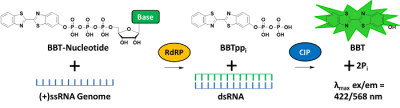
Fluorescence-Based Alkaline Phosphatase-Coupled Polymerase Assay (FAPA)
The fluorescence-based alkaline phosphatase-coupled polymerase assay (FAPA)[1] (Fig. 1) is a highly sensitive method to study the kinetic features of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRPs). It has found broad application in research on flaviviral replication such as the
- determination of kinetic replication parameters[1-3]
- identification of potential antiviral drugs[4]
under high throughput conditions. To this end, 2′-(2-benzothiazoyl)-6′-hydroxybenzothiazole-(BBT)-modified nucleotides have been proposed as well-suited fluorescent probes, combining excellent enzymatic acceptance with
- a high extinction coefficient (ε = 26,484 M-1cm-1)
- a large Stokes’ shift (λmax ex/em = 422/566 nm)
- excellent photostability