Indigo Applications
Simple & Effective Solutions for Accelerating Drug Discovery
Run our full portfolio of receptor assays for a comprehensive overview of your therapeutic candidates, or focus on a single receptor assay to rapidly supplement your existing data. Shorten your hands-on time in the lab with our reporter assays, and get clear results within days! No cell culture required.
With INDIGO’s effective and affordable in vitro solutions, streamline your drug discovery process and develop first-in-class medicines in record time.

Perform Quick Compound Evaluation with a Customized Drug Discovery Panel
Analyze your drug candidates using a drug discovery panel, and rapidly access essential information including:
- On- and off-target effects.
- Activity in agonist, inverse-agonist, or antagonist modes.
- Efficacy and EC50/IC50 values.
Directly in your lab or through our services, get the most comprehensive data for your investment with quick turnaround times.
Avoid unnecessary steps backward and get promising leads to the next phase of drug discovery faster!
Simplify Your Cross-Species Comparisons with Our Ortholog Assays
Covering more than 40 nuclear receptors and six species, INDIGO’s ortholog portfolio enables researchers to assess drug-specific differences between their animal model and humans accurately.
Select the most representative human-surrogate model for your trial and retrospectively gain insight into previous animal studies.
Perform cross-species comparisons efficiently, and confidently move to in vivo or clinical trials!
Select The Best Drug Lead for Your Disease-Specific Research
Screen your therapeutic candidates with INDIGO’s cell-based receptor assays, specifically suited for your target disease.
Explore INDIGO’s assays by disease state target, including:
Get accurate and reproducible results and gain insights into the underlying mechanisms of your disease of interest fast.
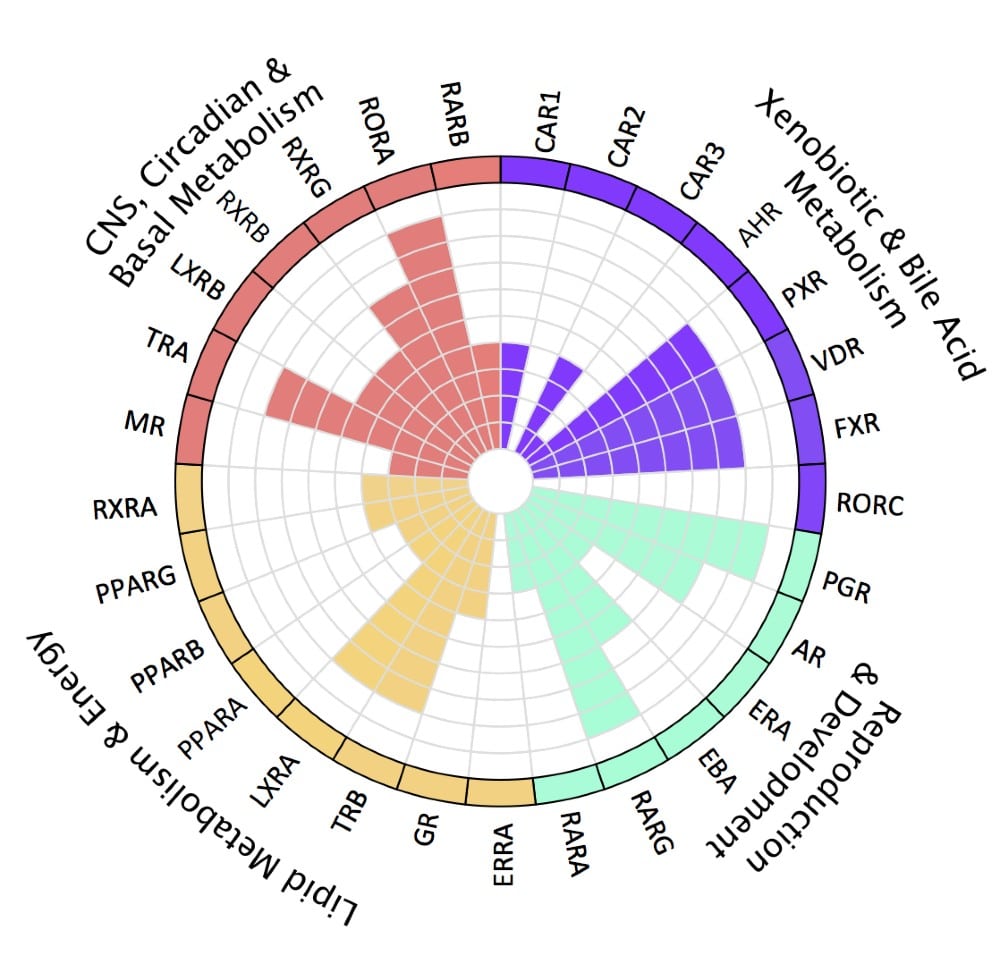
Easily Access Nuclear Receptor Profiling Data Through Functional Classifications
Screening a compound’s entire nuclear receptor profile provides crucial information on its efficacy and toxicity. Still, it can become overwhelming, considering receptors’ involvement in many cellular functions such as development, reproduction, and metabolism.
To facilitate the profiling process, nuclear receptors can be grouped according to their functional characteristics:
- CNS, Circadian & Basal Metabolism
- Lipid Metabolism & Energy
- Reproduction & Development
- Xenobiotic & Bile Acid Metabolism
With INDIGO’s nuclear receptor profiling, following the functional classification principle, you can understand a compound’s on-target and off-target effects and potential liabilities on overlapping nuclear receptor pathways and functions easily.
Disease State Targets
Supercharge your drug discovery and development with INDIGO Biosciences’ cell-based assays. Gain deep insights by unlocking the potential of multi-target interactions for enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Transform your research today!
Unlock the power of polypharmacology with INDIGO Biosciences’ advanced solutions and revolutionize your drug discovery efforts.
- Target specific disease mechanisms with precision and effectiveness
- Get holistic evaluation for enhanced compound efficacy and safety
- Maximize therapeutic potential by targeting multiple pathways simultaneously
Review Various Disease States and their Receptors
Anemia & Kidney Disease
INDIGO’s assay kits and services can provide valuable information for your anemia & kidney disease research. Whether you are interested in a single-receptor assay or a full-panel study, we can help you obtain the data you need quickly.
Indigo Assays for Anemia & Kidney Disease Research
INDIGO Biosciences offers assays for receptors that are implicated as promising therapeutic targets for drug discovery in anemia and kidney disease:
Receptors for Anemia & Kidney Disease Research
Various receptors are targets for anemia and chronic kidney disease research due to their involvement in the signaling pathways for metabolism, immune response, and inflammation. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the involvement of various receptors in the pathogenesis of certain anemias and chronic kidney disease, as well as the complications and comorbidities that result from it may offer targets for the development of new treatments.
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the blood has a low number of red blood cells. This results in reduced oxygen flow to the body. Anemia is the most common blood condition in the United Stated affecting almost 6% of the population. There are three main causes for anemia including, blood loss, lack of red blood cell production, and high rates of red blood cell apoptosis.
Symptoms may include fatigue, cold hands and feet, pale or yellow skin, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or a fast heartbeat. Comorbidities of anemia are hypertension, hypothyroidism, cancer, cardiovascular disease, rheumatologic disease, and chronic kidney disease.
Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (chronic renal disease) includes a variety of conditions that damage the kidneys and decrease their functioning. As kidney disease progresses, less waste gets filtered out, and it can build to high levels. There is an increased risk for developing chronic kidney disease for those with a family history of kidney disease, as well as those with the comorbidities diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease. More than 37 million people in the United States may have chronic kidney disease.
There typically are no symptoms in the early stages of chronic kidney disease, but as kidney damage progresses, signs and symptoms can include, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue and weakness, sleep problems, more frequent urination, swelling of feet and ankles, persistent itching, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Complications of chronic kidney disease include fluid retention, cardiovascular disease, anemia, decreased sex drive, damage to the CNS, decreased immune response, pericarditis, and end-stage kidney disease. Chronic kidney disease can be diagnosed using a blood test to measure the glomerular filtration rate or a urine test to check for albumin. Imaging tests, and kidney biopsy can also be performed to understand the type of kidney disease and how much damage has occurred to recommend treatment.
Once damage to the kidney has occurred it is permanent. Treatment of chronic kidney disease largely depends on the underlying cause, but usually consists of measures to help control signs and symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. If the disease progresses to end-stage kidney disease when less than 15% of the kidney is functioning, treatments to maintain health include dialysis and kidney transplantation.
Related Products and Services
Autoimmune Disease & Inflammation
INDIGO’s assay kits and services can provide valuable information for your autoimmune disease and inflammation research. Whether you are interested in a single-receptor assay or a full-panel study, we can help you obtain the data you need quickly.

Receptors for Autoimmune Disease & Inflammation Research
Nuclear receptors and other receptors are targets for autoimmune research due to their involvement in the signaling pathways for inflammation and immunity. Autoimmune diseases also cause damage to the endocrine system causing over or underproduction of certain hormones. This makes therapies that are full or partial agonists, or antagonists of nuclear hormone receptors involved in endocrine function important for managing perturbations caused by specific autoimmune diseases.
Indigo Assays for Autoimmune Disease & Inflammation Research
INDIGO Biosciences offers assays for receptors that are implicated as promising therapeutic targets for drug discovery in autoimmune disease and inflammation:
Autoimmune Disease & Inflammation
A healthy immune system defends the body against disease and infection, but if the immune system malfunctions, it can mistakenly attack healthy cells, tissues, and organs. Collectively diseases that result from dysfunction of the immune system, whether from abnormally low activity or over activity, are called autoimmune disease. These attacks can affect any part of the body, weakening bodily function and even turn life-threatening. More than 23 million people in the United States have an autoimmune disease and there are more than 80 known types of autoimmune diseases including type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and multiple sclerosis.
Many autoimmune diseases have similar symptoms. One of the classic signs of an autoimmune disease is the redness, heat, pain, and swelling caused by inflammation. Though inflammation is critical for the body’s normal immune responses, chronic inflammation has been shown to cause tissue damage. For these reasons and others, avenues for autoimmune disease research include the role of inflammation associated with immune system response.
Treatments for autoimmune diseases vary depending on the disease, but mostly consist of ways to reduce symptoms and reduce the immune systems abnormal response. Currently, the cause for autoimmune diseases is unknown but, due to the rise of incidences of autoimmune disease, researchers suspect environmental factors play a role.
Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease (chronic renal disease) includes a variety of conditions that damage the kidneys and decrease their functioning. As kidney disease progresses, less waste gets filtered out, and it can build to high levels. There is an increased risk for developing chronic kidney disease for those with a family history of kidney disease, as well as those with the comorbidities diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease. More than 37 million people in the United States may have chronic kidney disease.
There typically are no symptoms in the early stages of chronic kidney disease, but as kidney damage progresses, signs and symptoms can include, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue and weakness, sleep problems, more frequent urination, swelling of feet and ankles, persistent itching, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Complications of chronic kidney disease include fluid retention, cardiovascular disease, anemia, decreased sex drive, damage to the CNS, decreased immune response, pericarditis, and end-stage kidney disease. Chronic kidney disease can be diagnosed using a blood test to measure the glomerular filtration rate or a urine test to check for albumin. Imaging tests, and kidney biopsy can also be performed to understand the type of kidney disease and how much damage has occurred to recommend treatment.
Once damage to the kidney has occurred it is permanent. Treatment of chronic kidney disease largely depends on the underlying cause, but usually consists of measures to help control signs and symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. If the disease progresses to end-stage kidney disease when less than 15% of the kidney is functioning, treatments to maintain health include dialysis and kidney transplantation.
Related Products and Services
Cancer
INDIGO’s assay kits and services can provide valuable information for your cancer research. Whether you are interested in a single-receptor assay or a full-panel study, we can help you obtain the data you need quickly.
Nuclear Receptors for Cancer Research
Nuclear receptors have long been targets in oncology research and the role of dysregulated nuclear receptor mediated signaling pathways in tumorigenesis has been well documented in a variety of cancers. Small molecule drugs that modulate nuclear receptors have proven to be effective therapeutic targets, such as with antagonists of the androgen receptor (AR) in patients with prostate cancer or the estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) in patients with ERα positive breast cancer. Nuclear receptors also play critical roles in the signaling pathways for inflammation and immunity and these pathways have been widely implicated in oncogenesis and may be potent therapeutic avenue for new cancer treatments.
Growth Factor Receptors for Cancer Research
Growth factor receptors are important targets in oncology because mutations that lead to constitutive activation of these signal pathways result in the progression of various types of cancers. Overexpression of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK), which include the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) family, among others, have been found in many tumors. Mutations in serine/threonine-specific protein kinase receptors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβR) have also been linked to growth of many tumors due to defects in the cellular growth inhibition response to TGFβ. As discovery research continues, growth factors and growth factor signaling pathways remain promising targets in the development of oncologic therapeutics.

Indigo Assays for Cancer Research
INDIGO Biosciences offers assays for receptors that are implicated as promising therapeutic targets for drug discovery in cancer treatment:
Related Products and Services
Cardiovascular Disease
INDIGO’s assay kits and services can provide valuable information for your cardiovascular disease research. Whether you are interested in a single-receptor assay or a full-panel study, we can help you obtain the data you need quickly.

Receptors for Cardiovascular Disease Research
Nuclear receptors and other receptors are critical regulators of metabolism, inflammation, and regeneration. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the involvement of nuclear receptors, as well as other receptors in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis may offer targets for the development of new treatments.
Indigo Assays for Cardiovascular Disease Research
Related Products and Services
Diabetes
INDIGO’s assay kits and services can provide valuable information for your diabetes research. Whether you are interested in a single-receptor assay or a full-panel study, we can help you obtain the data you need quickly.

Receptors for Diabetes Research
Nuclear receptors and other receptors are targets for diabetes research due to their involvement in the signaling pathway for carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the involvement of various receptors in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus, as well as the complications that result from the disease may offer targets for the development of new treatments.
Indigo Assays for Diabetes Research
INDIGO Biosciences offers assays for receptors that are implicated as promising therapeutic targets for diabetes:
Related Products and Services
Endocrinology
INDIGO’s assay kits and services can provide valuable information for your endocrinology research. Whether you are interested in a single-receptor assay or a full-panel study, we can help you obtain the data you need quickly.

Receptors for Endocrinology Research
Nuclear receptors are a critical part of endocrine functioning. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the involvement of nuclear receptors in the pathogenesis of endocrine disorders may offer targets for the development of new treatments, as well as creating better treatments for correcting hormone imbalances caused by endocrine disorders.
Indigo Assays for Endocrinology Research
INDIGO Biosciences offers assays for receptors that are implicated as promising therapeutic targets for endocrinology:
Related Products and Services
NAFLD/NASH
INDIGO’s assay kits and services can provide valuable information for your NAFLD/NASH research. Whether you are interested in a single-receptor assay or a full-panel study, we can help you obtain the data you need quickly.
Receptors for NAFLD/NASH Research
Understanding the mechanisms underlying the involvement of nuclear receptors in the pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) or Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) may offer targets for the development of new treatments for this liver disease. The most common nuclear receptors used in drug and treatment discovery are ligand-activated nuclear receptors, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), pregnane X receptor (PXR), and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), which were first identified as key regulators of the responses against chemical toxicants. Numerous studies using mouse disease models and human samples have revealed critical roles for these receptors and others, such as PPARβ/δ, PPARγ, farnesoid X receptor (FXR), and liver X receptors (LXR), in maintaining nutrient/energy homeostasis in part through modulation of the gut-liver-adipose axis.
NAFLD is associated with altered nuclear receptor function and perturbations along the gut-liver axis. These perturbations include obesity, abnormal hepatic lipid metabolism, increased inflammation, and insulin resistance. Nuclear receptors are essential to understanding the physiology and pathology of liver diseases like NAFLD/NASH, as they are at the crossroads of metabolism, inflammation, and regeneration. Modulation of nuclear receptors has been shown to reduce hepatic steatosis, inflammation, insulin resistance, fibrosis, and obesity, making them attractive – and effective – therapeutic targets.

Indigo Assays for NAFLD/NASH Research
INDIGO Biosciences offers assays for receptors that are implicated as promising therapeutic targets for NAFLD/NASH:
Related Products and Services
Obesity
INDIGO’s assay kits and services can provide valuable information for your obesity research. Whether you are interested in a single-receptor assay or a full-panel study, we can help you obtain the data you need quickly.

Receptors for Obesity Research
Nuclear receptors and other receptors are targets for obesity research due to their involvement in the signaling pathway for regulating metabolism, as well as energy and lipid homeostasis. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the involvement of various receptors in the pathogenesis of obesity, as well as the complications and comorbidities that result from it may offer targets for the development of new treatments.
Indigo Assays for Obesity Research
INDIGO Biosciences offers assays for receptors that are implicated as promising therapeutic targets for obesity:
Related Products and Services
Harness Polypharmacology to Improve the Potential for Clinical Efficacy
Advances in systems biology are revealing a phenotypic robustness and a network structure that strongly suggests that exquisitely selective compounds, compared with multi-target drugs, may exhibit lower than desired clinical efficacy. This new appreciation of the role of polypharmacology has significant implications for the two major sources of attrition in drug development, efficacy, and toxicity. Thus defining the biological niche of each receptor as well as understanding overlapping pathways and functions provides valuable context for evaluating a compound’s liabilities and promise.
Defining the system that each receptor participates in can be approached in several ways, such as sequence similarity, potential disease implication, or transcriptional networks. By choosing a select group of receptors to study based on disease state, it is possible to better understand the biological effects of your compounds. With INDIGO’s extensive portfolio of receptor assays, you can design your own panel based on a disease state or talk to our experts to assist in developing a plan of study.
Applications for INDIGO’s Luciferase Reporter Assays


Drug Discovery
Rapidly evaluate the efficacy and safety profile of a drug candidate with INDIGO’s Reporter Assay Services and streamline the development process to safer, more effective pharmaceutical agents.
Environmental Testing
Effectively screen environmental samples, with INDIGO’s Reporter Assay Services and actively contribute to building a safer environment.
Disease State Targets
Quickly gain insights into the mechanisms underlying the involvement of key receptors in various diseases with INDIGO’s Reporter Assay Services
Environmental Testing
Improve Environmental Testing With INDIGO’s Cell-Based Assays
Actively contribute to creating a safer environment with cell-based luciferase reporter assays specifically developed for use in environmental testing applications.
Screen samples for endocrine disrupting chemicals and rapidly and reliably detect potential toxicity from:
- Estrogen-, androgen-, and dioxin-like compounds
- Contaminants of emerging concern
- Known contaminants
- Unknown substances
With INDIGO’s environmental testing assays we can fast-track our way to a cleaner future.

Understand Chemical Threats to Improve Environmental Testing


What is Environmental Testing?
Environmental testing is a series of procedures designed to evaluate the effects of manufactured and natural chemicals on living organisms and the environment.
Environmental testing includes, but is not limited to:
- Water & Air Quality Monitoring
- Soil and Sediment Analysis
- Industrial Chemical Evaluation (ex: new materials, polymers)
- Agrochemical Assessment (ex: pesticides, fungicides)
Every day, chemicals build up to potentially harmful concentrations in our environment, which is why it is essential to develop better testing procedures to reduce contamination risks and help guide remediation.
The Importance of PAH Testing
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) are a naturally occurring chemical class produced by incomplete combustion of organic materials.
PAHs are highly persistent in the environment, causing long-term soil, water, and air contamination.
Due to their toxic and carcinogenic properties, there is an urgent need for reliable and quick PAH testing methods for assessing exposure levels to better apprehend and minimize their emissions.
Daily Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals
Endocrine disrupting chemicals, or EDCs, are substances that can interfere with the normal functioning of the endocrine system by blocking, altering, or mimicking our natural hormones.
Widely present in pesticides, processed food, dust, and daily-life products, EDCs continuously contaminate our households, water, and soil, representing a growing threat to humans and wildlife.
To further understand and reduce EDC impacts on our environment, we need accurate screening methods specifically designed and validated for studying endocrine receptors.
The Challenge of Emerging Contaminants
Contaminants of emerging concern are environmental substances posing risks to human health and ecosystems. Despite known toxic properties and omnipresence, the environmental risk of emerging contaminants are still poorly understood.
Emerging contaminants may include:
- Pesticides
- Industrial chemicals
- Medications
- Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
- Personal care products
- Cleaning products
Accurately Unravel the Effects of Complex Mixtures with INDIGO’s Assays
Toxicologic profiling is essential to monitor and regulate environmental samples’ substances properly. However, when combined as a mixture, chemicals can exert different effects, representing a challenge for researchers and regulatory authorities.
By screening for total bioactivity in environmental samples, INDIGO Biosciences’ cell-based reporter assays can accurately detect substances’ cumulative effects on a specific pathway and help guide decisions to limit chemicals’ environmental impact.
Through a shared standardized workflow, we provide scientists with a quick screening method to analyze samples on multiple nuclear receptors easily.

Build a Safer Environment: INDIGO’s Certified Bioassays for Water Monitoring
Thanks to their accuracy and ease-of-use, INDIGO’s reporter assays are becoming a valuable tool in surface, recycled water, and wastewater monitoring.
Recently, INDIGO received approval from California Water Boards for the use of its Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) and Estrogen Receptor Alpha (ERα) bioassays as bioanalytical screening tools for Constituents of Emerging Concern in recycled water.