Western blotting with JIR secondary antibodies
Western blotting is an analytical technique used to detect specific proteins or peptides in biological samples or solutions containing complex mixtures. Initially, linearized proteins are separated by gel electrophoresis to resolve them by size. They are then transferred onto a membrane such as nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) which immobilizes the protein. Subsequently, the membrane is blocked and then probed with a primary antibody directed against the specific protein of interest. A secondary antibody conjugated to a reporter molecule is then used to identify the analyte using colorimetric, chemiluminescent or fluorescent detection.
Detection Methods
Colorimetric
Reporter enzyme conjugates alkaline phosphatase (AP) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) can be used for colorimetric detection. The conjugated reporter enzyme catalyzes the conversion of the chromogenic substrate to a colored precipitate, which is visualized directly on the blotting membrane. Colorimetric detection can offer quick and easily obtained results without the need for expensive detectors or extensive optimization.
Chemiluminescent
Enzyme-linked conjugates can also be used for chemiluminescent signal detection. HRP conjugates produce signal by oxidizing a chemiluminescent substrate (luminol) to a form which emits light. AP conjugates produce signal when the enzyme dephosphorylates a specific substrate (e.g. 1,2-dioxetane) to a light emitting product. The signal can then be captured by exposing photographic film to the membrane or using a cooled charge-coupled device (CCD) camera. Chemiluminescent detection offers excellent sensitivity, however quantification and probing for multiple targets can be limited, and development may require refinement to optimize signal capture.
Fluorescent
Fluorescent detection uses a fluorescent dye conjugate to visualize antigen on the membrane. Light at a wavelength specific to the dye’s spectral characteristic is absorbed, exciting the dye’s electrons to a higher electronic state, and as they return to their ground state they emit photons at the emission wavelength characteristic to the fluorophore. The light emitted is detected by a digital imager fitted with appropriate filters. Fluorescent Western blotting allows for quantitative analysis and multiplex probing without the need for stripping and reblotting. Jackson ImmunoResearch offers a range of fluorescent dyes covering the spectrum.
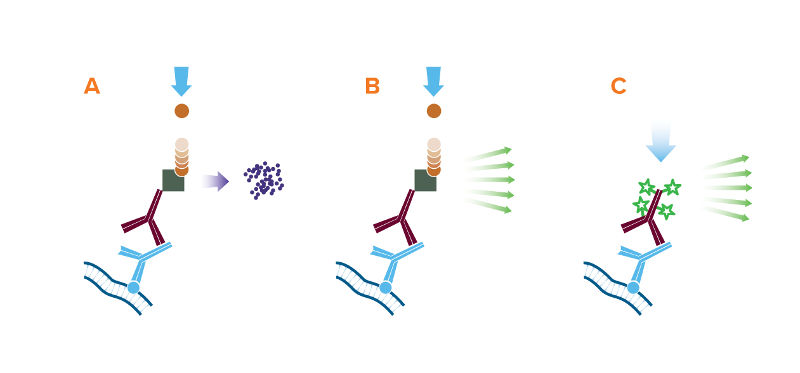
The 3 detection methods for Western blot: (A) Colorimetric, (B) Chemiluminescent, and (C) Fluorescent;
A. The reporter enzyme conjugate catalyzes the conversion of a chromogenic substrate to a colored insoluble precipitate, visible by eye on the blotting membrane.
B. The reporter enzyme conjugate catalyzes a reaction which converts the chemiluminescent substrate to a light emitting form, and the emitted light is detected by X-ray film or CCD camera.
C. The reporter fluorescent dye is excited by its characteristic wavelength light, and resulting emitted light is captured by a digital imager.
Jackson ImmunoResearch produces the largest diversity of species specific secondary antibody conjugates for use in Western blotting. JIR offers antibodies and streptavidin conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP), alkaline phosphatase and Biotin-SP for use in traditional blots developed with chromogenic or chemiluminescent (ECL) substrates. In addition, secondary antibodies conjugated with fluorescent dyes, including far-red and infrared-emitting dyes, are available for multicolor imaging in modern readers.
Jackson ImmunoResearch also offers affinity-purified anti-horseradish peroxidase which may be used to detect HRP or to enhance signal by binding to HRP-conjugated molecules. Conjugated anti-HRP may be used to convert an HRP conjugate into a different signal.
Western blotting after Immunoprecipitation (IP)
Probing in the 50 kDa range after IP
If diluted properly, anti-light chain specific antibodies do not bind to the reduced and denatured IgG heavy chain band (50 kDa) on blots. Therefore, by using anti-light chain specific antibodies, detection of antigens with molecular weights near 50 kDa is not obscured by large amounts of reduced and denatured IgG heavy chains from primary antibodies used for immunoprecipitation (IP).
Probing in the 25 kDa range after IP
If the protein of interest (POI) has a reduced and denatured molecular weight near 25 kDa, anti-IgG, Fc fragment specific antibodies may be used to detect IgG primary antibodies, without binding to reduced and denatured IgG light chains on Western blots. Clear detection of a POI near 25 kDa requires blocking degraded heavy chain that migrates to 25 kDa.
Near-Infrared (NIR) fluorescent conjugates
Antibodies conjugated with far-red- and infrared-emitting dyes are suitable for a variety of techniques requiring the highest sensitivity. Alexa Fluor® 680 and 790 dyes are more sensitive than visible light-emitting dyes due to lower fluorescence quenching of the conjugates and higher extinction coefficients of the dyes. Low sample autofluorescence in this region of the spectrum results in lower background signal compared with other fluorophores.
Alexa Fluor® 680 and 790 conjugates can be used for high sensitivity Western blots, quantitative Western blots, in-gel Western blots, microWestern arrays, in-cell Western assays, on-cell Western assays, and other techniques that require the brightest dyes.
Usage Guidance
Membrane blocking buffer
Normal serum from the host species of the labeled antibody (5% v/v) is an excellent block, although 5% non-fat milk and 3% BSA are commonly used and may also be effective. Avoid milk or BSA when using a primary antibody derived from goat or sheep.
Diluting antibodies for Western blotting
PBS/Tween 20 (0.05% v/v) or TBS/Tween, without carrier proteins, is recommended as the secondary antibody diluent. Especially when using anti-goat or anti-sheep secondary antibodies, avoid using milk or BSA in the diluent buffer. Bovine IgG in the milk or BSA may interact with the antibody due to homologous epitopes of the related species.
Recommended dilution ranges for our conjugated secondaries in Western blotting are shown in the tables below.