Everything you need for microRNA research
Integrated solutions for microRNA analysis
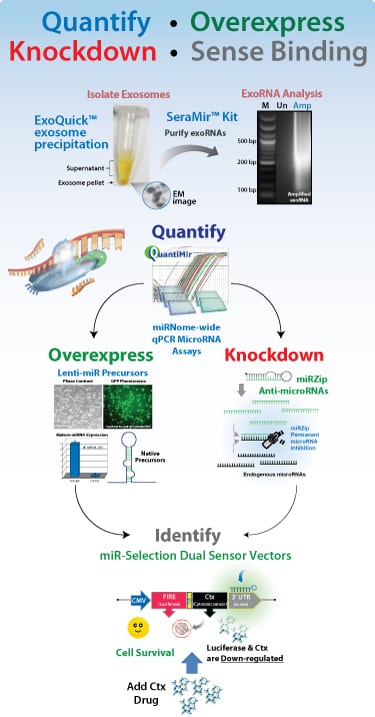
SBI has developed innovative technologies and tools for qPCR Expression profiling, Cloning, Overexpression and Knockdown of microRNAs as well as 3’UTR identification systems to enhance your research discoveries.
MicroRNA functional analysis
- Isolate from exosomes
- Profile by qPCR
- Overexpress
- Knockdown
Profiling and Cloning
Overexpression
Knockdown
3’UTR Target Identification
|
 |
Small RNAs with very large impacts
MicroRNAs are a class of naturally-occurring, small non-coding RNAs that control gene expression by translational repression or mRNA degradation; they are widely expressed throughout the plant and animal kingdoms and may comprise 1-5% of animal genes. Since the discovery of lin-4 and let-7 in Caenorhabditis elegans, over six thousand microRNAs have been identified through genomic and bioinformatic approaches. Like protein-coding genes, microRNAs are transcribed in the nucleus as long primary transcripts (pri-microRNAs). However, distinct from protein-coding genes, they are subsequently cleaved by the nuclear RNase III enzyme Drosha to produce structured, stem-loop precursor molecules (pre-microRNAs) of 70-100 nucleotides (nt) in length. The pre-microRNAs are then exported to the cytoplasm in a process involving exportin-5, where the RNase III enzyme Dicer further processes them into mature microRNAs (~22 nt). One strand of the microRNA duplex is subsequently incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) that regulates target gene expression. Although the mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene silencing are not yet fully understood, evidence indicates that targeted mRNAs may be translationally repressed or de-adenylated and turned over, a process termed target mRNA decay.