How many receptors are in the nuclear receptor superfamily?
To date, over 300 nuclear receptors (NRs) have been found. A large number of nuclear receptors have been identified through sequence similarity to known receptors, but as of yet have no identified natural ligand and are referred to as ”orphan receptors.” Of the identified NRs, only 48 are found in humans with several of them being orphan receptors.
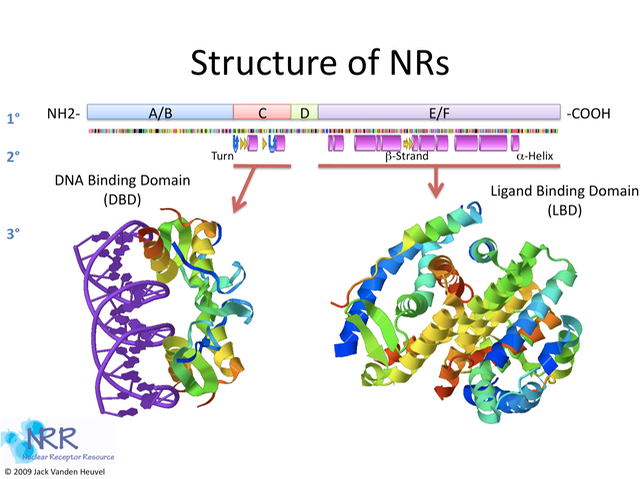
To organize he nuclear receptors in the nuclear receptor superfamily, an organizational nomenclature based on the NR’s phylogenetic tree was created by the Nuclear Receptors Nomenclature Committee in 1999. The form structure decided on is NRxyz, where x is the sub-family, y is the group, and z is the gene. For example, FXR is classified as NR1H4, meaning FXR is an NR in subfamily 1, group H, and is the fourth member of that group. There are seven different subfamilies indicated by NR1, NR2, NR3, NR4, NR5, NR6, and NR0. These subfamilies are classified based on the evolution of two domains found in the nuclear receptor superfamily, specifically the DNA binding domain (DBD) and the ligand binding domain (LBD). The exception to the rule is NR0, which are a subfamily of receptors that do not contain a DNA-binding domain, but instead bind to other nuclear receptors.