Cap Analogs – Enhance mRNA stability and translation efficiency
Many eukaryotic and viral mRNAs are modified at their 5′ ends by addition of 7-Methylguanosine (N7-methyl guanosine or m7G), known as “Cap”. “Capping” of the mRNA structure plays a crucial role in a variety of cellular processes which include translation initiation[1], splicing[2], intracellular transport[3] and turnover[4].
Consistently, successful downstream application of in vitro transcribed mRNAs strongly depends on the 5′ Cap structure. Capped mRNAs are generally more efficiently translated in wheat germ and reticulocyte in vitro translation systems[5], and they are less susceptible to exonuclease degradation during microinjection experiments compared to uncapped mRNAs[6].
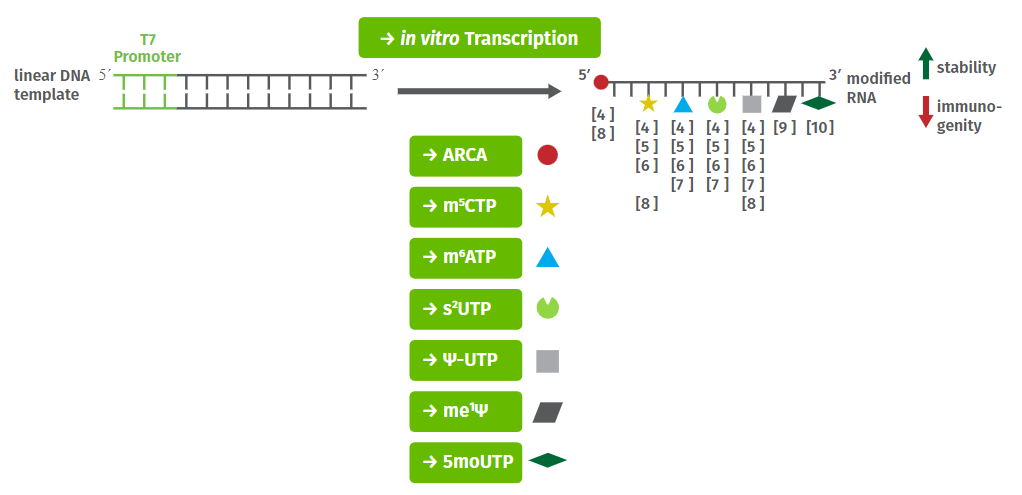
In vitro synthesis of capped mRNAs is performed by bacteriophage RNA polymerase (T7, SP6 or T3)-mediated in vitro transcription that co-transcriptionally incorporate cap analogs at the 5′-end of the transcripts (Fig. 1).
Reactions with traditional cap analogs (GpppG, m7GpppG or m2,2,7GpppG) routinely yield a mixture of mRNAs containing the cap analog incorporated both in a correct or reverse orientation[7]. Thus about 50 % of the resulting capped mRNAs are recognized by the translational machinery. Translational efficiency however, can be markedly increased by usage of the “anti-reverse” cap analog (ARCA, m7,3′-OGpppG)[8]. This is due to substitution of the 3′-OH of the m7 guanine moiety by a 3′-O-methyl group that forces ARCA incorporation in the correct orientation and subsequently results in a 100 % translatable mRNA population.