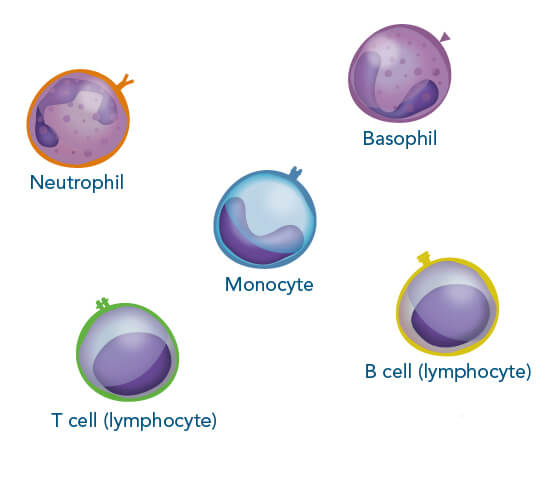
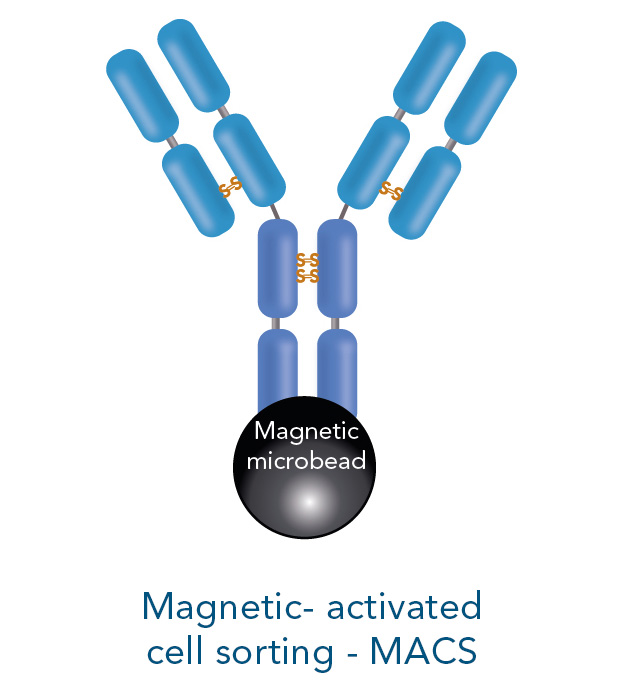
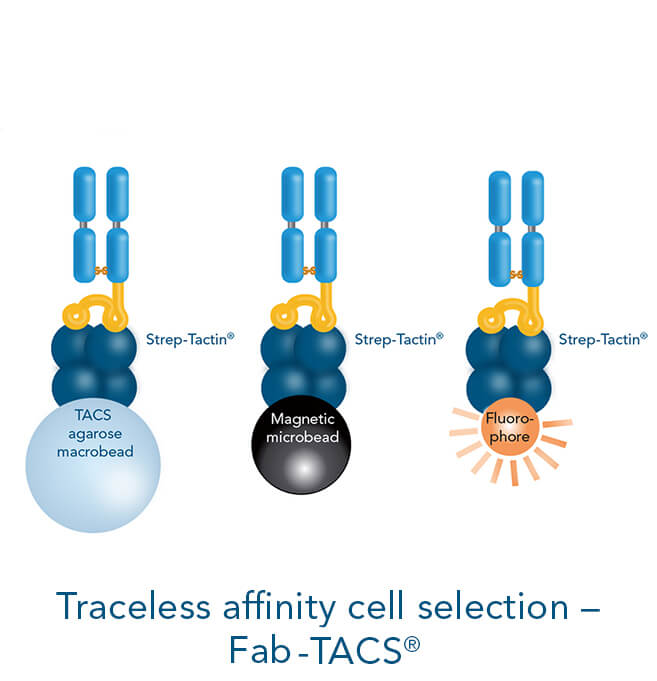
Cells serve as an important research tool to investigate different mechanisms in health and disease. They are also suitable for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, making them attractive for a broad area of research fields. Immune cells have a wide range of functions such as controlling body homeostasis, which includes elimination of infected or cancerous tissue. Therefore, these cells are frequently employed for different analyses and model systems. The advantage of using immune cells is that they are abundant in, for example, human blood or mouse spleen, two sources that are relatively easily accessible for research purposes.
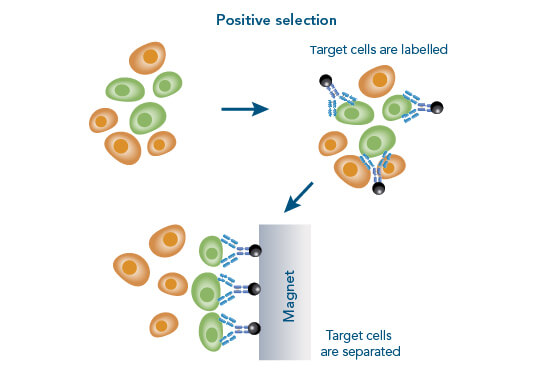
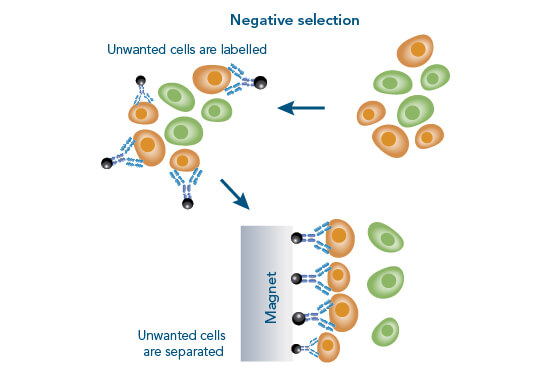
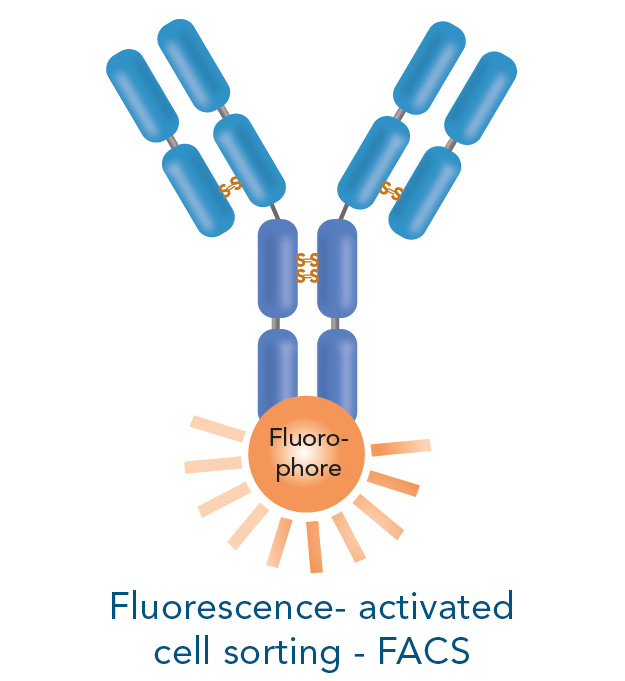
The interaction of cells with each other is very complex and for some experimental setups it is necessary to isolate one specific population for further downstream applications and analyses. Those include for example DNA/RNA isolation, single cell RNA sequencing, protein purification, Western blot or various cell culture experiments.