosis is staggering, so additional research is essential for developing preventative approaches in conjunction with therapeutic agents that can minimize the long-term effects of these progressive maladies.
Metabolism
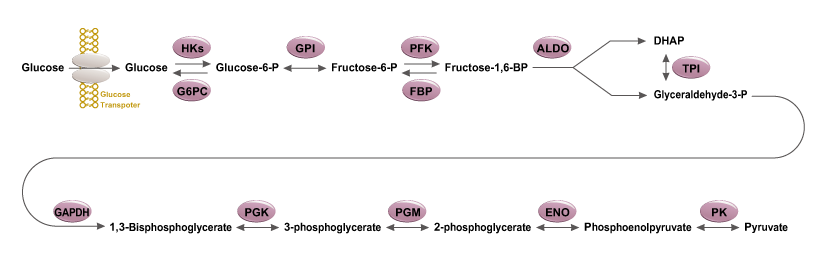
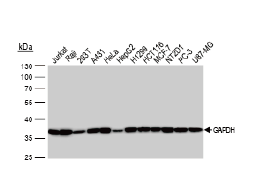
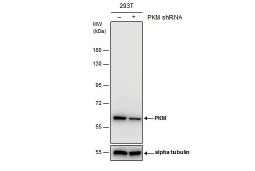
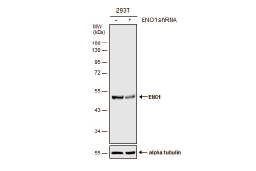
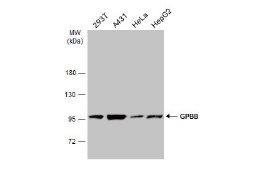
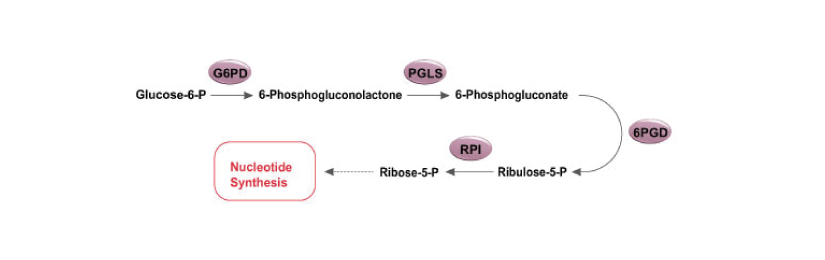
Glycolysis is a universal catabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate through a sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions, and generates the high-energy molecules ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). Its primary function is to provide energy and intermediates for other metabolic pathways. The glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: the preparatory/investment phase (first five reactions in the figure above) where ATP is consumed, and the pay-off phase (final five reactions in the figure above) where ATP is produced.
Glycolysis is an oxygen-independent metabolic pathway. Therefore, it not only plays important roles in generating energy to support normal cell homeostasis, but also is the major energy production pathway in hypoxic cancer cells.
Highlighted Products
![]()
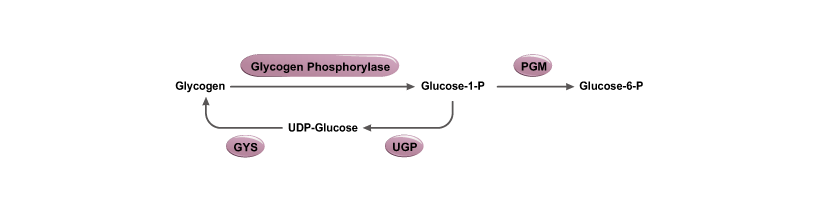
Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen branches through catabolic reactions via the sequential removal of glucose monomers via phosphorolysis, catalyzed by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase. Glycogen is cleaved from glycogen (n) to produce glucose-1-phosphate and glycogen (n-1). Phosphoglucomutase (PGM) then converts glucose-1-phosphate into glucose-6-phosphate, which then enters the glycolytic pathway. Glycogenolysis takes place in muscle and liver cells in response to hormonal (i.e., glucagon, insulin, and epinephrine) and neural signals
Glycogenesis, in contrast, is the process of anabolic synthesis of glycogen. Glucose molecules are phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate, converted to glucose-1-phosphate and UDP-glucose, and added to glycogen chains for storage.
Highlighted Products
![]()
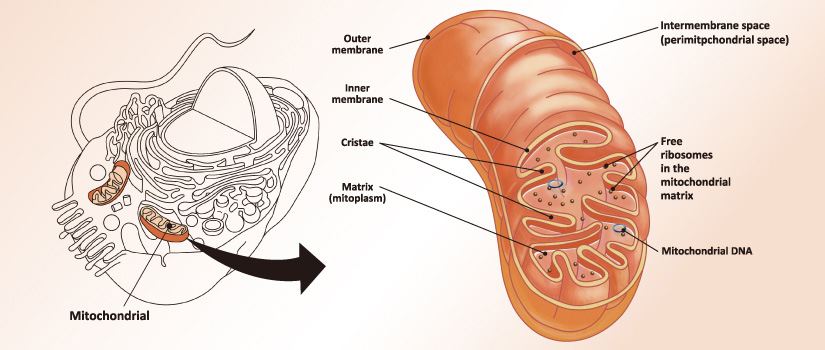
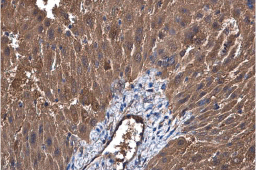
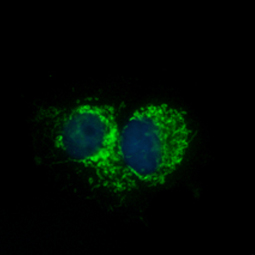
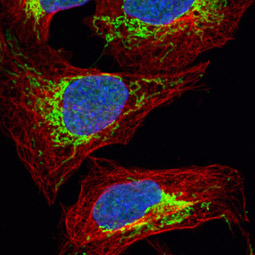
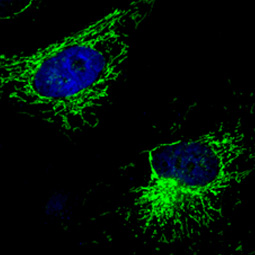
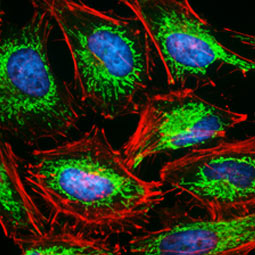
Mitochondria are dual-membrane organelles essential for the production of >90% of the metabolic energy in the eukaryotic cell. Their structural features include inner and outer membranes that bound an intermembrane space. The inner membrane is arranged into folds called cristae, which reach into the central matrix. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to such natural processes as aging in addition to being a key factor in a plethora of neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, metabolic, autoimmune, and neoplastic pathologies that plague humans. GeneTex proudly offers a selection of high quality mitochondrial markers.
| Highlighted Products | |||||
|
|
|||||
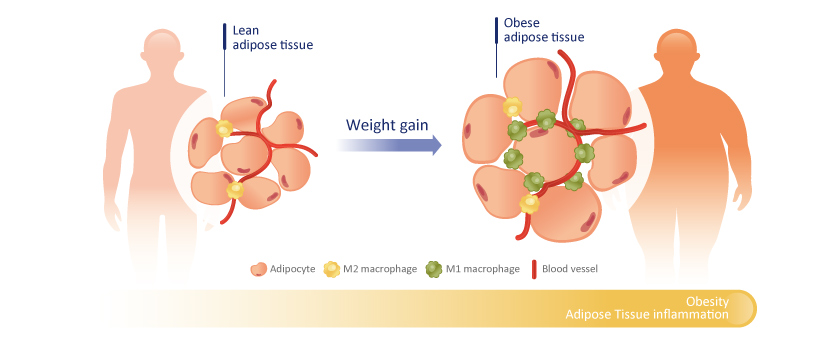
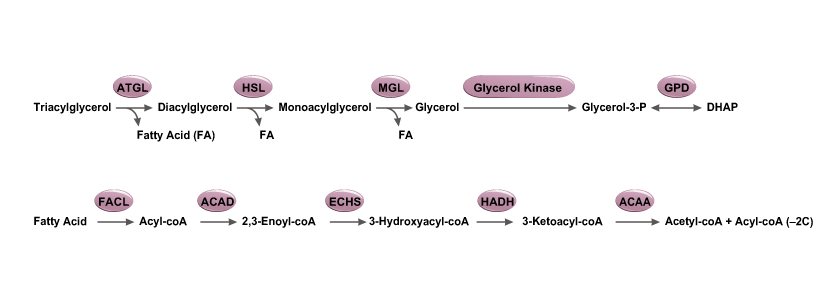
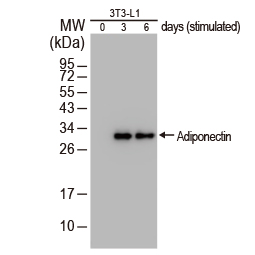
Obesity is characterized by increased lipid accumulation in adipocytes, leading to white adipose tissue hypertrophy, impaired lipolysis, and ectopic fat deposition in other tissues. Adipocytes are also highly active secretory cells, producing proteins and hormones that function well beyond metabolism. The worldwide epidemic of obesity has led to a dramatic increase in metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes mellitus, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, steatohepatitis, asthma, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases that are related to the generation of low‑grade, chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes is caused by obesity-driven insulin resistance in white adipose tissue, the liver, and skeletal muscle combined with impaired secretion of insulin by pancreatic β-cells. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that promote obesity-related diseases will accelerate the development of new therapeutic approaches for these often devastating conditions.
GeneTex is proud to offer an outstanding selection of antibodies to study adipogenesis, adipocyte biology, and insulin resistance signaling for obesity research. These antibodies are validated for various applications to facilitate your efforts in this exciting field. Please see the highlighted products below.
Highlighted Products
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
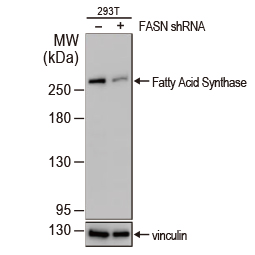
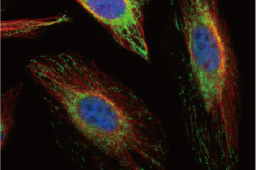
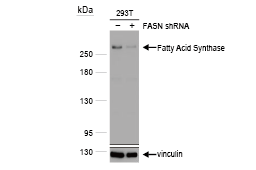
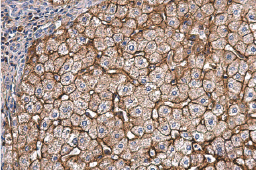
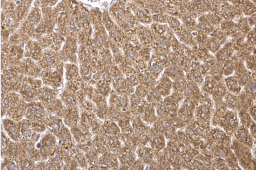
Fatty Acid Synthase antibody [N1], N-term (GTX109833) |
Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) |
FABP4 antibody [N3C3] (GTX116036) |