Direct and Indirect Western blotting
 Western blotting is a robust technique employing antibodies to detect proteins immobilized on a blotting membrane after separation by electrophoresis. The technique can be performed either directly or indirectly. Each method can offer advantages depending on the experimental requirements.
Western blotting is a robust technique employing antibodies to detect proteins immobilized on a blotting membrane after separation by electrophoresis. The technique can be performed either directly or indirectly. Each method can offer advantages depending on the experimental requirements.
Once proteins have been separated by gel electrophoresis and transferred onto a blotting membrane, Western blotting can be performed in either one or two steps.
Direct – One step method
In the direct detection method (Figure 1 (A)), a primary antibody directly conjugated to a reporter enzyme or fluorescent dye is used to detect the protein antigen on the blotting membrane after a single incubation step. Although this one step method is quicker, it is not widely used. Figure 1(B) illustrates one of the problems of directly conjugating the primary antibody, whereby the reporter molecule can occlude the antigen binding region of the primary antibody, preventing good recognition of the antigen and leading to reduced sensitivity. Excess primary may compensate for this effect but may lead to poor reproducibility and increased background.
Indirect – Two step method
The two step, indirect detection method of Western blotting avoids such interference with antigen detection. An unlabeled primary antibody forms a complex with the antigen bound to the blot membrane. After washing, the blot is incubated with a secondary antibody conjugated with the reporter enzyme or fluorophore. Multiple secondary antibodies bind to epitopes on the primary antibody, creating a labeled antigen-antibody complex (Figure 1(C)). Although the indirect method requires one more wash and incubation step, it presents numerous advantages over the direct method, including amplification of signal and flexibility.
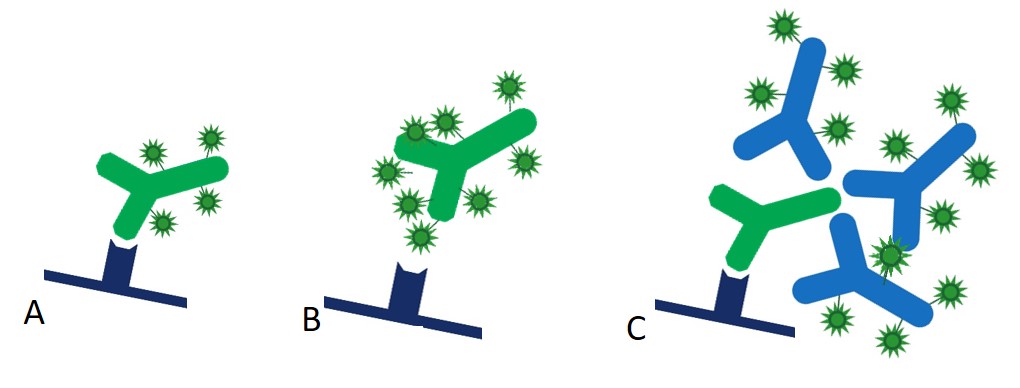
Figure 1: (A) Directly conjugated primary antibody binds antigen bound to membrane. (B) Directly conjugated primary antibody binds poorly to antigen bound to membrane, since reporter enzyme or fluorophore can conjugate into antigen-binding region and reduce affinity of the antibody for its target. Using a secondary eliminates this. (C) Indirect method – multiple conjugated secondary antibodies bind to an unconjugated primary antibody.
The advantages and disadvantages of the direct and indirect detection methods are detailed in the table below. They apply to Western blotting but may also be relevant to other techniques, such as IHC/ICC, ELISA and Flow Cytometry.
Table 1: Advantages and disadvantages of direct and indirect Western blotting methods.
| Direct Detection Method | Indirect detection method | |||
| Disadvantages | Advantages | Disadvantages | Advantages | |
| Time | Labeling individual primary antibodies is time-consuming. | One incubation step means that direct detection methods can be rapid. | The addition of the secondary antibody incurs extra steps. | Many reliable commercially available labeled secondaries reduce time consuming optimization steps. |
| Flexibility and availability | The number of conjugated primary antibodies is limited. | Secondary antibodies offer a wide range of conjugate options and antibody specificities. | ||
| Sensitivity | The signal from direct method may appear weaker than indirect method. | Signal amplification – each primary antibody can accommodate multiple secondary antibodies, increasing the number of molecules available to produce signal. | ||
| Immunoreactivity | Primary antibodies may have reduced immunoreactivity due to conjugate interference with antigen binding. | Immunoreactivity of the primary antibody is preserved, and signal is provided by the conjugated secondary. | ||
| Cost | Conjugated primary antibodies may be expensive, and more antibody may be required to counteract loss of sensitivity. | One secondary antibody can be used to detect any primary antibody raised in the same host species, reducing cost. | ||
| Signal enhancement options | Sample concentration may be required for low abundance proteins prior to loading. | Secondary antibodies can be used to enhance signal in numerous ways. | ||