Check out Neuromics’ various categories of antibodies that target proteases. Including Presenilins, Kallikreins/KLKs, Matrix Metalloproteinases, and Capspaes and Cathepsins
Antibodies / Markers
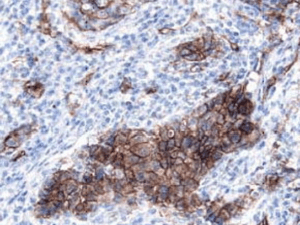
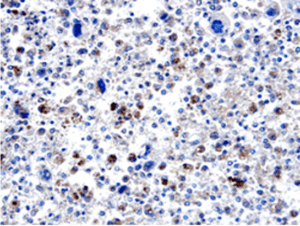
Kallikrein 6 (GT15097) satining paraffin embedded of breast cancer tissue sections Tissues were stained using anti-goat HRPDAB (brown) and counter-stained with hematoxylin (blue).
Presenilins are a family of related multi-pass transmembrane proteins that function as a part of the gamma-secretase protease complex. Presenilins undergo cleavage in an alpha helical region of one of the cytoplasmic loops to produce a larger N-terminal and a smaller C-terminal fragment which together form part of the functional protein. Cleavage of presenilin 1 can be prevented by a mutation which causes the loss of exon 9, and results in loss of function. Presenilins play a key role in the modulation of intracellular Ca2+ involved in presynaptic neurotransmitter release and long-term potentiation induction.
Dominant mutations in the genes that encode presenilin proteins are the most common cause of familial early-onset Alzheimer’s disease.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Presenilin 1 | RA18020 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IP | 200 ul |
| Presenilin 2 | RA18004 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
Kallikriens are serine proteinases. The human tissue kallikrein gene family contains 15 members that play important roles in cancer. KLK6 has been implicated in Parkison’s and Alzheimer’s and shown be elevated in animal models of multiple sclerosis. KLK8 has been shown to be elevated in the hippocampus on Alzheimer’s patients’ brains and animal models of autoimmune encephalomyelitis
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Aurora A/B/C kinase | MO22139 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Aurora B kinase | MO22138 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Kallikrein 5/KLK5/KLKL2 | RA19046 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
| KLK-3 (PSA) | RA19044 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
| KLK-L1 | RA19045 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
| KLK-L3 (KLK9) | RA19047 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
| KLK-L4 | RA19048 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
| KLK12 | RA19049 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
| KLK14 | RA19050 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
| KLK15 | RA19051 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of zinc metalloendopeptidases secreted by cells, and are responsible for much of the turnover of matrix components. They are produced as zymogens, with a signal sequence and propeptide segment that must be removed during activation. In general, This signal sequence and propeptide plus a catalytic domain (containing the highly conserved zinc binding site) characterizes the structure of the MMPs.
MMPs are considered to play an important role in wound healing, apoptosis, bone elongation, embryo development, uterine involution, angiogenesis and tissue remodeling, and in diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, malignant gliomas, lupus, arthritis, periodontis, glumerulonephritis, atherosclerosis, tissue ulceration, and in cancer cell invasion and metastasis.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| ADAM15 | RA21008 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| CKB | GT34002 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Dog | WB, E | 100 ug |
| MMP1 (Matrix Mellatopeptidase 1), N terminal region | RA21020 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| MMP2 (Matrix Mellatopeptidase 2), C terminal region | RA21021 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| MMP9 (Matrix Mellatopeptidase 9), N terminal region | RA21022 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
Caspases and Cathepsins are proteases involved in apoptosis. They also are implicated in cancer and other research areas.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| CARD8 | RA30062 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| CARD9 | RA30063 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| Caspase-14 | RA30061 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| Caspase-3 (C terminal region) | RA21011 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Caspase-3 (N terminal region) | RA21012 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| Caspase-7 | MO25036 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ul |
Ion Channels are essential to neurotransmission. Check out the various channels and associated antibodies that are essential to your research.
Potassium channels are the most diverse group of the ion channel family. They are important in shaping the action potential, and in neuronal excitability and plasticity. In addition, they regulate heart rate, insulin secretion, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume.
Changes in K+ channel function have been associated with cardiac hypertrophy and failure, apoptosis and oncogenesis, and various neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| ATPase Na+/K+ transporting alpha 1 | MO25023 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Rabbit, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, FC, IF | 50 ul |
| KChIP1 K+ channel | MO50011 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish, Xenopus | ICC, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| KChIP2b K+ channel | MO50012 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish, Xenopus | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| Kir2.1 K+ channel | MO50013 | Mouse IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB | 100 ul |
| Kir2.2 K+ channel | MO50014 | Mouse IgG | Rat | ICC, WB | 100 ul |
| Kv1.1 K+ channel | MO50015 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| Kv1.2 K+ channel | MO50016 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish, Xenopus | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| Kv1.3 K+ channel | MO50017 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| Kv1.4 K+ channel | MO50018 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| Kv2.1 K+ channel | MO50019 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| Kv3.1 K+ channel (pSer503) | RA25020 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Kv3.1b K+ channel | MO50020 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB | 100 ul |
| Kv4.2 K+ channel | MO50021 | Mouse IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| Kv7.1/KCNQ1 K+ channel | MO50022 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| TREK 1 | RA25018 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ul |
Calcium (Ca2+) Channels are important in shaping the action potential, and in neuronal excitability and plasticity. In addition, they regulate heart rate, insulin secretion, epithelial electrolyte transport, smooth muscle contraction, and cell volume.
Neuromics offers many antibodies that allow one to research the function of these channels.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Bradykinin Receptor B2 | RA14137 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| CADM1/SynCAM | RA25084 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calbindin | CH22118 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calbindin | MO20016 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| Calreticulin | MO22164 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calretinin | CH22116 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calretinin | MO20024 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Calretinin | MO22166 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calretinin (IgG1) | MO22165 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| CaMKII | RA18006 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB | 100 ul |
| CaMKII2A | GT41019 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| Cav1.2 Ca2+ channel | MO50006 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Cav1.3 Ca2+ channel | MO50007 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Cav3.1 Ca2+ channel | MO50008 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| EpCAM (Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule)/Epithelial Specific Antigen | MO47063 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| MARCKS (Myristoylated Alanine Rich C Kinase Substrate) | RA22111 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurogranin precursor | GT41024 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| phospho-Synapsin (Ser9) | RA18009 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ul |
| S-100 | MO47059 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| SHANK1a C-terminus | RA19016 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| SHANK1a N-Terminus | RA19015 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ug |
| Striatin | RA25067 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| Synapsin | RA18010 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
Ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), also referred to as ionotropic receptors or channel-linked receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion channels that are opened or closed in response to the binding of a chemical messenger, (i.e., a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| GABA A receptor alpha 4 | GT41008 | Goat IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC, E | 100 ug |
| GABA A Receptor beta 3 | GT41011 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| GABA Receptor Associated Protein | RA19014 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ug |
| GluR2/AMPA2 | RA30012 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| GluR4/AMPA4 | GT41012 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IHC, E | 100 ug |
| Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 | GT41009 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC, E | 100 ug |
| NMDA NR1 Pan | MO25041 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB | 15 ug |
| NMDA Receptor 1, N1 | RA25036 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC | 25 ug |
| NMDA Receptor 2A | RA25037 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| NMDA Receptor 2B | RA25063 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IP | 10 ug |
| P2X1 | RA10107 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, IHC | 150 ul |
| P2X1 | RA10107 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, IHC | 50 ul |
| P2X2 | RA10108 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| P2X2 | RA10108 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| P2X2 | GP14106 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| P2X2 | GP14106 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| P2X3 | RA10109 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, FC | 150 ul |
| P2X3 | RA10109 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, FC | 50 ul |
| P2X3 | GP10108 | Guinea Pig IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| P2X3-Pure | RA14139 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, FC | 100 ul |
| phospho-NMDA Receptor 1 (Ser890) | RA18011 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Phospho-NMDA Receptor 1 (Ser896) | RA18012 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ul |
Transient Receptor Potential Channels (TRP Channels) are a group of ion channels located mostly on the plasma membrane of numerous animal cell types. There are many different types of TRP Channels (TRPA, TRPV, TRPM, etc.). These channels are an important part of neurons and their function is important to understand for neuroscience.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Trp-p8 | RA19043 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ul |
| TRPA1 | RA25013 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| TRPA1 | RA14135 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| TRPC4 | MO50009 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ug |
| TRPC5 | MO50010 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| TRPC7 | GT41031 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog | WB, E, IP | 100 ug |
| TRPM2 | RA25034 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| TRPM6 (Chak2) | GP14108 | Guinea Pig IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| TRPM7 | GT41030 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ug |
| VR1 C-terminus (TRPV1) | GP14100 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| VR1 C-terminus (TRPV1) | GP14100 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| VR1 C-Terminus (TRPV1) – mouse specific | RA14113 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| VR1 C-Terminus (TRPV1) – mouse specific | RA14113 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| VR1 N-Terminus (TRPV1) | RA10110 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 150 ul |
| VR1 N-Terminus (TRPV1) | RA10110 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 50 ul |
The acid-sensing ion channel family (ASIC) comprises six discrete ASIC subunits (ASIC 1A, ASIC 1B, ASIC 2A, ASIC 2B, ASIC 3, ASIC 4) that detect tissue acidosis (i.e. a decrease in pH). This acidosis phenomenon is a response to tissue injury, pain and inflammation.
Transcription factors are proteins involved with the gene regulation, and include the distinct feature of having DNA-binding domains allowing them to bind to specific sequences of DNA. Transcription factors play a role in the expression of genes in different cell types and during development.
Our selection of transcription factor antibodies include antibodies in the follow family: FOX, HIFs, and SOX.
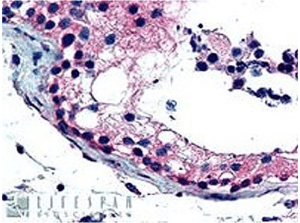
FOXE1 (dilution: 2.5µg/ml) staining of paraffin embedded Human Testis. Steamed antigen retrieval with citrate buffer pH 6, AP-staining. (GT41017)
FOX or Forkhead box Proteins are a family of transcriptional regulators that are defined by a conserved 100-amino acid DNA-binding domain. They regulate diverse cellular processes including differentiation, metabolism, development, proliferation, and apoptosis. Many are involved in embyrogensis and organogenesis. This includes the regulation of stem cells and progenitors.
The misregulation and/or mutation of FOX genes often induce human genetic diseases, promote cancer or deregulate ageing. Indeed, germinal FOX gene mutations cause diseases ranging from infertility to language and/or speech disorders and immunological defects.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| FOXC1 | GT41004 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| FOXD3 | RA25044 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| FOXE1 | GT41017 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ug |
| FOXN1 | GT41016 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ug |
| FOXP2 | GT41022 | Goat IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| FOXP3/Scurfin | GT41002 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
Hypoxia contributes significantly to the pathophysiology of major categories of human disease, including myocardial and cerebral ischemia, cancer, pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
HIFs (Hypoxia-inducible factors) respond to changes in available oxygen, especially hypoxia. They are critical for mainting oxygen homeostasis and preventing hypoxia. They are also vital to development. In mammals, deletion of the HIF-1 genes results in perinatal death. HIF-1 has been shown to be vital to chondrocyte survival, allowing the cells to adapt to low-oxygen conditions within the growth plates of bones.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Factor Inhibiting HIF-1/FIH | RA25046 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| HIF Prolyl Hydroxylase 2 | MO25046 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| HIF-1 alpha | RA25066 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Primate | WB | 100 ul |
| HIF-2 alpha Biotin | MO25044B | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| HIF-3 alpha | RA25075 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | WB | 100 ul |
The developmentally important Sox family has no singular function, and many members possess the ability to regulate several different aspects of development. While many Sox genes are involved in sex determination, some are also important in processes such as neuronal development. For example, Sox2 and Sox3 are involved in the transition between epithelial granule cells in the cerebellum to their migratory state. Granule cells then differentiate to granule neurons, with Sox11 being involved in this process. It is thought that some Sox genes may be useful in the early diagnosis of childhood brain tumours due to this sequential expression in the cerebellum, making them a target for significant research
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| SOX-10 | MO47006 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| SOX-2/SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2 | MO47038 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| SOX2 | RA25021 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| SOX6 | RA19023 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| SRY (Sex Determining Region Y)-Box 11/SOX-11 | MO47052 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factors are important in the development of cell activity.
Cell, and subcellular component markers make great tools to help identify specific cells and cellular structures. These antibodies can be used well as cellular makers. We have markers specific to dendrites, glia, neurons, synapses, oligodendrocytes and more.
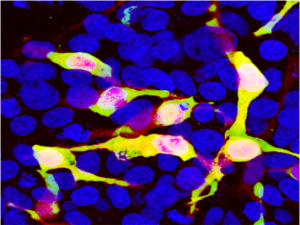
Cells which are transfected with Cherry are bright red. Staining with CH22115 is shown in Green. Green antibody staining is only seen cells which express Cherry, as expected, and the superimposition of the green and red results in an orange signal.
Specialized Stains and Markers for Cell Nuclei, Nucleolus, Membrane, Cytoplasm, RNA transcription and GFP
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| ATPase Na+/K+ transporting alpha 1 | MO25023 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Rabbit, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, FC, IF | 50 ul |
| Fibrillarin | MO22169 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 µl |
| Fibrillarin/Nop1p- Nucleolar Marker | MO22108 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IF | 500 ul |
| FluoGreen Tracer | SF41000 | Fluoro-Stain | Not Applicable | Fluoro-Imaging | 100 ul |
| GFP | GT22101 | Goat IgG | Not Applicable | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Green Fluorescent Protein | MO22184 | Mouse IgM | Not Applicable | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Green Fluorescent Protein | CH22124 | Chicken IgY | Not Applicable | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul of 1 mg/ml |
| Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) | RA22134 | Rabbit IgG | Not Applicable | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul of 1 mg/ml |
| Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) | MO22190 | Mouse IgM | Not Applicable | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) | CH23105 | Chicken IgY | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 400 ul |
| High-mobility group protein B1/HMGP1 | MO22134 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Porcine, Multiple Mammalian | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Lamin A/C | MO22124 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| mCherry | MO22192 | Mouse IgG | Not Applicable | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| mCherry – Mouse | MO22140 | Mouse IgG | Mammalian | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| mCherry-Chicken | CH22115 | Chicken IgY | Mammalian | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| mCherry-Rabbit | RA22117 | Rabbit IgG | Multiple Mammalian | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| MiTF (Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor) | MO47034 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 0.5 ml |
| Panspecific Nuclear Pore Complex Marker | MO22107 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IF | 500 ul |
| TAF15 | MO22114 | Mouse IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Tar DNA Binding Protein 43 (TDP43) | MO22117 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
CD Antibodies are commonly used as cell markers, with cells being defined based on what molecules are present on their surfaces. CD molecules can act in numerous ways including acting as receptors or ligands. CD proteins can have other functions such as cell adhesion.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| c-Kit/CD117 | RA14132 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC, FC, IF | 100 ul |
| Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) | MO47049 | Mouse IgM | Human | IHC | 0.5 ml |
| CD11b (OX-42) | CH23021 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| CD11b/c | RA25012 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, FC, IF | 100 ul |
| CD15/Leu-M1 | MO47020 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 0.5 ml |
| CD1a (Clone MT1B) | MO20005 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| CD2 (Cluster of Differentiation 2) | MO47017 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| CD34/HPCA1 | MO18004 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| CD34/HPCA1 | MO20026 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| CD36 | RA25035 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| CD39 | GP10103 | Guinea Pig IgG | Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| CD39 | GP10103 | Guinea Pig IgG | Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| CD43 (Clone MT1) | MO20006 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| CD44 Variant 3 | MO20007 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| CD44 (Cluster of Differentiation 44) | MO47055 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 0.5 ml |
| CD45 | MO18005 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 400 ul |
| CD45/LCA (Leukocyte Common Antigen) | MO47025 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| CD45R | MO47042 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| CD56/NCAM (Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule) | MO47043 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| CD57/NK1/B3GAT1 | MO47044 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 0.5 ml |
| CD71 (Cluster of Differentiation 71)/TfR1 (Transferrin Receptor Protein 1) | MO47070 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| CD9/Motility-Related Protein-1 | MO20046 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| E-Cadherin (Epithelial Cadherin)/Cadherin-1/CD324 | MO47027 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| Galectin-3 (LGAS3) | MO22119 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Galectin-3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | RA22131 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| IGF1R (Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor 1) | RA21017 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| KDR (Kinase Insert Domain Receptor) | RA21018 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| LAG3 (Lymphocyte-Activation Gene 3)/CD223 (Cluster of Differentiation 223) | MO47067 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ul |
| Lysosomal Associated Membrane Protein 1 (LAMP1) | MO22129 | Mouse IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Macrophage Scavenger Receptor I/CD204 | RA25074 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Bovine, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| OX40/CD134/TNFRSF4 | MO47051 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ul |
| PD-1 (Programmed Death 1)/CD279 (Cluster of Differentiation 279) | MO47019 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Prion Protein/CD230 | CH23027 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC | 200 ul |
| TLR6/CD286 | RA30053 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| TLR9/CD289 | RA25070 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | WB | 100 ul |
MAP2 antibodies are excellent for staining neuron perikarya and dendrites. In contrast tau is found predominantly in neuronal axons
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| MAP2 | GT22102 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| MAP2 | CH23032 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| MAP2 (Microtubule assoc. protein 2) | CH22103 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| MAP2 (Microtubule assoc. protein 2) | MO22116 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Tau | MO47000 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Tau | MO22191 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tau | CH23018 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Tau (Tau 46) | MO18002 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| Tau /MAPT+ | CH22113 | Chicken IgY | Human, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ul |
Glia, which includes astrocytes and microglia, are crucial in the development of the nervous system and processes such as synaptic plasticity and synaptogensis, and play a role in the regulation of repair of neurons after injury. Astrocytes enlarge and proliferate to form a scar and produce inhibitory molecules that inhibit regrowth of a damaged or severed axon. Microglia are are like specialized macrophages capable of phagocytosis that protect neurons of the central nervous system. They are derived from hematopoietic precursors rather than ectodermal tissue; they are commonly categorized as such because of their supportive role to neurons. These antibodies are great markers for glial-astrocytes.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Aldehyde Dehydrogenase H1L1 (ALDH1L1) | MO22155 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100ul |
| ALDH1L1 | MO22143 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| ALDH1L1 | RA22119 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Aldolase C | MO22135 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Multiple Mammalian | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Aldolase C | MO22156 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Aldolase C (C-terminus Specific) | MO22157 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| ATPase Na+/K+ transporting alpha 1 | MO25023 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Rabbit, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, FC, IF | 50 ul |
| Beta-Tubulin | MO22180 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| CD11b (OX-42) | CH23021 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| CD11b/c | RA25012 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, FC, IF | 100 ul |
| Coronin 1a/p57 | RA22108 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cat | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Coronin 1a/p57 | CH23017 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Galectin-3 (LGAS3) | MO22119 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Galectin-3 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | RA22131 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| GAP43 | MO22170 | Mouse IgM | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 µl |
| GAP43 | RA25086 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken | WB, IHC, FC | 100 ul |
| GAP43 | RA22115 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| GAP43 | MO22118 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| GAP43 (IgG) | MO22171 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 µl |
| GDNF Receptor Alpha 3 | RA30017 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| GFAP | CH22102 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| GFAP | MO22136 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Chicken, Rabbit, Bovine, Cat, Dog, Porcine, Equine | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| GFAP | RA22101 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| GFAP | MO45001 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat, Porcine | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| GFAP | CH23011 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 200 ul |
| Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) | MO22101 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| IBA1 Polyclonal Rabbit Antibody | RA22133 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| PEA-15 | MO22196 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| PEA-15 | MO22197 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| PTEN-induced kinase/PINK1 | RA19013 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| SOX-2/SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2 | MO47038 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| SRY (Sex Determining Region Y)-Box 11/SOX-11 | MO47052 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Survivin | RA19022 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ug |
| Vimentin | MO22179 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| Vimentin | GT22103 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | CH22108 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | CH23010 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | MO22115 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | RA22124 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Bovine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul of Serum |
| xCT | RA25026 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
Neural Progenitor Markers that are capable of tracking cells as they undergo expansion and differentiation from rosettes to neurons. Applications include immunostaining, immunoprecipitation, western blotting and FACs.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| α-Internexin/NF 66 | MO22102 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100ul |
| α-Internexin/NF 66 | MO22154 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| AP-2 Alpha | RA18023 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| ATPase Na+/K+ transporting alpha 1 | MO25023 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Rabbit, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, FC, IF | 50 ul |
| Doublecortin/DCX | MO22113 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| GAP43 | MO22170 | Mouse IgM | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 µl |
| GAP43 | RA25086 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken | WB, IHC, FC | 100 ul |
| GAP43 | MO22118 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| GAP43 (IgG) | MO22171 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 µl |
| Laminin | RA25038 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Laminin 111 | RA22121 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| MSX1/HOX7 | GT41015 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ug |
| Musashi-1 | RA14128 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| Nestin | MO22183 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| Nestin | CH22123 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Nestin | CH23001 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Nestin | RA22125 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Netrin-1 | CH23002 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Netrin-4 (NTN4) | RA21023 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | MO25017 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 500 ul |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | CH22101 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | FC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | RA22102 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Notch1 | RA19069 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Notch3 | RA19070 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| PAX-8 | MO47029 | Mouse IgG | WB | 100 ul | |
| PAX3 | GT41025 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| Podoplanin | MO47016 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| S-100 | MO47059 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| SOX-2/SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2 | MO47038 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| SOX2 | RA25021 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| SRY (Sex Determining Region Y)-Box 11/SOX-11 | MO47052 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Tuj 1 (Neuron-specific class III beta-tubulin) | CH23005 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | GT22103 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | CH22108 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | CH23010 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | MO22115 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | RA22124 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Bovine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul of Serum |
Antibodies that are ideal to labeling neurons and synapses.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| α-Internexin/NF 66 | MO22102 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100ul |
| α-Internexin/NF 66 | MO22154 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| 14-3-3 eta | MO22126 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Adenylate Cyclase III/ADCY3 | RA22114 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Alpha 2a Adrenergic Receptor | RA14110 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| Alpha 2a Adrenergic Receptor | RA14110 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| alpha-II-spectrin/alpha-Fodrin | MO22110 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Ankyrin 3 | RA22136 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100µL of 1 mg/mL |
| Ankyrin 3 | MO22185 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 uL |
| Ankyrin 3/Ankyrin G | CH22125 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Bovine | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul of 1 mg/ml |
| Annexin A5 | MO22200 | Mouse IgG | Human, Primate | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Annexin A5 | RA22139 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Equine | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| ANXA1 (Annexin A1) | MO47023 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| ATPase Na+/K+ transporting alpha 1 | MO25023 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Rabbit, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, FC, IF | 50 ul |
| c-Fos | MO22162 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| CADM1/SynCAM | RA25084 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calbindin | CH22118 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calbindin | MO22146 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calbindin | MO20016 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| Calbindin | MO22163 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calretinin | RA24445 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calretinin | CH22116 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calretinin | MO20024 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Calretinin | MO22166 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Calretinin (IgG1) | MO22165 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| ChAT | CH23000 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| ChAT | MO20019 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| CNP | RA22120 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| CNP/CNPase | MO22144 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| CNPase | CH23013 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| DCX/Doublecortin | CH23033 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Doublecortin/DCX | MO22113 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| FABP7 | RA22137 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul of 1 mg/ml |
| FABP7 | MO22188 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| FOX1 | MO22130 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| FOX3/NeuN | MO22122 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| FOX3/NeuN | RA22113 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| FOX3/NeuN | CH23022 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| GAD67 | CH23031 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| GAP43 | MO22170 | Mouse IgM | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 µl |
| GAP43 | RA25086 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken | WB, IHC, FC | 100 ul |
| GAP43 | RA22115 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| GAP43 | MO22118 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| GAP43 (Growth-Associated Protein, 43 kDa) | CH23004 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 200 ul |
| GAP43 (IgG) | MO22171 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 µl |
| Ki67 | MO47005 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Ki67 | RA25039 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Porcine | ICC, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| MAP2 | GT22102 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| MAP2 | CH23032 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| MAP2 (Microtubule assoc. protein 2) | CH22103 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| MAP2 (Microtubule assoc. protein 2) | MO22116 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| MARCKS (Myristoylated Alanine Rich C Kinase Substrate) | RA22111 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| MBP (Myelin Basic Protein) | RA34012 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Myelin Basic Protein | MO22121 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Myelin Basic Protein | CH22112 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) | MO22189 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) | GT22104 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | MO25017 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 500 ul |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | CH22101 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | FC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | RA22102 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-H | MO22120 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Guinea Pig, Chicken, Rabbit, Bovine, Cat, Dog, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-H | CH22104 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-H | MO22187 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| Neurofilament NF-H | MO22103 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-H | CH23015 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 200 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-H, phosphylated | RA22116 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | MO22193 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | MO22194 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | CH22105 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | MO22104 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, E | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | RA22138 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-M | CH22106 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-M | RA22105 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-M | MO22105 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-M | CH23014 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | IHC | 200 ul |
| Neuron Specific Enolase (NSE) | CH22126 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul of serum |
| Neuron Specific Enolase (NSE)/ENO2 | RA22110 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Neuron Specific Enolase (NSE)/ENO2 | CH23003 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| NMDA NR1 Pan | MO25041 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB | 15 ug |
| NMDA Receptor 1, N1 | RA25036 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC | 25 ug |
| NMDA Receptor 2A | RA25037 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| p11 (Calpactin I Light Chain / Annexin II) | CH14101 | Chicken IgY | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Parvalbumin | RA24428 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | IHC | 100 ul |
| Parvalbumin | CH22119 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Parvalbumin | MO22149 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Peripherin | MO22106 | Mouse IgG | Mouse, Rat, Cat, Porcine | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| PGP9.5 | MO20002 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| PGP9.5 | RA12103 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine | WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| PGP9.5 | RA12103 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine | WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| PGP9.5 (Clone: 31A3) | MO25010 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IHC, E | 100 ul |
| PGP9.5 175-191 | GP14104 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| PGP9.5 175-191 | GP14104 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| PGP9.5/UCHL1 | MO25040 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 500 ul |
| phospho-NMDA Receptor 1 (Ser890) | RA18011 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Phospho-NMDA Receptor 1 (Ser896) | RA18012 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ul |
| phospho-Synapsin (Ser9) | RA18009 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ul |
| phospho-Tyrosine Hydroxylase (Ser40) | RA18026 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| PLP (Proteolipid Protein) | CH23008 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| PTGDS | RA25023 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ul |
| SCP1 | RA25052 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| SCP3 | RA25051 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Secretagogin | RA22122 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Secretagogin Polyclonal Chicken Antibody | CH22121 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ug |
| SHANK1a C-terminus | RA19016 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| SHANK1a N-Terminus | RA19015 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ug |
| Splicing factor SF3B4 | MO22151 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| SPNS2 (Spingolipid Transporter 2) | MO47048 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ug |
| Survivin | RA19022 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ug |
| Synapsin | RA18010 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Synaptojanin 1 | MO25043 | Mouse IgG | Rat | ICC, WB, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| Synaptophysin | MO20000 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Synaptophysin (SYP) | RA21027 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Synaptosomal Associated Protein 25/SNAP25 | GT41027 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Dog | WB, IHC, E | 100 ug |
| Synaptosomal Associated Protein 25/SNAP25 | RA30045 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, E | 50 ug |
| Tau | MO47000 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Tau | MO22191 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tau | CH23018 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Tau (Tau 46) | MO18002 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| Tau /MAPT+ | CH22113 | Chicken IgY | Human, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Tuj 1 (Neuron-specific class III beta-tubulin) | CH23005 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | CH22122 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | MO22186 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | MO20001 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | RA21030 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | CH23006 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | RA22135 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | SO25000 | Sheep IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | MO22941 | Mouse IgM | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Ubiquilin 2 | MO22131 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Visinin-like protein 1/VSNL1 | MO22132 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Visinin-like protein 1/VSNL1 | MO22133 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cat, Porcine | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
Oligodendrocytes or oligodendroglia are cells that coat axons in the central nervous system (CNS) with their cell membrane forming a specialized membrane differentiation called myelin, producing the so-called myelin sheath. The myelin sheath provides insulation to the axon that allows electrical signals to propagate more efficiently. These antibodies work well as Oligodendrocyte, Oligodendroglial Lineage Markers.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| CNP | RA22120 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| CNP/CNPase | MO22144 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| CNPase | CH23013 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Olig1 | RA14141 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Olig2 | RA25081 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
Markers for neurons and glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Schwann cells provide myelination to axons in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). They also have phagocytotic activity and clear cellular debris that allows for regrowth of PNS neurons.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| α-Internexin/NF 66 | MO22102 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100ul |
| α-Internexin/NF 66 | MO22154 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Alpha 2a Adrenergic Receptor | RA14110 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| Alpha 2a Adrenergic Receptor | RA14110 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| Calretinin | MO20024 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| CD34/HPCA1 | MO20026 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| ChAT | CH23000 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| ChAT | MO20019 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | MO25017 | Mouse IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IF | 500 ul |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | CH22101 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | FC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament alpha-internexin/NF66 | RA22102 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-H | CH22104 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-H | MO22187 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| Neurofilament NF-H | MO22103 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-H | CH23015 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 200 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | MO22193 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | MO22194 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | CH22105 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | MO22104 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Cat | ICC, WB, IHC, E | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-L | RA22138 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-M | CH22106 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-M | MO22105 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurofilament NF-M | CH23014 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | IHC | 200 ul |
| Parvalbumin | RA24428 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | IHC | 100 ul |
| Parvalbumin | CH22119 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Parvalbumin | MO22149 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Peripherin | CH22111 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Peripherin | RA22109 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Cat | ICC, WB | 100 ul |
| Peripherin | CH23016 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | IHC | 200 ul |
| PGP9.5 | MO20002 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| PGP9.5 | RA12103 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine | WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| PGP9.5 | RA12103 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine | WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| PGP9.5 (Clone: 31A3) | MO25010 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IHC, E | 100 ul |
| PGP9.5 175-191 | GP14104 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| PGP9.5 175-191 | GP14104 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| PLP (Proteolipid Protein) | CH23008 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| PMP22 | MO25033 | Mouse IgG | Human, Primate | IHC | 100 ul |
| Po (P-Zero) | CH23009 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| TNFRSF1 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily, Member 1A), N terminal region | RA21029 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Transforming Growth Factor (TGF) beta 1, middle region | RA21028 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Vimentin | GT22103 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | CH22108 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | CH23010 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Vimentin | RA22124 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Bovine, Equine | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul of Serum |
Both growth factor and hormones are chemical messengers that play important roles in many cellular processes including growth, differentiation and signal transduction. This section includes antibodies that target growth factors and hormones including BDNFs, NGFs, FGFs, IGFs, GDNFs, VEGRs and more.
BMP-8 (GT15161) staining in paraffin-embedded human osteosarcoma tissue sections. Tissues were stained with HRP-DAB (brown) and hematoxylin (blue). Dilution-15 µg/ml.
Neurotrophin and Growth Factor Antibodies
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Angiopoietin-1 (ANG-1) | RA26000 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rabbit | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Artemin | RA19009 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ul |
| BDNF | GT41014 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ug |
| c-Kit/CD117 | RA14132 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC, FC, IF | 100 ul |
| CREB | MO18006 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, FC, IF | 100 ul |
| Cripto | RA25057 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ul |
| CYR61 | RA25061 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Enkephalin, pre-pro (ppENK) | RA14124 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| FGF-2 | MO27001 | Mouse IgM | Human | WB, E, IP | 500 ug |
| FOXD3 | RA25044 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| GATA3 | MO47046 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| GDNF Receptor Alpha 3 | RA30017 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| Her2/Neu | MO47003 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| IGF1R (Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor 1) | RA21017 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| KDR (Kinase Insert Domain Receptor) | RA21018 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Kidins220 (ARMS) | RA19019 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | WB | 100 ul |
| Notch1 | RA19069 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Notch3 | RA19070 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| PCNA | MO20014 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IHC, FC | 100 ul |
| phospho-CREB (Ser133) | RA18008 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| phospho-Kidins220 (ARMS) | RA19020 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | WB | 100 ul |
| phospho-TrkA(Tyr490) | RA18018 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| pre-pro Enkephalin | RA14142 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| PTGDS | RA25023 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ul |
| RHEB | RA30052 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| SMAD-2 | RA21025 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| SMAD3 | RA30033 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IHC, E | 50 ug |
| TGF beta | MO20012 | Mouse IgM | Human | IHC | 100 ul. |
| TGF beta RI (type1) | MO20011 | Mouse IgM | Human | IHC | 100 ul. |
| TNFRSF1 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily, Member 1A), N terminal region | RA21029 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Transforming Growth Factor (TGF) beta 1, middle region | RA21028 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| VEGF R2 (FLK1/KDR) | RA25011 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| VEGF R2 (FLK1/KDR) | RA25011 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 500 ul |
| VEGF R3 (Flt-4) | MO20013 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Wnt10a | RA30027 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| Wnt2b | RA30030 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| Wnt8a | RA30029 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
Transforming growth factor (sometimes referred to as Tumor growth factor, or TGF) is used to describe two classes of polypeptide growth factors, TGFα and TGFβ.
- TGFα is upregulated in some human cancers. It is produced in macrophages, brain cells, and keratinocytes, and induces epithelial development.
- TGFβ exists in three known subtypes in humans, TGFβ1, TGFβ2, and TGFβ3. These are upregulated in some human cancers, and play crucial roles in tissue regeneration, cell differentiation, embryonic development, and regulation of the immune system. Isoforms of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β1) are also thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia. TGFβ receptors are single pass serine/threonine kinase receptors.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Activin RIA | GT41003 | Goat IgG | Human | WB, IHC, E | 100 ug |
| TGF beta | MO20012 | Mouse IgM | Human | IHC | 100 ul. |
| TGF beta RI (type1) | MO20011 | Mouse IgM | Human | IHC | 100 ul. |
BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) and NFG (nerve growth factor) Antibodies
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| BDNF | GT41014 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ug |
Fibroblast Growth Factor Antibodies
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| FGF-2 | MO27001 | Mouse IgM | Human | WB, E, IP | 500 ug |
IGF (insulin-like growth factor) Antibodies. This superfamily of binding proteins includes the six high-affinity IGF binding proteins (IGFBP) and several low-affinity binding proteins referred to as IGFBP related proteins (IGFBP-rP)
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| IGF1R (Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor 1) | RA21017 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
VEGFs (vascular endothelial growth factor) Antibodies. VEGFs are an important growth factor for vascular endothelial cells, and their up-regulation is found in many tumors.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| KDR (Kinase Insert Domain Receptor) | RA21018 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| VEGF R2 (FLK1/KDR) | RA25011 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| VEGF R2 (FLK1/KDR) | RA25011 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 500 ul |
| VEGF R3 (Flt-4) | MO20013 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| VEGF-D | RA26005 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
There are many different types of receptors; that have many different functions. Neuromics selection of receptor antibodies includes antibodies in the following families; GABA, Leptin, NMDA, Neuropeptide, Neurotensin, Opioid, 5HT Serotonin, Purinergic, TLRs, Semaphorins, mGluRs, Trks, G-protein coupled, and iGluRs. With a wide range of families come a large range of functions. In vertebrates, GABA acts as an inhibitory synapses in the brain. Neuropeptides are neuronal signaling molecules. Chemokine receptors play roles in development, homeostasis, inflammation and infection. Opioids are important targets in pain and addiction research. 5HT Serotonin are involved in regulation of mood and appetite and have various other functions in the CNS and PNS
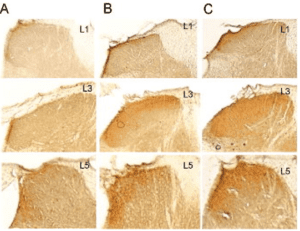
Changes in expression of μ-opioid receptor (μOR), green fluorescent protein (GFP), and overlapping μOR immunoreactivity (-ir) with GFP in L3–L5 dorsal root ganglia at 4 weeks after topical hind paw infection with herpes simplex virus encoding the gene for the μOR in antisense (SGAMOR) or sense (SGMOR) direction relative to the cytomegalovirus promoter, or the viral control encoding β-galactosidase (SGZ). Compared with control SGZ infection, infection with SGAMOR decreases the percentage of μOR-ir neurons in the L3–L5 dorsal root ganglia. In contrast, infection with SGMOR increases the percentage of μOR-ir neurons in the L3–L5 dorsal root ganglia. Full publication: doi:10.1097/01.anes.0000299836.61785.79
5-HT or 5-hydroxytryptamines(serotonins) are monoamine neurotransmitters. They originate in neurons deep in the midline of the brainstem. Because these neurons profile diffusely throughout the brain, serotonin can affect various brain functions. It also interacts with many other neurotransmitters, either directly through neurons that use both serotonin and another neurotransmitter, or by serotonin neurons influencing neurons that primarily use these other transmitters. They are involved in the regulation of mood and appetite and play a role is a variety of other functions in the CNS and PNS.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| 5-HIAA-High Titer | RA24274 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HT (Serotonin) | GT20079 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HT (Serotonin) -High Titer | RA20080 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HT (Serotonin) 1A Receptor, 5HT1A R | RA24504 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HT (Serotonin) 1E Receptor, 5HT1E R | RA30000 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| 5HT (Serotonin) 1F Receptor, 5HT1F R | RA30002 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 50 ug |
| 5HT (Serotonin) 2A Receptor, 5HT2A R | RA24288 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HT (Serotonin) 2C Receptor, 5HT2C R | RA24505 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HT (Serotonin) 5A Receptor, 5HT5A R | RA24429 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HT (Serotonin) 5A Receptor, 5HT5A R | RA30001 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 50 ug |
| 5HT (Serotonin) 7 Receptor, 5HT7 R | RA24430 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HT (Serotonin) Transporter | RA24330 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| 5HTP (5-Hydroxytryptophan) | RA24446 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
In vertebrates, GABA acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre- and postsynaptic neuronal processes. This binding causes the opening of ion channels to allow the flow of either negatively charged chloride ions into the cell or positively charged potassium ions out of the cell. This action results in a negative change in the transmembrane potential, usually causing hyperpolarization. Two general classes of GABA receptor are known: GABAA in which the receptor is part of a ligand-gated ion channel complex, and GABAB metabotropic receptors, which are G protein-coupled receptors that open or close ion channels via intermediaries (G proteins).
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| GABA A receptor alpha 4 | GT41008 | Goat IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC, E | 100 ug |
| GABA A Receptor beta 3 | GT41011 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| GABA A Receptor beta 3 | MO50001 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| GABA A Receptor, delta subunit | MO50002 | Mouse IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| GABA B Receptor1 | RA20003 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| GABA Receptor Associated Protein | RA19014 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ug |
| GAT-2 | RA24459 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
The amino-acid glutamate is the primary excitatory transmitter in the mammalian CNS. Fast excitatory actions of glutamate are mediated by ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) N-methyl-D-aspartates (NMDAs), alpha-amino-3-hydroxi-5-methyl-ioxyzole-4-propionic acid, and kainate receptors.
Leptin is produced by adipose tissue and interacts with six types of receptor (LepRa–LepRf).
The metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) are G-protein coupled receptors that bind with glutamate to activate neurotransmission. The are expressed in neurons, glia and astrocytes.
They are involved in learning, memory, anxiety, and the perception of pain. mGluRs are found in synapses of the hippocampus, cerebellum, and the cerebral cortex, as well as other parts of the brain and in peripheral tissues.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| mGluR1 | CH23023 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR1 alpha | RA19065 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR1/5 | MO50004 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rabbit | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR2 | CH23024 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR2/3 | RA13102 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR3 | CH23025 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR3 | RA13103 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR5 | CH23026 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR5 | RA16100 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| mGluR5b | RA13106 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ul |
| mGluR6 | RA13105 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| mGluR6/7 | RA25041 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC | 500 ul |
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) comprises a large and diverse group of membrane receptors for eukaryotes. This diverse cell surface receptor family play a role in a wide range of functions.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Alpha 2a Adrenergic Receptor | RA14110 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| Alpha 2a Adrenergic Receptor | RA14110 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| Alpha 2c Adrenergic Receptor | RA19064 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| Alpha 2c Adrenergic Receptor | RA19064 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| Bradykinin Receptor B2 | RA14137 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Corticotropin Releasing Hormone Receptor 1 | GT41006 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IF | 100 ug |
| Frizzled 7 | RA30031 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | IHC | 50 ug |
| Frizzled 9 | RA30032 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| GPR12 | RA30050 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| GPR49 | RA25071 | Rabbit IgG | Human | ICC, IHC, FC, IF | 100 ul |
| GPRC6A | RA30049 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| Oxytocin | RA24604 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Rhodopsin (A531) | MO22128 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Rhodopsin (B630) | MO22127 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Somatostatin Receptor-1-SSTR1 | RA25004 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Somatostatin Receptor-2-SSTR2 | RA25005 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Vasopressin V1B Receptor | GT41005 | Goat IgG | Human | WB, IHC, E | 100 ug |
| Vasopressin V1B Receptor | GT41021 | Goat IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, E | 100 ug |
The amino-acid glutamate is the primary excitatory transmitter in the mammalian CNS. Fast excitatory actions of glutamate are mediated by ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluRs) N-methyl-D-aspartates (NMDAs), alpha-amino-3-hydroxi-5-methyl-ioxyzole-4-propionic acids, and kainate receptors. Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) mediate slower glutamate responses through G-protein coupling to various intracellular signaling cascades that can modulate, or fine-tune, iGluR function.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| NMDA NR1 Pan | MO25041 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB | 15 ug |
| NMDA Receptor 1, N1 | RA25036 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC | 25 ug |
| NMDA Receptor 2A | RA25037 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| NMDA Receptor 2B | RA25063 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IP | 10 ug |
| phospho-NMDA Receptor 1 (Ser890) | RA18011 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Phospho-NMDA Receptor 1 (Ser896) | RA18012 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ul |
Neuropeptides are neuronal signaling molecules, influence the activity of the brain in specific ways and are thus involved in particular brain functions, like analgesia, reward, food intake, learning and memory
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| beta-Lipotropin | RA21003 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ul |
| CCK-8 (Cholecystokinin Octapeptide) | RA20078 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| CGRP | CH14100 | Chicken IgY | Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| CGRP | CH14100 | Chicken IgY | Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| CGRP | RA24112 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Enkephalin, pre-pro (ppENK) | RA14124 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| FMRFamide | RA20002 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| FMRFamide | RA20002 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| Leu-Enkephalin | RA21007 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Met-Enkephalin | RA21006 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Neurokinin-1 (NK 1) Receptor | RA25001 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Guinea Pig | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Neurokinin-1 (NK 1) Receptor | RA25003 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC, FC | 100 ul |
| Neurokinin-2 (NK 2) Receptor | RA30006 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| Neurokinin-3 (NK 3) Receptor | RA25002 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| Neuropeptide FF1 Receptor | RA19017 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ug |
| Neuropeptide FF2 Receptor | RA19018 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 ug |
| Neuropeptide Q/NPQ | RA14131 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Neuropeptide Q2/NPQ2 | GP14109 | Guinea Pig IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Neuropeptide Q3/NPQ3 | RA14134 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurotensin | RA21024 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Neurotensin Receptor 1 (NTS1) | CH14110 | Chicken IgY | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurotensin Receptor 1 (NTS1) | GP14020 | Guinea Pig IgG | Rat | ICC, IHC | 50 ul |
| Neurotensin Receptor 2 (NTS2) | RA17100 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| NPY | RA24603 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Guinea Pig, Chicken, Cat, Zebrafish | IHC | 100 ul |
| NPY Y1 Receptor | RA24506 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| NPY Y2 Receptor | RA14112 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| NPY Y2 Receptor | RA14112 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 50 ul |
| NPY Y2 Receptor-C/N Terminus | RA14136 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| NPY Y2 Receptor-C/N Terminus | RA14136 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| PGP9.5 | MO20002 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| PGP9.5 | RA12103 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine | WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| PGP9.5 | RA12103 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine | WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| PGP9.5 (Clone: 31A3) | MO25010 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IHC, E | 100 ul |
| PGP9.5 175-191 | GP14104 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| PGP9.5 175-191 | GP14104 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| ppNPY | GP14107 | Guinea Pig IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| ppNPY | GP14107 | Guinea Pig IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| pre-pro Enkephalin | RA14142 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| proNeurokinin B (proNKB or P2) | RA25008 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | IHC | 100 ul |
| Somatostatin Receptor-1-SSTR1 | RA25004 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Somatostatin Receptor-2-SSTR2 | RA25005 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Substance P | RA20064 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Substance P | GP14103 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| Substance P | GP14103 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| Substance P-Pure | GP14110 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| VIP | RA20077 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat, Primate, Guinea Pig | IHC | 100 ul |
Neurotensin is a 13-amino acid neuropeptide involved in neurotransmission in the CNS and PNS. The neurotensin receptors (NTS or NTSRs) are transmembrane receptors that bind neurotensin. NTSR1 and NTSR2 contain seven transmembrane helices and are G protein coupled whereas NTSR3 has a single transmembrane domain.
By selective targeting or blockade of specific neurotensin receptors, investigators have identified potential drugs for use in the treatment of schizophrenia, alcoholism, chronic pain, or cancer.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Neurotensin | RA20072 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurotensin | RA21024 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Neurotensin Receptor 1 (NTS1) | CH14110 | Chicken IgY | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurotensin Receptor 1 (NTS1) | GP14020 | Guinea Pig IgG | Rat | ICC, IHC | 50 ul |
| Neurotensin Receptor 2 (NTS2) | RA17100 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurotensin Receptor 3 (NTS3)/Sortilin | RA25040 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
Opioid Receptors are found throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems; and are often important targets in pain and addiction research.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) | RA21005 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| beta-Endorphin | RA21004 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| beta-Lipotropin | RA21003 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ul |
| Delta Opioid Receptor 3-17 | RA19072 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB | 100 ul |
| Delta Opioid Receptor 361-372 | RA19073 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Delta Opioid Receptor 358-372 | RA10101 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC | 150 ul |
| Delta Opioid Receptor 358-372 | RA10101 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | ICC | 50 ul |
| Endomorphin 1 | RA21001 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Endomorphin 1 and 2 | RA21002 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Endomorphin-2 | RA21015 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Enkephalin, pre-pro (ppENK) | RA14124 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| Kappa Opioid Receptor | RA10103T | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC | 150 ul |
| Kappa Opioid Receptor | RA10103T | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC | 50 ul |
| Leu-Enkephalin | RA21007 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Met-Enkephalin | RA21006 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| MOR-1C | RA20001 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| MOR-1C | RA20001 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| Mu Opioid Receptor | RA10104 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| Mu Opioid Receptor | RA10104 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| Mu Opioid Receptor | GP10106 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, IHC | 100 ul |
| Mu Opioid Receptor | GP10106 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, IHC | 50 ul |
| Mu Opioid Receptor | RA14138 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| OPMC-L | RA26002 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| ORL 1 | RA14133 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| ORL 1 | RA14140 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| phospho-Mu Opioid Receptor (Ser375) | RA18001 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IP | 100 ul |
| pre-pro Enkephalin | RA14124 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| proDynorphin | GP10110 | Guinea Pig IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 150 ul |
| proDynorphin | GP10110 | Guinea Pig IgG | Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ul |
| proDynorphin (GP Reactive) | GP10109 | Guinea Pig IgG | Guinea Pig | IHC | 150 ul |
| proDynorphin (GP Reactive) | GP10109 | Guinea Pig IgG | Guinea Pig | IHC | 50 ul |
Extracellular ATP interacts with specific ionotropic (P2X) or metabotropic (P2Y) membrane receptors having different molecular characteristics. Discrete cell-specific expression of various subtypes of ATP receptors allows specificity and selectivity of purinergic responses in many body organs. At single cell level, the ATP effects are susceptible to modulation by crosstalk with other receptors and by intracellular molecular pathways, allowing refinement and plasticity of cell responses. ATP and related nucleotides are now recognized key players in many tissue and cell responses during physiological states or disease conditions, like in chronic pain, inflammation, neurologic disorders and cancer. By Elsa Fabbretti, University of Nova Gorica and user of these antibodies.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| P2X1 | RA10107 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, IHC | 150 ul |
| P2X1 | RA10107 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | ICC, IHC | 50 ul |
| P2X2 | RA10108 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| P2X2 | RA10108 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| P2X2 | GP14106 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 150 ul |
| P2X2 | GP14106 | Guinea Pig IgG | Human, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC | 50 ul |
| P2X3 | RA10109 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, FC | 150 ul |
| P2X3 | RA10109 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, FC | 50 ul |
| P2X3 | GP10108 | Guinea Pig IgG | Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
| P2X3-Pure | RA14139 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, FC | 100 ul |
| P2Y2 | RA14103 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| P2YR8 | RA30005 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
Semaphorins family of cell signaling molecules have functions many different areas such as neuronal development, immunological disease, vascular development and bone disorders. Plexins serve as signal partners for some classes of semaphorins.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Semaphorin 3B | RA25088 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Bovine, Dog | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ul |
| Semaphorin 5A | GT41026 | Goat IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
Toll like receptors (TLR) are highly conserved throughout evolution and have been implicated in the innate defense to many pathogens. In mammals, TLR identified as type I transmembrane signaling receptors with pattern recognition capabilities have been implicated in the innate host defense to pathogens.
These microbial molecular markers may be composed of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and/or combinations thereof. Individual TLRs recognize distinct pathogen-associated PAMPs, initiating signaling cascades that promote the immune response. Structurally, TLRs are type I transmembrane receptors that possess varying numbers of extracellular N-terminal leucine-rich repeat (LRR) motifs, followed by a cysteine-rich region, a TM domain, and an intracellular Toll/IL-1 R (TIR) motif.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| TLR2/CD282 | RA30054 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| TLR6/CD286 | RA30053 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 50 ug |
| TLR9/CD289 | RA25070 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat, Primate | WB | 100 ul |
Trk receptors are a family of tyrosine kinases that regulates synaptic strength and plasticity in the mammalian nervous system. These can include transmission of pain, regulation of respiration and more. Trk receptors affect neuronal survival and differentiation through several signal cascades. However, the activation of these receptors also has significant effects on functional properties of neurons.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| GATA3 | MO47046 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ug |
| Her2/Neu | MO47003 | Mouse IgG | Human | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| phospho-TrkA(Tyr490) | RA18018 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Rat | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
| ROS1 (Proto-Oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase ROS) | MO47068 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC, E | 100 ul |
More antibodies including antibodies the following categories: CRISPR/Cas9, ERKs/MAPKs/SAPKs, Heat Shock Proteins, Western Blotting controls, Wnts/FZDs/DKKs, Biogenic Amines, Cytokines, and Transmitters.
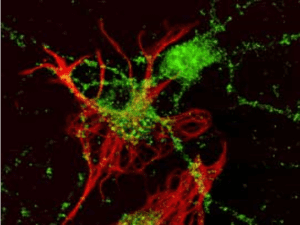
Ephrin-A2 (GT15025) staining of rat embryonic hippocampal neuron (green). Glial cells (red) were labeled by using anti-GFAP antibodies
Biogenic Amines are a large group of naturally occurring biologically active compounds, most of which act as neurotransmitters. The most dominant, norepinephrine, is involved in such physiologic functions as emotional reactions, memory, sleep, and arousal from sleep. Other biochemicals of the group include three catecholamines: histamine, serotonin, and dopamine. These substances are active in regulating blood pressure, elimination, body temperature, and many other centrally mediated body functions.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| DOPA decarboxylase | RA25065 | Mouse IgG | Rat | WB | 100 ul |
| Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase | RA24600 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| phospho-Tyrosine Hydroxylase (Ser40) | RA18026 | Rabbit IgG | Rat | WB, IHC, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | CH22122 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | MO22186 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | MO20001 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | RA21030 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 50 ug |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | CH23006 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse | ICC, WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | RA22135 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | SO25000 | Sheep IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Tyrosine Hydroxylase | MO22941 | Mouse IgM | Human, Mouse | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
Several varieties of Cas9 have been studied and there appear to be several other related enzymes with similar properties in bacteria. Two Cas9 homologs include Streptococcus pyogense and Staphylococcus aureus. Staphylococcus aureus is significantly smaller and so presents less problems when packaged into vectors. The S. pyogenes protein is rather large at 1,368 amino acids, ~160kDa, so the corresponding DNA is also rather large at about 4.2 kb.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Cas9 from S. pyogenes | RA22126 | Rabbit IgG | Not Applicable | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
| Cas9 from Staphylococcus aureus | CH22120 | Chicken IgY | Not Applicable | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Cas9 from Staphylococcus aureus | RA22127 | Rabbit IgG | Not Applicable | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Cas9 from Staphylococcus aureus | MO22175 | Mouse IgG | Not Applicable | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| Cas9 from Streptococcus pyogenes | MO22174 | Mouse IgG | Not Applicable | ICC, WB, IF | 100 ul |
Cytokines are a loose category of small secreted proteins that have an effect on the interactions and communications between cells.
ERK1 and ERK2 (also known as MAPK3 and MAPK1) are part of the Ras-Raf-ERK signal transduction cascade often found downstream of growth factor receptor activation. ERK1 and ERK2 were initially isolated and cloned as kinases activated in response to insulin and NGF. They are expressed in most, if not all, mammalian tissues.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| c-Jun | RA18019 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IHC, IP | 100 ul |
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are present in most cells, serving as molecular chaperones, and they play a role in cell protection from damage in response to stress stimuli. These capabilities make HSPs excellent for studying pathogenesis of diseases. These include autoimmmunity (inflammatory response), neurodegenerative disease, certain cancers and atherosclerosis.
Heat-shock proteins are named according to their molecular weight. For example, Hsp60, Hsp70 and Hsp90 refer to families of heat shock proteins on the order of 60, 70 and 90 kilodaltons in size, respectively.Note: The protein ubiquitin, which marks proteins for degradation, also has features of a heat shock protein.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| HSP27/HSBP1 | MO22123 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IF | 100 ul |
| HSP60 | CH22117 | Chicken IgY | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 ul |
| HSP60 (D307) | RA18029 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IHC, FC, IF | 100 ul |
| HSP60 (D85) | RA18030 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate | WB, IHC, FC, IF | 100 ul |
| HSP60 (Heat Shock Protein 60) | MO22172 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | ICC, WB, IHC, IF | 100 µl |
Neurotransmitters communication information throughout the brain. These are antibodies against neurotransmitters.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Alpha-MSH/Melanocyte-stimulating hormone | RA20074 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat, Guinea Pig | IHC | 100 ul |
| Corticotropin Releasing Hormone Receptor | RA20084 | Goat IgG | Rat | IHC, IF | 100 ug |
| Glutamine Synthetase | RA25062 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
| Goat IgG Control | GT15900 | Goat IgG | Not Applicable | All Fluorescent Images | 1 mg |
| LHRH/GnRF | RA20075 | Rabbit IgG | Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish | IHC | 100 ul |
| Neurotrypsin | RA30051 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 50 ug |
| nNOS (Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase) | RA19011 | Rabbit IgG | Human | WB | 100 uL |
| nNOS-C-terminus (Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase) | RA24287 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Primate, Guinea Pig, Cat | WB, IHC | 100 uL |
| NOS1AP/CAPON | GT41020 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC, E | 100 ug |
| PSD-95/SAP90 | MO50000 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC, IP, IF | 100 ul |
| Somatostatin | RA20067 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish, Xenopus | IHC | 100 ul |
| Vesicular Acetylcholine Transporter | GT24286 | Goat IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat | IHC | 100 ul |
These controls bind to “house keeping” protein which are generally not altered much in expression as a result of experimental manipulations. This makes them excellent the western blot standards against which the band density of other proteins can be compared.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Actin | MO22125 | Mouse IgG | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IF | 100 ug |
| GAPDH | MO25038 | Mouse IgM | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine, Porcine | WB, IHC | 100 ul |
Wnt proteins are key regulators of embryonic development. Many receptors and inhibitors influence the Wnt-signaling pathway to ultimately regulate beta-Catenin stability and availability. Understanding Wnt and beta-Catenin signaling and the role of their antagonists (including Frizzled proteins) is important to elucidating the events controlling stem cell organization and maintenance, embryonic development, tissue differentiation, cell adhesion and migration, as well as tumorigenesis and cancer induction and progression.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Dkk-1 | GT30000 | Goat IgG | Human | WB, IHC, E | 50 ug |
| Frizzled 7 | RA30031 | Rabbit IgG | Human, Mouse | IHC | 50 ug |
| Frizzled 9 | RA30032 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| Glypican-3 (GLP3) | MO47069 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| Wnt10a | RA30027 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| Wnt2b | RA30030 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| Wnt5b | RA30025 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
| Wnt8a | RA30029 | Rabbit IgG | Human | IHC | 50 ug |
DNA Mismatch Repair (MMR) is a natural system that recognizes and repairs insertion, deletions, and mis-incorporation errors that occur during DNA replication. Mutations in the DNA Mismatch Repair genes can have major implications in various cancers.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| MLH1 (MutL Homolog 1) | MO47010 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| MSH2 (MutS Homolog 2) | MO47026 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| MSH6 (MutS Homolog 6) | MO47011 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
| PMS2 (Postmeiotic Segregation Increased 2) | MO47015 | Mouse IgG | Human | IHC | 100 ul |
Secondary antibodies to help with the detection of primary antibodies.
Our secondary antibodies include CHROMEOsity anti-rabbit & anti-mouse secondaries for enhanced fluorescent detection. These antibodies have unrivaled fluorescent intensity, low background and limited photobleaching. Additionally, we offer EZ-HRP™ Polymer Detection Antibodies which enhance avidin-biotin detection when compared with conventional secondary antibodies.
U2OS cells stained with propidium iodide were incubated with rabbit anti-tubulin antibody. Chromeo 488 Goat anti-Rabbit IgG secondary antibody was then used at 1:1000
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| 488 Goat-anti-Mouse IgG | GT26000 | Goat IgG | Mouse | IHC, IF | 1 mg |
| 546 Goat-anti-Mouse IgG | GT26003 | Goat IgG | Mouse | IHC, IF | 1 mg |
| 546 Goat-anti-Rabbit IgG | GT26004 | Goat IgG | Rabbit | IHC, IF | 1 mg |
| 642 Goat-anti-Mouse IgG | GT26005 | Goat IgG | Mouse | IHC, IF | 1 mg |
| 642 Goat-anti-Rabbit IgG | GT26006 | Goat IgG | Rabbit | IHC, IF | 1 mg |
| Alkaline Phosphatase Goat Anti-Chicken IgY | CH23102 | Goat IgG | Chicken | WB, IHC, IF | 1000 ul |
| Biotinylated Goat anti-Chicken IgY | CH23103 | Goat IgG | Chicken | IHC, FC, IF | 500 ul |
| Fluorescein Goat Anti-Chicken IgY | CH23101 | Goat IgG | Chicken | IHC, IF | 500 ul |
| Goat anti-guinea pig IgG (H+L), FITC Labeled | GP40100 | Guinea Pig IgG | Guinea Pig | IHC, IF | 1.0 ml |
| Hen Blocker | CH23106 | Blocking Reagent | Chicken | ICC, WB, IHC, E, IF | 100 ml |
| Horse anti-goat IgG, Biotin | HO30002 | Goat IgG | Rabbit | IHC | 750 ug |
| Horseradish Peroxidase Goat Anti-Chicken IgY | CH23104 | Chicken IgY | Chicken | WB, IHC, IF | 400 ul |
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a state of the art technique which requires not only high-affinity primary antibodies but a robust and sensitive detection chemistry allowing to visualize low abundant protein targets. Conventional Avidin-Biotin detection is time-consuming, has a mediocre sensitivity and often results in producing a non-specific background. To overcome these drawbacks, we utilized a proprietary 3D polymerization technology and developed EZ-HRP™ Polymer Detection. This new conjugation strategy does not affect the affinity of antibodies and improves their penetration capacity into tissue sections.
Products designed to help facilitate the use of antibodies; including i-Brite – a mounting media to extending light-emitting capacity of fluorescent dyes, FluoMute – an auto fluorescence blocking agent, and blocking peptides and ELISA Buffers, ELISA Conjugate Diluents, ELISA Assay Diluents, ELISA Sample Diluents, and more.
i-BRITE Plus is a glycerol based liquid. It can be used to stain cells and can be easily added to wells. It also will not shrink tissue. In addition standard to IHC/IF applications, it can be used to visualize GFP transfections and more.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Size |
| i-BRITE Plus | SF40000-10 | Kit | Not Applicable | 10 ml |
| i-BRITE Plus | SF40000-10 | Kit | Not Applicable | 10 ml |
Autofluorescence is a major obstacle to using immunofluorescence detection in cells and tissues. There are two major sources of autofluorescence:
- Native – Caused by such substances as porphyrins, flavins, and lipofuscins
- Fixation-induced – Caused by formation of fluorescent substances as a result of interaction between aldehyde fixatives with amines
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Applications | Size |
| FluoMute | SF40005 | Blocking Reagent | Fluoro-Imaging | 100 ml |
Peptides which are comprised of the amino acid sequence specific to an antibody’s epitope that block the antibody binding. Blocking peptides are useful in determining non-specific binding.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| Activin RIA | P41003 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Alpha 2a Adrenergic Receptor | P14110 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Alpha 2c Adrenergic Receptor | P10102 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Alsin/ALS2 | P41001 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| ASIC Beta | P10101 | Peptide | Rat | IHC | 20 ug Blocking Peptide |
| BDNF | P41014 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| CADM4 | P41018 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| CCK A Receptor | P15049 | Peptide | Human, Mouse, Rat | WB, IHC | 100 ul @ 2 mgs/ml |
| CD39 Blocking Peptide | P10103 | Peptide | 20 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Corticotropin Releasing Hormone Receptor 1 | P41006 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Cripto1 | P25091 | Peptide | Human | IHC | 50 ug Blocking Peptide |
| Delta Opioid Receptor 3-17 | P10100 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Delta Opioid Receptor 361-372 | P19073 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Delta Opioid Receptor 358-372 | P10105 | Peptide | 20 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Dynactin 1 | P41007 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Endomorphin 2 | P10132 | Peptide | 20 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| FOXC1 | P41002 | Peptide | 100 ug | ||
| FOXN1 | P41016 | Peptide | 100 ug | ||
| FOXP2 | P41022 | Peptide | 100 ug | ||
| GABA A receptor alpha 4 | P41012 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| GABA A Receptor beta 3 | P41011 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Laforin | P41023 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| LepRb/OBRb | P14104 | Peptide | ICC | 100 ug Blocking Protein | |
| Macrophage Scavenger Receptor I/CD204 | P25074 | Peptide | 50 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| mGluR2/3 | P13102 | Peptide | 20 ug blocking peptide | ||
| mGluR5 | P16100 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| mGluR6 | P13105 | Peptide | 50 ul @ 2mgs/ml Blocking Peptide | ||
| Mu Opioid Receptor Blocking Peptide | P10104 | Peptide | 50 ul Blocking Peptide @ 2mgs/ml | ||
| Neurogranin precursor | P41019 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Neurotensin Receptor 1 (NTS1) | P14020 | Peptide | Rat | ICC | 100 ug Blocking Peptide |
| Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 | P41009 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| nNOS-C-terminus (Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase) | P24287 | Peptide | 50 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| NOS1AP/CAPON | P41020 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| NPY Y2 Receptor | P14112 | Peptide | 50 ul. @ 2 mgs/ml Blocking Peptide | ||
| NPY Y2 Receptor-C/N Terminus | P14136 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Olig1 | P14141 | Peptide | 100 ul @ 1mg/ml | ||
| OPA1 | P25019 | Peptide | 50 ul. Blockig Peptide | ||
| ORL 1 | P14133 | Peptide | 100 ul@1mg/ml Blocking Peptide | ||
| Orphanin FQ/Nociceptin | P10111 | Peptide | 50 ul. @ 2 mg/ml. Blocking Peptide | ||
| P2X1 | P10112 | Peptide | 20 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| P2X2 | P10109 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| P2X3 Blocking Peptide | P10108 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| P2Y2 | P10139 | Peptide | 50 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| PAX3 | P41025 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| PGP9.5 175-191 | P10135 | Peptide | 20 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| ppNPY | P10141 | Peptide | 20 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| proDynorphin | P10116 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| proDynorphin (GP Reactive) | P10115 | Peptide | 20 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Semaphorin 5A | P41026 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| SNX26 | P41013 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| SOX2 | P25021 | Peptide | 50 ul. Blocking Peptide | ||
| Substance P | P14103 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Synaptosomal Associated Protein 25/SNAP25 | P41027 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Synaptosomal Associated Protein 25/SNAP25 | P14027 | Peptide | 100 ug | ||
| TRIM2 | P41028 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| TRPM7 | P41030 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Vasopressin V1B Receptor | P41005 | Chicken IgY | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| Vasopressin V1B Receptor | P41021 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| VR1 C-terminus (TRPV1) | P14100 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| VR1 C-Terminus (TRPV1) – mouse specific | P14113 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide | ||
| VR1 N-Terminus (TRPV1) | P10110 | Peptide | 100 ug Blocking Peptide |
All blocking buffers contain proprietary additives that stabilize the antigenic and functional regions of the coated protein by maintaining the water of hydration during the drying and storage process. These buffers also contain inert additives that block any “sticky” nonspecific binding regions of the adsorbed protein, and any uncoated regions of the polystyrene plate surface. This reduces nonspecific binding of the conjugate and random deposits of sample proteins, thus reducing background noise and increasing the specific signal.
Buffers also include an antimicrobial agent to prevent bacterial growth during the blocking process (which allows blocking to be done at room temperature) and to extend the useful shelf-life of the plates.
Energize your ELISA Assays with our Buffers:
- By saving valuable reagents.
- By promoting a higher specific signal, less protein may be needed to coat the plate and less of the detection molecules may be needed to generate a signal when this buffer is used.
- By increasing the shelf-life of your plates. Depending on the activity of the coated protein, plates may be stored at RT or 2°-8°C for several months, or even years under proper conditions.
- By increasing reproducibility.
- By using consistent reagents from a reliable source, your ELISAs may become more reproducible.
- By increasing the signal of the ELISA. If the antibody or antigen is not sticking to the plate, or unwanted proteins are interfering with binding, the plate will have an overall low specific signal. CB1 may foster adsorption and reduce interference.
- By decreasing background noise. If excess proteins are sticking to the plate, plate will have overall high backgrounds (a high signal overall, but a low specific signal). CB1 may reduce interference.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| 3 Blocking Buffer Sample Pack | KF17340 | Blocking Buffer | E | 3 x 100 ml | |
| General Blocking Buffer-BB1 | KF17337 | Blocking Buffer | E | 1 L | |
| General Blocking Buffer-BB1 | KF17337 | Blocking Buffer | E | 10 L | |
| General Blocking Buffer-BB1 | KF17337 | Blocking Buffer | E | 100 ml | |
| General Blocking Buffer-BB1 | KF17337 | Blocking Buffer | E | 500 ml | |
| Neptune Blocking Buffer-BB2 | KF17338 | Blocking Buffer | E | 1 L | |
| Neptune Blocking Buffer-BB2 | KF17338 | Blocking Buffer | E | 10 L | |
| Neptune Blocking Buffer-BB2 | KF17338 | Blocking Buffer | E | 100 ml | |
| Neptune Blocking Buffer-BB2 | KF17338 | Blocking Buffer | E | 500 ml | |
| Plate Coating Buffer-CB1 | KF17336 | Coating Buffer | E | 1 L | |
| Plate Coating Buffer-CB1 | KF17336 | Coating Buffer | E | 10 L | |
| Plate Coating Buffer-CB1 | KF17336 | Coating Buffer | E | 100 ml | |
| Plate Coating Buffer-CB1 | KF17336 | Coating Buffer | E | 500 ml | |
| SynBlock Blocking Buffer-BB3 | KF17339 | Blocking Buffer | E | 1 L | |
| SynBlock Blocking Buffer-BB3 | KF17339 | Blocking Buffer | E | 10 L | |
| SynBlock Blocking Buffer-BB3 | KF17339 | Blocking Buffer | E | 100 ml | |
| SynBlock Blocking Buffer-BB3 | KF17339 | Blocking Buffer | E | 500 ml | |
| Wash Buffer | KF17356 | Wash Buffer | E | 1 L | |
| Wash Buffer | KF17356 | Wash Buffer | E | 10 L | |
| Wash Buffer | KF17356 | Wash Buffer | E | 100 ml | |
| Wash Buffer | KF17356 | Wash Buffer | E | 500 ml |
We offer a group of 6 unique stabilizing diluents designed to prolong the shelf-life of HRP-conjugated proteins and enhance their utility in ELISA applications.
These unique stabilizing buffers designed to prolong the shelf-life of HRP-conjugated proteins and enhance their utility in ELISA applications. These conjugate stabilizer diluents can be used to reconstitute lyophilized conjugates, and to dilute concentrated conjugates into the useful range of the assay.
The proprietary formulations preserve the integrity of the protein conjugate component (for example, the IgG-HRP complex) while also maintaining the enzymatic functionality of the HRP enzyme.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal -Rabbit Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD5]]> | KF17345 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 1 L | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal -Rabbit Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD5]]> | KF17345 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 10 L | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal -Rabbit Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD5]]> | KF17345 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 100 ml | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal -Rabbit Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD5]]> | KF17345 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 25 ml | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal -Rabbit Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD5]]> | KF17345 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 500 ml | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal-Goat Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD4]]> | KF17344 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 1 L | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal-Goat Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD4]]> | KF17344 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 10 L | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal-Goat Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD4]]> | KF17344 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 100 ml | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal-Goat Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD4]]> | KF17344 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 25 ml | |
| <![CDATA[Monoclonal-Goat Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD4]]> | KF17344 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 500 ml | |
| <![CDATA[Polyclonal-Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD3]]> | KF17343 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 1 L | |
| <![CDATA[Polyclonal-Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD3]]> | KF17343 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 10 L | |
| <![CDATA[Polyclonal-Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD3]]> | KF17343 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 100 ml | |
| <![CDATA[Polyclonal-Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD3]]> | KF17343 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 25 ml | |
| <![CDATA[Polyclonal-Polyclonal Conjugate Diluent & Stabilizer-CD3]]> | KF17343 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 500 ml | |
| Conjugate Stock Stabilizing Reagent -CD6 | KF17346 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 1 L | |
| Conjugate Stock Stabilizing Reagent -CD6 | KF17346 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 10 L | |
| Conjugate Stock Stabilizing Reagent -CD6 | KF17346 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 100 ml | |
| Conjugate Stock Stabilizing Reagent -CD6 | KF17346 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 25 ml | |
| Conjugate Stock Stabilizing Reagent -CD6 | KF17346 | Conjugate Diluent | E | 500 ml |
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| All Assay Diluents Sample Pack | KF17351 | Assay Diluent | E | 4X100 ml | |
| Antigen-Down Assay Diluent-AD4 | KF17350 | 1 L | |||
| Antigen-Down Assay Diluent-AD4 | 10 L | ||||
| Antigen-Down Assay Diluent-AD4 | 100 ml | ||||
| Antigen-Down Assay Diluent-AD4 | 500 ml | ||||
| General Assay Diluent-AD1 | KF17347 | 1 L | |||
| General Assay Diluent-AD1 | 10 L | ||||
| General Assay Diluent-AD1 | 100 ml | ||||
| General Assay Diluent-AD1 | 500 ml | ||||
| IgM Reducing Assay Diluent-AD2 | KF17348 | 1 L | |||
| IgM Reducing Assay Diluent-AD2 | 10 L | ||||
| IgM Reducing Assay Diluent-AD2 | 100 ml | ||||
| IgM Reducing Assay Diluent-AD2 | 500 ml | ||||
| Neptune Assay Diluent-AD3 | KF17349 | 1 L | |||
| Neptune Assay Diluent-AD3 | 10 L | ||||
| Neptune Assay Diluent-AD3 | 100 ml | ||||
| Neptune Assay Diluent-AD3 | 500 ml |
These sample diluents can be used to titrate rabbit, mouse, goat, and chicken serum samples, along with monoclonal cell culture supernatants. Antigen samples may also be diluted with sample diluents for evaluation in sandwich ELISA formats.
| Name | Catalog # | Type | Species | Applications | Size |
| All Sample Diluents Sample Pack | KF17355 | Sample Diluent | E | 3X100 ml | |
| General Purpose Sample Diluent-SD1 | KF17352 | Sample Diluent | E | 1 L | |
| General Purpose Sample Diluent-SD1 | Sample Diluent | E | 10 L | ||
| General Purpose Sample Diluent-SD1 | Sample Diluent | E | 100 ml | ||
| General Purpose Sample Diluent-SD1 | Sample Diluent | E | 500 ml | ||
| Neptune Sample Diluent-SD3 | KF17354 | Sample Diluent | 1 L | ||
| Neptune Sample Diluent-SD3 | Sample Diluent | 10 L | |||
| Neptune Sample Diluent-SD3 | Sample Diluent | 100 ml | |||
| Neptune Sample Diluent-SD3 | Sample Diluent | 500 ml | |||
| Plasma Sample Diluent (Antigen-Down)-SD2 | KF17353 | Sample Diluent | 1 L | ||
| Plasma Sample Diluent (Antigen-Down)-SD2 | Sample Diluent | 10 L | |||
| Plasma Sample Diluent (Antigen-Down)-SD2 | Sample Diluent | 100 ml | |||
| Plasma Sample Diluent (Antigen-Down)-SD2 | Sample Diluent | 500 ml |