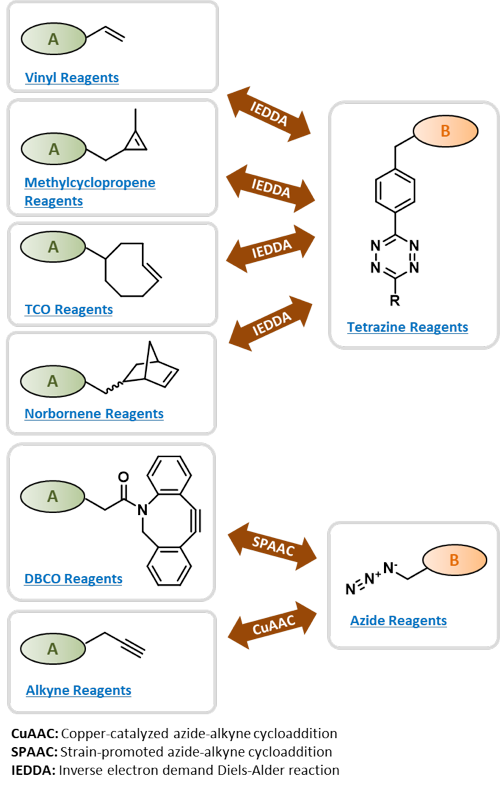
Click Chemistry[1] describes pairs of functional groups that rapidly and selectively react (“click”) with each other under mild, aqueous conditions. The concept of Click Chemistry has been transformed into convenient, versatile and reliable two-step coupling procedures of two molecules A and B[1-5] that are widely used in biosciences[6-8], drug discovery[9] and material science[10].
Click Reagents by Chemistry
Vinyl-containing Click Reagents
Vinyl-containing nucleotides can be labeled with Tetrazine-tagged reporter molecules via Copper-free Tetrazine-Alkene Ligation that allows to introduce a Biotin group for subsequent purification (via
Tetrazine-containing Biotinylation Reagents) or a fluorescent group for subsequent microscopic imaging (via Tetrazine-containing Fluorescent Dyes).
Search for nucleotides that are suitable for enzymatic click functionalization of DNA or enzymatic click functionalization of RNA
Vinyl-containing nucleosides can be labeled with Tetrazine-tagged reporter molecules via Copper-free Tetrazine-Alkene Ligation that allows to introduce a Biotin group for subsequent purification (via Tetrazine-containing Biotinylation Reagents) or a fluorescent group for subsequent microscopic imaging (via Tetrazine-containing Fluorescent Dyes).
They are suitable for DNA synthesis monitoring or RNA synthesis monitoring, respectively.
Methylcyclopropene-containing Click Reagents
Methylcyclopropene-containing monosaccharides can be used to attach methylcyclopropene groups to glycoconjugates via metabolic labeling [1-3] followed by subsequent labeling with Tetrazine-containing detection reagents via Cu(I)-free Tetrazine-Cyclopropene Ligation[4].
A number of CLICKable monosaccharides are available for metabolic glycan labeling.
Selected References
[1] Spaete et al. (2014) Expanding the scope of cyclopropene reporters for the detection of metabolically engineered glycoproteins by Diels–Alder reactions. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 10:2235.
[2] Spaete et al. (2014) Rapid labeling of metabolically engineered cell-surface glycoconjugates with a carbamate-linked cyclopropene reporter. Bioconj. Chem. 25:147.
[3] Patterson et al. (2014) Improved cyclopropene reporters for probing protein glycosylation. Mol. BioSyst. 10:1693.
[4] Patterson et al. (2012) Functionalized cyclopropenes as bioorthogonal chemical reporters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134:18643.
TCO-containing Click Reagents
Bifunctional TCO-containing Reagents
Trans-Cyclooctene-containing bifunctional reagents can be used for the introduction of
- a functional group (e.g. Amine or NHS Ester) to Tetrazine-labeled molecules via Cu-free Click Chemistry
- an Cyclooctene group to various targets e.g. via NHS Ester- or Maleimide-based chemistry
Table 1: Available Trans-Cyclooctene-containing Bifunctional Reagents
| Functional Groups | Trans-Cyclooctene |
| NHS ester | TCO-NHS ester TCO-PEG4-NHS ester |
| Maleimide | TCO-PEG3-Maleimide |
| Amine (-NH2) | TCO-Amine |
Selected References:
Selvaraj et al. (2013) trans-Cyclooctene – a stable voracious dienophile for bioorthogonal labeling. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 17:753.
Trans-Cyclooctene-containing nucleotides can be attached to Tetrazine-tagged biomolecules via Cu-free Click Chemistry.
| Products & Ordering |
| 5-TCO-PEG4-dUTP CLK-035 5-trans-Cyclooctene-PEG4-dUTP |
TCO Agarose is suitable to covalently capture Tetrazine-tagged biomolecules via Cu-free Click Chemistry. The proteins of interest need to be metabolically, enzymatically or chemically Tetrazine-tagged.
| Products & Ordering |
| TCO Agarose CLK-1198 |
DBCO-containing Click Reagents
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)*-containing fluorescent dyes can be used for the fluorescent labeling of Azide-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC). Both Standard Dyes (e.g. Cy3, Tamra or Texas Red) and novel Alternative Dyes have been thoroughly selected to cover the whole UV-Vis spectrum.
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne)
Table 1: Available DBCO-containing Fluorescent Dyes
| Emission colour | Dye | Product |
| blue-green | ATTO 425 | DBCO-PEG4-ATTO-425 |
| green | BDP-FL (also known as BODIPY® FL) | BDP-FL-PEG4-DBCO |
| 5/6-Fluorescein (5/6-FAM) | DBCO-PEG4-5/6-FAM | |
| AF488 (also known as Alexa Fluor®488) | DBCO-AF488 | |
| ATTO 488 | DBCO-PEG4-ATTO-488 | |
| 5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110 | DBCO-PEG4-5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110 | |
| yellow | 5/6-TAMRA | DBCO-PEG4-5/6-TAMRA |
| Sulfo-Cy3 | DBCO-Sulfo-Cy3 | |
| AF546 (also known as Alexa Fluor®546) | DBCO-AF546 | |
| AF555 (structural analog to Alexa Fluor®555) | DBCO-AF555 | |
| orange | AF594 (also known as Alexa Fluor®594) | DBCO-AF594 |
| red | Sulfo-Cy5 | DBCO-Sulfo-Cy5 |
| AF647 (structural analog to Alexa Fluor®647) | DBCO-AF647 | |
| Cy5.5 | DBCO-Cy5.5 |
| Products & Ordering | |
| DBCO-PEG4-ATTO-425 CLK-085 Abs/Em = 436/484 nm Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-ATTO-425 | BDP-FL-PEG4-DBCO CLK-040 also known as BODIPY® FL-PEG4-DBCO Abs/Em = 503/512 nm |
| DBCO-PEG4-5/6-FAM CLK-051 Abs/Em = 492/517 nm Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-5/6-FAM | DBCO-AF488 CLK-1278 Abs/Em = 494/517 nm also known as Alexa Fluor® 488-DBCO |
| DBCO-PEG4-ATTO-488 CLK-052 Abs/Em = 501/523 nm Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-ATTO-488 | DBCO-PEG4-5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110 CLK-A127 Abs/Em = 501/526 nm Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110 |
| DBCO-PEG4-5/6-TAMRA CLK-A131 Abs/Em = 560/565 nm Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-5/6-Tetramethylrhodamine | DBCO-Sulfo-Cy3 CLK-A140 Abs/Em = 553/563 nm Dibenzylcyclooctyne-Sulfo-Cy3 |
| DBCO-AF546 CLK-1286 Abs/Em = 554/570 nm also known as Alexa Fluor® 546-DBCO | DBCO-AF555 CLK-093 Abs/Em = 555/572 nm structural analog to Alexa Fluor® 555 |
| DBCO-AF594 CLK-1298 Abs/Em = 590/617 nm also known as Alexa Fluor® 594-DBCO | DBCO-Sulfo-Cy5 CLK-A130 Abs/Em = 646/661 nm Dibenzylcyclooctyne-Sulfo-Cy5 |
| DBCO-AF647 CLK-1302 Abs/Em = 648/671 nm structural analog to Alexa Fluor® 647 | DBCO-Cy5.5 CLK-1046 Abs/Em = 678/694 nm Dibenzylcyclooctyne-Cy5.5 |
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)*-containing (desthio) biotinylation reagents can be used for the labeling of Azide-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC).
A number of (desthio) biotinylation reagents with
-
- different solubility characteristics (PEG- and Sulfo-linker for increased molecule solubility)
- different cleavability characteristics (chemically or photocleavable linke)
are available to fit specific application & molecule requirements.
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne) or DIBAC (= Dibenzoazacyclooctyne)
Table 1: Available DBCO-containing (Desthio) Biotinylation Reagents
| Label | DBCO |
| Biotin | DBCO-PEG4-Biotin Sulfo-DBCO-Biotin |
| Biotin with chemically cleavable linker | Diazo Biotin-DBCO Dde Biotin-DBCO |
| Biotin with photocleavable linker | Photocleavable Biotin-DBCO |
| Desthiobiotin | DBCO-PEG4-Desthiobiotin |
| Products & Ordering | |
| DBCO-PEG4-Biotin Conjugate CLK-A105P4 Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-Biotin Conjugate | Sulfo-DBCO-Biotin Conjugate CLK-A116 Sulfo-Dibenzylcyclooctyne-Biotin Conjugate |
| Diazo Biotin-DBCO CLK-1043 | Dde Biotin-DBCO CLK-1138 |
| DBCO-PEG4-Desthiobiotin CLK-1108 Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-Desthiobiotin | Photocleavable Biotin-DBCO CLK-1120 |
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)*-containing FLAG tag reagents can be used for the introduction of a FLAG-tag to Azide-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC). Molecule solubility and efficient FLAG-tag detection is ensured by the integrated PEG-linker.
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne) or DIBAC (= Dibenzoazacyclooctyne)
| Products & Ordering |
| DBCO-PEG4-FLAG CLK-033 Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-FLAGtag (DYKDDDDK) |
Selected References
[1] Hopp et al. (1988) A Short Polypeptide Marker Sequence Useful for Recombinant Protein Identification and Purification. Bio/Technology 6:1204.
[2] Einhauer et al. (2001) The FLAG peptide, a versatile fusion tag for the purification of recombinant proteins. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 49:455.
[3] Brizzard et al. (1997) Epitope tagging of recombinant proteins. Current Protocols in Neuroscience:5.8.1.
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)*-containing bifunctional reagents can be used for the introduction of
- a functional group to Azide-labeled molecules via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC)
- an DBCO group to various targets e.g. via NHS Ester- or Maleimide-based chemistry
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne) or DIBAC (= Dibenzoazacyclooctyne)
Table 1: Available DBCO-containing Bifunctional Reagents
| Functional Groups | DBCO | Functional Groups | DBCO |
| NHS ester | DBCO-NHS ester DBCO-PEG4-NHS ester DBCO-Sulfo-NHS ester | Acid (-COOH) | DBCO-Acid |
| Maleimide | DBCO-Maleimide DBCO-PEG4-Maleimide | Amine (-NH2) | DBCO-Amine DBCO-PEG4-Amine |
| Alcohol (-OH) | DBCO-PEG3-Alcohol | DBCO | DBCO-PEG4-DBCO |
| Products & Ordering | |
| DBCO-NHS ester CLK-A133 Dibenzylcyclooctyne-NHS ester | DBCO-PEG4-NHS ester CLK-A134 Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-NHS ester |
| DBCO-Sulfo-NHS ester (sodium salt) CLK-A124 Sulfo-Dibenzylcyclooctyne-NHS ester | DBCO-Maleimide CLK-A108 Dibenzylcyclooctyne-Maleimide |
| DBCO-PEG4-Maleimide CLK-A108P Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-Maleimide | DBCO-PEG3-Alcohol CLK-A104PN Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG3-Alcohol |
| DBCO-Acid CLK-A101N Dibenzylcyclooctyne-Acid | DBCO-Amine CLK-A103 Dibenzylcyclooctyne-Amine |
| DBCO-PEG4-Amine CLK-A103P Dibenzylcyclooctyne-PEG4-Amine |
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)*-modified polyethylene glycol (PEG) polymers can be used for the introduction of a PEG moiety (“PEGylation”) to Azide-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC), respectively.
PEGylation of biomolecules such as proteins increases their water solubility and often improves their pharmacokinetic properties e.g. by a reduced immunogenicity and antigenicity.
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne) or DIBAC (= Dibenzoazacyclooctyne)
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)*-containing nucleotides can be attached to Azide-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC).
Search for nucleotides that are suitable for enzymatic click functionalization of DNA or enzymatic click functionalization of RNA
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne) or DIBAC (= Dibenzoazacyclooctyne)
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)*-containing nucleosides can be attached to Azide-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC).
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne) or DIBAC (= Dibenzoazacyclooctyne)
| Products & Ordering |
| 5-Dibenzylcyclooctyne-2′-deoxyuridine (5-DBCO-dU) CLK-082 5-Dibenzylcyclooctyne-dU |
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)* Agarose is suitable to covalently capture Azide-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC).
The proteins of interest need to be metabolically, enzymatically or chemically azide-tagged. Subsequently, the DBCO Agarose containing the covalently attached proteins can be washed with high stringency, virtually eliminating any non-specifically bound proteins.
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne) or DIBAC (= Dibenzoazacyclooctyne)
| Products & Ordering |
| DBCO Agarose CLK-1034 |
Dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO)* Magnetic Beads are suitable to covalently capture Azide-tagged biomolecules onto magnetic beads via Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC).
The proteins of interest need to be metabolically, enzymatically or chemically azide-tagged. Subsequently, the DBCO Magnetic Beads containing the covalently attached proteins can be washed with high stringency, virtually eliminating any non-specifically bound proteins.
*DBCO is also known as ADIBO (= Azadibenzocyclooctyne) or DIBAC (= Dibenzoazacyclooctyne)
| Products & Ordering |
| DBCO Magnetic Beads CLK-1037 |
Alkyne-containing Click Reagents
Alkyne-containing Fluorescent dyes can be used for the fluorescent labeling of Azide-tagged molecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry reaction (CuAAC).
Standard Dyes (e.g. Cy3, Tamra or Texas Red) have been thoroughly selected to cover the whole UV-Vis spectrum.
Table 1: Available Alkyne-containing Fluorescent Dyes
| Emission colour | Dye | Product |
| green | BDP-FL (also known as BODIPY® FL) | Alkyne – BDP-FL |
| 5-FAM | 5-FAM-Alkyne | |
| 6-FAM | 6-FAM-Alkyne | |
| AF488 (also known as Alexa Fluor®488) | AF488-Alkyne | |
| 5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110 | 5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110-PEG4-Alkyne | |
| yellow | 5-TAMRA | 5-TAMRA-Alkyne |
| 5/6-TAMRA | 5/6-TAMRA-PEG4-Alkyne | |
| Sulfo-Cy3 | Sulfo-Cy3-Alkyne | |
| AF546 (also known as Alexa Fluor®546) | AF546-Alkyne | |
| AF555 (structural analog to Alexa Fluor®555) | AF555-Alkyne | |
| orange | 5/6-Texas Red | 5/6-Texas Red-PEG4-Alkyne |
| AF594 (also known as Alexa Fluor®594) | AF594-Alkyne | |
| red | Sulfo-Cy5 | Sulfo-Cy5-Alkyne |
| AF647 (also known as Alexa Fluor®647) | AF647-Alkyne | |
| Cy5.5 | Cy5.5-Alkyne | |
| near-IR | Cy7 | Cy7-Alkyne |
| Products & Ordering | |
| Alkyne-BDP-FL CLK-045 Abs/Em = 503/512 nm also known as Alkyne-BODIPY® FL | 5-FAM-Alkyne CLK-057 Abs/Em = 490/513 nm 5-Fluorescein-Alkyne |
| 6-FAM-Alkyne CLK-058 Abs/Em = 490/513 nm 6-Fluorescein-Alkyne | AF488-Alkyne CLK-1277 Abs/Em = 494/517 nm also known as Alexa Fluor® 488-Alkyne |
| 5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110-PEG4-Alkyne CLK-TA106 Abs/Em = 501/525 nm Acetylene-Fluor 488 | 5-TAMRA-Alkyne CLK-059 Abs/Em = 556/563 nm 5-Carboxytetramethylrhodamine-Alkyne |
| 5/6-TAMRA-PEG4-Alkyne CLK-TA108 Abs/Em = 546/565 nm 5/6-Carboxytetramethylrhodamine-PEG4-Alkyne, Acetylene-Fluor 545 | Sulfo-Cy3-Alkyne CLK-TA117 Abs/Em = 553/566 nm |
| AF546-Alkyne CLK-1285 Abs/Em = 554/570 nm also known as Alexa Fluor® 546-Alkyne | AF555-Alkyne CLK-092 Abs/Em = 555/572 nm structural analog to Alexa Fluor® 555 |
| 5/6-Texas Red-PEG4-Alkyne CLK-TA110 Abs/Em = 584/603 nm 5/6-Sulforhodamine 101-PEG4-Alkyne, Acetylene-Fluor 585 | AF594-Alkyne CLK-1297 Abs/Em = 590/617 nm also known as Alexa Fluor® 594-Alkyne |
| Sulfo-Cy5-Alkyne CLK-TA116 Abs/Em = 647/663 nm | AF647-Alkyne CLK-1301 Abs/Em = 648/671 nm structural analog to Alexa Fluor® 647 |
| Cy5.5-Alkyne CLK-1060 Abs/Em = 678/694 nm | Cy7-Alkyne CLK-1053 Abs/Em = 753/775 nm |
Alkyne-containing (desthio) biotinylation reagents can be used for the labeling of Azide-tagged biomolecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry reaction (CuAAC).
A number of (desthio) biotinylation reagents with
-
- improved solubility & detection characteristics (PEG-linker for increased molecule solubility & optimal streptavidin binding)
- different cleavability characteristics (chemically or photocleavable linker)
are available to fit specific application & molecule requirements.
Table 1: Available Alkyne-containing (Desthio) Biotinylation Reagents
| Label | Alkyne |
| Biotin | Acetylene-PEG4-Biotin |
| Biotin with chemically cleavable linker | Diazo Biotin-Alkyne Dde Biotin-Alkyne |
| Biotin with photocleavable linker | Photocleavable Biotin-Alkyne |
| Desthiobiotin | Acetylene-PEG4-Desthiobiotin |
| Products & Ordering |
| Alkyne-PEG4-FLAG CLK-088 Alkyne-PEG4-FLAGtag (DYKDDDDK) |
Selected References
[1] Hopp et al. (1988) A Short Polypeptide Marker Sequence Useful for Recombinant Protein Identification and Purification. Bio/Technology 6:1204.
[2] Einhauer et al. (2001) The FLAG peptide, a versatile fusion tag for the purification of recombinant proteins. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 49:455.
[3] Brizzard et al. (1997) Epitope tagging of recombinant proteins. Current Protocols in Neuroscience:5.8.1.
Alkyne-containing reagents can be used for the introduction of
- a functional group to Azide-labeled molecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry reaction (CuAAC)
- an Alkyne group to various targets e.g. via NHS Ester- or Maleimide-based chemistry
Table 1: Available Alkyne-containing Bifunctional Reagents
| Reactive Group | Alkyne |
| NHS ester | Propargyl-NHS ester Acetylene-PEG4-NHS ester |
| Maleimide | Propargyl-Maleimide Acetylene-PEG4-Maleimide |
| Acid (-COOH) | Acetylene-PEG4-Acid |
| Amine (-NH2) | Acetylene-PEG4-Amine |
| Products & Ordering | |
| Propargyl-NHS ester CLK-TA111 | Acetylene-PEG4-NHS ester CLK-TA103N |
| Propargyl-Maleimide CLK-TA113 | Acetylene-PEG4-Maleimide CLK-TA104 |
| Acetylene-PEG4-Acid CLK-TA102N | Acetylene-PEG4-Amine CLK-TA101 |
Alkyne-containing nucleotides can be attached to Azide-tagged biomolecules or incorporated into DNA, RNA or proteins followed by subsequent labeling with Azide-containing reporter molecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry reaction (CuAAC).
Search for nucleotides that are suitable for enzymatic click functionalization of DNA or enzymatic click functionalization of RNA
| Products & Ordering | |
| N6-Propargyl-ATP (N6pATP) CLK-NU-001 | γ-Propargyl-ATP CLK-T10 |
| γ-[(Propargyl)-imido]-ATP CLK-T11 | 2-Ethynyl-ATP (2-EATP) CLK-NU-004 |
| C8-Alkyne-dCTP CLK-T06 | C8-Alkyne-dUTP CLK-T05 |
| 5-Ethynyl-UTP (5-EUTP) CLK-T08 | 5-Ethynyl-dUTP (5-EdUTP) CLK-T07 |
| 3′-(O-Propargyl)-ATP NU-945 | 3′-(O-Propargyl)-GTP NU-946 |
| 3′-(O-Propargyl)-CTP NU-947 | 3′-(O-Propargyl)-UTP NU-948 |
| pCp-Alkyne NU-1709 |
Alkyne-containing nucleosides can be labeled with Azide-containing reporter molecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry reaction (CuAAC).
A number of cell-permeable CLICK-functionalized nucleosides are suitable for:
DNA synthesis monitoring,
RNA synthesis monitoring,
the analysis of poly A tail dynamics or
Protein synthesis monitoring.
| Products & Ordering | |
| 2-Ethynyl-adenosine CLK-N005 | 7-Deaza-7-ethynyl-2′-deoxyadenosine (EdA) CLK-099 |
| N6-Propargyl-adenosine CLK-N004 | O-Propargyl-puromycin NU-931 |
| 2-Ethynyl-Adenosine-NAD+ CLK-043 (2-EA-NAD+) | 5-Ethynyl-cytidine (5-EC) CLK-087 |
| 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxycytidine (5-EdC) CLK-N003 | 6-O-Propynyl-2′-deoxyguanosine CLK-108 (PdG) |
| 5-Ethynyl-uridine (5-EU) CLK-N002 | 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (5-EdU) CLK-N001 |
| (2’S)-2′-Deoxy-2′-fluoro-5-ethynyluridine (F-ara-EdU) CLK-1403 |
Alkyne-containing amino acids can be labeled with Azide-containing reporter molecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry reaction (CuAAC).
A number of cell-permeable Click-functionalized amino acids are randomly incorporated instead of methionine during translation and are therefore suitable for residue selective protein synthesis monitoring.
| Products & Ordering |
| L-Homopropargylglycine (L-HPG) CLK-1067 |
Alkyne Agarose is suitable to covalently capture Azide-tagged biomolecules by a Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click chemistry reaction (CuAAC). The proteins of interest need to be metabolically, enzymatically or chemically Azide-tagged. Subsequently, the Alkyne Agarose containing the covalently attached proteins can be washed with high stringency, virtually eliminating any non-specifically bound proteins.
Alkyne Magnetic Beads are suitable to covalently capture Azide-tagged biomolecules onto magnetic beads by a Cu(I)-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click chemistry reaction (CuAAC).
The proteins of interest need to be metabolically, enzymatically or chemically azide-tagged. Subsequently, the Alkyne Magnetic Beads containing the covalently attached proteins can be washed with high stringency, virtually eliminating any non-specifically bound proteins.
| Products & Ordering |
| Alkyne Magnetic Beads CLK-1035 |
| Products & Ordering |
| 5-Ethynyluracil CLK-089 |
Tetrazine-containing Click Reagents
Tetrazine-containing fluorescent dyes are suitable for fluorescent labeling of Cyclooctene-labeled molecules via Cu-free Click Chemistry. Both Standard Dyes (e.g. Cy3 or Tamra) and novel Alternative Dyes have been thoroughly selected to cover the whole UV-Vis spectrum.
Two Tetrazine versions with different reactivities and stability characteristics are available to meet specific application requirements. Tetrazine reagents are the ideal choice if a rapid reaction kinetic is the key aspect whereas 6-Methyl-Tetrazine reagents are ideally suited if an improved chemical stability is required1.
Table 1: Available Tetrazine-containing Fluorescent Dyes
| Products & Ordering | |
| 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-BDP-FL CLK-037 also known as 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-BODIPY® FL Abs/Em = 503/512 nm | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-5-FAM CLK-018 Abs/Em = 492/517 nm |
| Tetrazine-5-FAM CLK-013 Abs/Em = 492/517 nm | Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-5-FAM CLK-096 Abs/Em = 492/517 nm |
| Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-AzDye488 CLK-103 Abs/Em = 494/517 nm | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-ATTO-488 CLK-021 Abs/Em = 501/523 nm |
| 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-ATTO-488 CLK-021 Abs/Em = 501/523 nm | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-ATTO-532 CLK-022 Abs/Em = 532/553 nm |
| Tetrazine-ATTO-532 CLK-011 Abs/Em = 532/553 nm | Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-ATTO-532 CLK-105 Abs/Em = 532/553 nm |
| 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-5-TAMRA CLK-019 Abs/Em = 545/575 nm | Tetrazine-5-TAMRA CLK-017 Abs/Em = 545/575 nm |
| Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-5-TAMRA CLK-097 Abs/Em = 545/575 nm | Tetrazine-Cy3 CLK-014 Abs/Em = 550/570 nm |
| Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-Cy3 CLK-100 Abs/Em = 550/570 nm | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-Sulfo-Cy3 CLK-1018 Abs/Em = 553/566 nm |
| Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-AzDye555 CLK-098 Abs/Em = 555/572 nm | Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-ATTO-643 CLK-101 Abs/Em = 643/665 nm |
| Tetrazine-Cy5 CLK-015 Abs/Em = 649/670 nm | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-Sulfo-Cy5 CLK-1019 Abs/Em = 647/663 nm |
| 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-ATTO-647N CLK-020 Abs/Em = 644/669 nm | Tetrazine-ATTO-647N CLK-012 Abs/Em = 644/669 nm |
| Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-ATTO-647N CLK-104 Abs/Em = 644/669 nm | Pyrimidyl-Tetrazine-AzDye647 CLK-102 Abs/Em = 648/671 nm |
Selected References
[1] Karver et al. (2011) Synthesis and Evaluation of a Series of 1,2,4,5-Tetrazines for Bioorthogonal Conjugations. Am. Chem. Soc. 22:2263.
Tetrazine-containing biotinylation reagents can be used for the labeling of cyclooctene (e.g. TCO) via Cu(I)-free Click Chemistry.
Two Tetrazine versions with different reactivities and stability characteristics are available to meet specific application requirements. Tetrazine reagents are the ideal choice if a rapid reaction kinetic is the key aspect whereas 6-Methyl-Tetrazine reagents are ideally suited if an improved chemical stability is required [1]. Both biotinylation reagents contain a PEG linker for increased molecule solubility and optimal streptavidin binding.
Selected References
[1] Karver et al. (2011) Synthesis and Evaluation of a Series of 1,2,4,5-Tetrazines for Bioorthogonal Conjugations. Am. Chem. Soc. 22:2263.
Tetrazine-containing reagents are suitable for the introduction of
- a functional group (e.g. Amine or NHS Ester) to Cyclooctene-labeled molecules via Cu-free Click Chemistry
- an Tetrazine group to various targets e.g. via NHS Ester- or Maleimide-based chemistry
Two Tetrazine versions with different reactivities and stability characteristics are available to meet specific application requirements. Tetrazine reagents are the ideal choice if a rapid reaction kinetic is the key aspect whereas 6-Methyl-Tetrazine reagents are ideally suited if an improved chemical stability is required[1].
Table 1: Available Tetrazine-containing Bifunctional Reagents
| Functional Groups | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine | Tetrazine |
| NHS ester | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-PEG5-NHS ester | Tetrazine-PEG5-NHS ester |
| Azide | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-PEG4-Azide | |
| Alkyne | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-PEG5-Alkyne | Tetrazine-PEG4-Alkyne |
| DBCO | Sulfo-6-Methyl-Tetrazine-DBCO | |
| Amine (-NH2) | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-Amine | Tetrazine-Amine |
Selected References
[1] Karver et al. (2011) Synthesis and Evaluation of a Series of 1,2,4,5-Tetrazines for Bioorthogonal Conjugations. Am. Chem. Soc. 22:2263.
| Products & Ordering | ||
| 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-PEG5-NHS ester CLK-A138 | Tetrazine-PEG5-NHS ester CLK-023 | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-PEG4-Azide CLK-1014N |
| 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-PEG5-Alkyne CLK-1013 | Tetrazine-PEG4-Alkyne CLK-095 | Sulfo-6-Methyl-Tetrazine-DBCO CLK-1022 Sulfo-6-Methyl-Tetrazine-Dibenzylcyclooctyne |
| 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-Amine (Acetate) CLK-002 | 6-Methyl-Tetrazine-Amine (HCl salt) CLK-1011 | Tetrazine-Amine (HCl salt) CLK-1130 |
Tetrazine Agarose is suitable to covalently capture TCO-tagged biomolecules via Cu-free Click Chemistry. The proteins of interest need to be metabolically, enzymatically or chemically TCO-tagged.
| Products & Ordering |
| Methyl-Tetrazine Agarose CLK-1199N |
Norbornene-containing Click Reagents
| Products & Ordering |
| 3-Norbornene-L-serine CLK-109 2-amino-3-{bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl}-3-hydroxypropanoic acid |
The efficiency of a copper (Cu(I))-catalyzed Azide-Alkyne click chemistry reaction (CuAAC) strongly depends on the presence of copper ions in the +1 oxidation state (Cu(I)).
Different copper catalyst sources, reduction reagents and Cu(I) stabilizing ligands are available however, for most bioconjugation applications the combination of CuSO4 as copper catalyst source, sodium ascorbate as a reduction reagent and a water-soluble Cu(I) stabilizing ligand such as THPTA[1,2] or BTTAA[3,4] is recommended.
An optimal balance between reaction speed and Cu(I) concentration can be achieved using THPTA or BTTAA in combination with Picolyl-Azide detection reagents (Picolyl-Azides of Biotin or Picolyl-Azides of fluorescent dyes) that contain an additional internal copper chelating moiety[4].
Presolski et. al.[1] (Download pdf) and Hong et. al.[2] (Download pdf & supplemental information) provide a general protocol for CuAAC reactions that may be used as a starting point for the set up and optimization of individual assays.
Single Substances
- Copper (Cu) catalyst: CuSO4
- Reduction reagent: Sodium Ascorbate
- Cu(I) stabilizing Ligand: THPTA
- Cu(I) stabilizing Ligand: BTTAA
Reaction Kits
- CuAAC Reaction Ligand Test Kit (THPTA & BTTAA based)
- CuAAC Cell Reaction Buffer Kit (THPTA based)
- CuAAC Cell Reaction Buffer Kit (BTTAA based)
- CuAAC Biomolecule Reaction Buffer Kit (THPTA based)
- CuAAC Biomolecule Reaction Buffer Kit (BTTAA based)
- Click Chemistry Capture Kit
| Products & Ordering | |
| CuSO4 – click chemistry grade CLK-MI004 (Copper(II)-Sulphate) | Na-Ascorbate – click chemistry grade CLK-MI005 |
| THPTA CLK-1010 Tris((1-hydroxy-propyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)amine | BTTAA CLK-067 2-(4-((bis((1-(tert-butyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl)amino)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)acetic acid |
| Click Chemistry Capture Kit CLK-1065 | CuAAC Biomolecule Reaction Buffer Kit (BTTAA based) CLK-071 |
| CuAAC Biomolecule Reaction Buffer Kit (THPTA based) CLK-072 | CuAAC Cell Reaction Buffer Kit (BTTAA based) CLK-073 |
| CuAAC Cell Reaction Buffer Kit (THPTA based) CLK-074 | CuAAC Reaction Ligand Test Kit (THPTA & BTTAA based) CLK-075 |
Selected references:
[1] Presolski et al. (2011) Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry for Bioconjugation. Current Protocols in Chemical Biology 3:153.
[2] Hong et al. (2011) Analysis and Optimization of Copper-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition for Bioconjugation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48:9879.
[3] Besanceney-Webler et al. (2011) Increasing the Efficiacy of Bioorthogonal Click Reactions for Bioconjugation: A Comparative Study. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50:8051.
[4] Uttamapinant et al. (2012) Fast, Cell-Compatible Click Chemistry with Copper-Chelating Azides for Biomolecular Labeling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51:5852.
Azide-containing Click Reagents
(Picolyl-) Azides of fluorescent dyes can be used for the fluorescent labeling of terminal Alkyne and strained Alknye (e.g DBCO)-labeled molecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
Standard Dyes such as Cy3, Tamra or Texas Red have been thoroughly selected to cover the whole UV-Vis spectrum. Novel Alternative Dyes are available as well.
Table 1: Available (Picolyl-) Azide-containing Fluorescent Dyes
| Emission colour | Dye | Azide |
| blue | 3-Azido-7-hydroxycoumarin | 3-Azido-7-hydroxycoumarin |
| green | BDP-FL (also known as BODIPY® FL) | Azide – BDP-FL |
| 5-Fluorescein (5-FAM) | 5-FAM-Azide | |
| 6-Fluorescein (6-FAM) | 6-FAM-Azide | |
| 5/6-Fluorescein (5/6-FAM) | Picolyl-Azide-5/6-FAM | |
| AzDye488 | AzDye488-Azide | |
| AzDye488-Picolyl-Azide | ||
| 5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110 | 5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110-PEG3-Azide | |
| yellow- green | 5-SIMA | 5-SIMA-Azide |
| yellow | 5-TAMRA | 5-TAMRA-Azide |
| 5/6-TAMRA | 5/6-TAMRA-PEG3-Azide | |
| Picolyl-Azide-5/6-TAMRA | ||
| Cy3 | Cy3-Azide | |
| Sulfo-Cy3 | Sulfo-Cy3-Azide | |
| Picolyl-Azide-Sulfo-Cy3 | ||
| AzDye546 | AzDye546-Azide | |
| AzDye546-Picolyl-Azide | ||
| AzDye555 | AzDyeDye555-Azide | |
| AzDye555-Picolyl-Azide | ||
| orange | 5/6-Texas Red | 5/6-Texas Red-PEG3-Azide |
| AzDye594 | AzDye594-Azide | |
| AzDye594-Picolyl-Azide | ||
| red | Cy5 | Cy5-Azide |
| Sulfo-Cy5 | Sulfo-Cy5-Azide | |
| Picolyl-Azide-Sulfo-Cy5 | ||
| AzDye647 | AzDye647-Azide | |
| AzDye647-Picolyl-Azide | ||
| Cy5.5 | Cy5.5-Azide | |
| Picolyl-Azide-Cy5.5 | ||
| near-IR | Cy7 | Picolyl-Azide-Cy7 |
| Products & Ordering | |
| 3-Azido-7-hydroxycoumarin CLK-FA047 Abs/Em = 404/477 nm | Azide-BDP-FL CLK-044 Abs/Em = 503/512 nm also known as Azide-BODIPY® FL |
| 5-FAM-Azide CLK-80101 Abs/Em = 494/520 nm 5-Fluorescein-Azide | 6-FAM-Azide CLK-80105 Abs/Em = 496/516 nm 6-Fluorescein-Azide |
| Picolyl-Azide-5/6-FAM CLK-1180 Abs/Em = 490/510 nm | AzDye488-Azide CLK-1275 Abs/Em = 494/517 nm |
| AzDye488-Picolyl-Azide CLK-1276 Abs/Em = 494/517 nm | 5/6-Carboxyrhodamine 110-PEG3-Azide CLK-AZ105 Abs/Em = 501/525 nm Azide-Fluor 488 |
| 5-SIMA-Azide CLK-80103 Abs/Em = 533/557 nm | 5-TAMRA-Azide CLK-FA008 Abs/Em = 546/579 nm 5-Carboxytetramethylrhodamine-Azide |
| 5/6-TAMRA-PEG3-Azide CLK-AZ109 Abs/Em = 546/565 nm 5/6-Carboxytetramethylrhodamine-PEG3-Azide, Azide-Fluor 545 | Picolyl-Azide-5/6-TAMRA CLK-1179 Abs/Em = 553/565 nm |
| Cy3-Azide CLK-046 Abs/Em = 555/570 nm | Sulfo-Cy3-Azide CLK-AZ119 Abs/Em = 553/566 nm |
| Picolyl-Azide-Sulfo-Cy3 CLK-1178 Abs/Em = 555/565 nm | AzDye546-Azide CLK-1283 Abs/Em = 554/570 nm also known as AzDye 546-Azide |
| AzDye546-Picolyl-Azide CLK-1284 Abs/Em = 554/570 nm | AzDye555-Azide CLK-090 Abs/Em = 555/572 nm structural analog to AzDye 555 |
| AzDye555-Picolyl-Azide CLK-091 Abs/Em = 555/572 nm structural analog to AzDye 555 | 5/6-Texas Red-PEG3-Azide CLK-AZ110 Abs/Em = 584/603 nm 5/6-Sulforhodamine 101-PEG3-Azide, Azide-Fluor 585 |
| AzDye594-Azide CLK-1295 Abs/Em = 590/617 nm | AzDye594-Picolyl-Azide CLK-1296 Abs/Em = 590/617 nm also known as AzDye 594-Picolyl-Azide |
| Cy5-Azide CLK-047 Abs/Em = 646/662 nm | Sulfo-Cy5-Azide CLK-AZ118 Abs/Em = 647/663 nm |
| Picolyl-Azide-Sulfo-Cy5 CLK-1177 Abs/Em = 647/663 nm | AzDye647-Azide CLK-1299 Abs/Em = 648/671 nm structural analog to AzDye 647 |
| AzDye647-Picolyl-Azide CLK-1300 Abs/Em = 648/671 nm structural analog to AzDye 647 | Cy5.5-Azide CLK-1059 Abs/Em = 678/694 nm |
| Picolyl-Azide-Cy5.5 CLK-1182 Abs/Em = 678/694 nm | Picolyl-Azide-Cy7 CLK-1183 Abs/Em = 753/775 nm |
(Picolyl-) Azides of (desthio) biotinylation reagents can be used for the labeling of terminal Alkyne- and strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-labeled biomolecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
A number of (desthio) biotinylation reagents with
-
- different solubility characteristics (PEG-linker for increased molecule solubility)
- different cleavability characteristics (chemically or photocleavable linker)
are available to fit specific application & molecule requirements.
Table 1: Available (Picolyl) Azide-containing (Desthio) Biotinylation Reagents
| Label | (Picolyl) Azide |
| Biotin | Azide-PEG3-Biotin Biotin-Azide Picolyl-Azide-PEG4-Biotin |
| Biotin with chemically cleavable linker | Diazo Biotin-Azide Dde Biotin-Azide Disulfide Biotin-Azide DADPS Biotin-Azide |
| Biotin with photocleavable linker | Photocleavable Biotin-Azide |
| Desthiobiotin | Azide-PEG3-Desthiobiotin |
| Products & Ordering | ||
| Azide-PEG3-Biotin Conjugate CLK-AZ104P4 | Biotin-Azide CLK-1265 PEG4-carboxamide-6-azidohexanyl-Biotin | Picolyl-Azide-PEG4-Biotin CLK-1167 |
| Diazo Biotin-Azide CLK-1041 | Dde Biotin-Azide CLK-1136 | Disulfide Biotin-Azide CLK-1168 |
| DADPS Biotin-Azide CLK-1330 | Photocleavable Biotin-Azide CLK-1119 | Azide-PEG3-Desthiobiotin CLK-1107 |
Azide-containing FLAG tag reagents can be used for the introduction of a FLAG-tag to terminal Alkyne and strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-labeled biomolecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
Molecule solubility and efficient FLAG-tag detection is ensured by the integrated PEG-linker.
| Products & Ordering |
| Azide-PEG3-FLAG CLK-032 Azide-PEG3-FLAGtag (DYKDDDDK) |
Selected References
[1] Hopp et al. (1988) A Short Polypeptide Marker Sequence Useful for Recombinant Protein Identification and Purification. Bio/Technology 6:1204.
[2] Einhauer et al. (2001) The FLAG peptide, a versatile fusion tag for the purification of recombinant proteins. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 49:455.
[3] Brizzard et al. (1997) Epitope tagging of recombinant proteins. Current Protocols in Neuroscience:5.8.1.
Azide-containing bifunctional reagents are suitable for the introduction of
- a functional group to terminal Alkyne-tagged or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged molecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively
- an Azide group to various targets e.g. via NHS Ester- or Maleimide-based chemistry
Table 1: Available Azide-containing Bifunctional Reagents
| Functional Group | Azide |
| NHS ester | Azido-PEG4-NHS ester Azidoacetic Acid NHS ester |
| Maleimide | Azido-PEG3-Maleimide |
| Acid (-COOH) | Azido-PEG4-Acid |
| Amine (-NH2) | Azido-PEG3-Amine Azido-Propylamine |
TAMRA-Azide-Biotin is a trifunctional biotinylation reagent that is suitable for the simultaneous labeling of terminal Alkyne- or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO = ADIBO)-tagged biomolecules with both a Biotin and a Fluorescent moiety (Fig. 1).
The Azide moiety (1st function) enables the attachment to terminal Alkyne- or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged molecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively. The Biotin moiety (2nd function) allows the subsequent affinity purification/immobilization of the labeled molecule with Streptavidin Agarose. Optimal streptavidin binding is ensured by the introduction of hydrophilic PEG spacers that increase the water solubility and reduce steric hindrance. The carboxytetramethylrhodamine (TAMRA) fluorophore (3rd function) can be used for the sensitive detection of the immobilized protein.

Figure 1: Chemical structure of TAMRA-Azide-Biotin. 1. Azide moiety, 2. Biotin moiety, 3. TAMRA moiety.
Thymidines
Azide-containing nucleotides can be attached to terminal Alkyne- or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
enzymatic click functionalization of DNA or enzymatic click functionalization of RNA.
| Products & Ordering | |
| AzTMP NU-1601 Zidovudine monophosphate, Sodium Salt | AzTTP NU-989 Zidovudine triphosphate |
Cytidines
Azide-containing nucleotides can be attached to terminal Alkyne- or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
enzymatic click functionalization of DNA or enzymatic click functionalization of RNA.
| Products & Ordering | |
| 5-Azido-PEG4-CTP CLK-053 | 5-Azido-PEG4-dCTP CLK-070 |
| 3′-Azido-3′-dCTP NU-993 | pCp-Azide NU-1708 |
Uridines
Azide-containing nucleotides can be attached to terminal Alkyne- or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
enzymatic click functionalization of DNA or enzymatic click functionalization of RNA.
| Products & Ordering | |
| 3′-Azido-3′-dUTP NU-992 | 3′-Azido-2’,3′-ddUTP NU-251 |
| 5-Azido-PEG4-UTP CLK-054 | 5-Azido-C3-UTP NU-157 |
| 5-Azidomethyl-UTP CLK-083 | 5-Azidomethyl-dUTP CLK-084 |
| Azide-PEG4-aminoallyl-dUTP NU-1705 | |
Guanosines
Azide-containing nucleotides can be attached to terminal Alkyne- or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
enzymatic click functionalization of DNA or enzymatic click functionalization of RNA.
| Products & Ordering | |
| 3′-Azido-3′-dGTP NU-991 | 3′-Azido-2’,3′-ddGTP NU-999 |
Adenosines
Azide-containing nucleotides can be attached to terminal Alkyne- or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged biomolecules via Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
enzymatic click functionalization of DNA or enzymatic click functionalization of RNA.
| Products & Ordering | |
| 8-Azido-AMP NU-158 | 8-Azido-ADP NU-159 |
| 8-Azido-ATP NU-155 | 2′-Azido-2′-dATP NU-976 2′-Azido-dATP |
| 3′-Azido-3′-dATP NU-990 | 3′-Azido-2’,3′-ddATP NU-882 |
| γ-(2-Azidoethyl)-ATP NU-1701 | γ-(6-Azidohexyl)-ATP NU-1702 |
| γ-[(6-Azidohexyl)-imido]-ATP CLK-T12 | N6-(6-Azido)hexyl-ATP CLK-NU-003 |
| N6-(6-Azido)hexyl-dATP CLK-NU-002 | N6-(6-Azido)hexyl-3′-dATP NU-1707 (Cordycepin triphosphate derivative) |
Azide-containing nucleosides can be labeled with terminal Alkyne or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged reporter molecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Alknye-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
A number of cell-permeable CLICK-functionalized nucleosides are suitable for:
DNA synthesis monitoring,
RNA synthesis monitoring,
the analysis of poly A tail dynamics or
Protein synthesis monitoring.
| Products & Ordering | |
| 2-Azido-adenosine N-1061 | 3′-Azido-3′-deoxyadenosine CLK-094 |
| 5-Azidomethyl-uridine (5-AmU) CLK-063 | 5-Azidomethyl-2′-deoxyuridine (5-AmdU) CLK-064 |
| 5-(3-Azidopropyl)-2′-deoxyuridine CLK-034 |
Azides of amino acids can be labeled with terminal Alkyne or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged reporter molecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Alkyne-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
A number of cell-permeable Click-functionalized amino acids are randomly incorporated instead of methionine during translation and are therefore suitable for residue selective protein synthesis monitoring.
| Products & Ordering | |
| 3-Azido-D-alanine HCl CLK-AA004 (R)-2-Amino-3-azidopropanoic acid hydrochloride | 3-Azido-L-alanine HCl CLK-AA003 (S)-2-Amino-3-azidopropanoic acid hydrochloride |
| 4-Azido-D-homoalanine HCl CLK-AA006 (R)-2-Amino-4-azidobutanoic acid hydrochloride | 4-Azido-L-homoalanine HCl (L-AHA) CLK-AA005 (S)-2-Amino-4-azidobutanoic acid hydrochloride |
| 4-Azido-D-phenylalanine CLK-AA002 | 4-Azido-L-phenylalanine CLK-AA001 |
| 5-Azido-D-ornithine HCl CLK-AA008 5-Azido-D-norvaline HCl (R)-2-Amino-5-azidopentanoic acid hydrochloride | 5-Azido-L-ornithine HCl CLK-AA007 5-Azido-L-norvaline HCl (S)-2-Amino-5-azidopentanoic acid hydrochloride |
| 6-Azido-D-lysine HCl CLK-AA010 (R)-2-Amino-6-azidohexanoic acid hydrochloride | 6-Azido-L-lysine HCl CLK-AA009 (S)-2-Amino-6-azidohexanoic acid hydrochloride |
Azides of monosaccharides can be labeled with terminal Alkyne or strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged reporter molecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Alkyne-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
| Products & Ordering | |
| Ac4ManNAz CLK-1084 N-azidoacetylatedmannosamine-tetraacylated (Ac4ManAz) | Ac4GlcNAz CLK-1085 N-azidoacetylglucosamine-tetraacylated (Ac4GlcNAz) |
| Ac4GalNAz CLK-1086 N-azidoacetylgalactosamine-tetraacylated (Ac4GalNAz) | UDP-GalNAz CLK-077 UDP-N-azidoacetylgalactosamine |
| UDP-6-azide-glucose CLK-076 | 6-Azido-Trehalose CLK-078 6-TreAz |
| pLEG-Azide CLK-079 pLEG-N3 Man2NAc4NAc6-N3 | Kdo-Azide CLK-080 Kdo-N3 |
Azide Agarose is suitable to covalently capture terminal Alkyne and strained Alkyne (e.g DBCO)-tagged biomolecules via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Alkyne-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
The proteins of interest need to be metabolically, enzymatically or chemically terminal Alkyne- or DBCO-tagged. Subsequently, the Azide Agarose containing the covalently attached proteins can be washed with high stringency, virtually eliminating any non-specifically bound proteins.
Azide Magnetic Beads are suitable to covalently capture terminal Alkyne and strained Alkyne (e.g. DBCO)-tagged biomolecules onto magnetic beads by via a Cu(I)-catalyzed Alkyne-Azide (CUAAC) or Cu(I)-free strain-promoted Alkyne-Azide Click Chemistry (SPAAC) reaction, respectively.
The proteins of interest need to be metabolically, enzymatically or chemically terminal Alkyne- or DBCO-tagged. Subsequently, the Azide Magnetic Beads containing the covalently attached proteins can be washed with high stringency, virtually eliminating any non-specifically bound proteins.
| Products & Ordering |
| Azide Magnetic Beads CLK-1036 |
Selected References
Introduction to the concept of Click Chemistry
[1] Kolb et al. (2001) Click chemistry: diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40 (11):2004.
[2] Sletten et al. (2009) Bioorthogonal Chemistry: Fishing for Selectivity in a Sea of Functionality. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.48:6998.
[3] Jewett et al.(2010) Cu-free click cycloaddition reactions in chemical biology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 39 (4):1272.
[4] Best et al. (2009) Click Chemistry and Bioorthogonal Reactions: Unprecedented Selectivity in the Labeling of Biological Molecules. Biochemistry.48:6571.
[5] Lallana et al. (2011) Reliable and Efficient Procedures for the Conjugation of Biomolecules through Huisgen Azide–Alkyne Cycloadditions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50:8794.
Overview of Click Chemistry Applications
[6] Grammel et al. (2013) Chemical Reporters for biological discovery. Nature Chemical Biology 9:475.
[7] Xie et al. (2013) Cell-selective metabolic labeling of biomolecules with bioorthogonal functionalities. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 17:747.
[8] Su et al. (2013) Target identification of biologically active small molecules via in situ methods. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 17:768.
[9] Zeng et al. (2013) The Growing Impact of Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry on the Development of Radiopharmaceuticals. J Nucl Med 54:829.
[10] Evans et al. (2007) The Rise of Azide–Alkyne 1,3-Dipolar ‘Click’ Cycloaddition and its Application to Polymer Science and Surface Modification. Australian Journal of Chemistry 60 (6):384.
