The newly identified coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV), has led to pneumonia (COVID-19) that sickened over 240,000 people worldwide. SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the Betacoronavirus Genus, which also includes SARS CoV (2003) and MERS CoV (2012). Same as all other coronaviruses, the genome of SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) encodes the spike protein, the envelope protein, the membrane protein, and the nucleocapsid protein.
The spike protein (S-protein) mediates receptor binding and membrane fusion. Spike protein contains two subunits, S1 and S2. S1 contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which is responsible for recognizing and binding with the cell surface receptor. S2 subunit is the “stem” of the structure, which contains other basic elements needed for the membrane fusion. The spike protein is the common target for neutralizing antibodies and vaccines. It’s been reported that SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) (ref.) can infect the human respiratory epithelial cells through interaction with the human ACE2 receptor. Indeed, the recombinant Spike protein can bind with recombinant ACE2 protein.
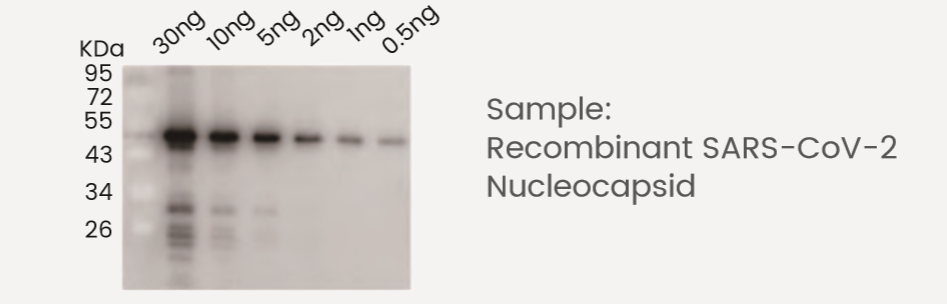
The Nucleocapsid Protein (N-protein) is the most abundant protein in coronavirus. The N-protein is a highly immunogenic phosphoprotein, and it is normally very conserved. The N protein of coronavirus is often used as a marker in diagnostic assays.
To aid the efforts of developing vaccines and neutralizing antibodies against this virus, Sino Biological Inc. has developed a panel of research reagents for SARS-CoV-2, including recombinant antigens (the N protein, S protein, the S1 and S2 subunits of the S protein, and the RBD domain of the S proteins), antibodies, antigen detection kits and genes.
Sino Biological COVID-19
Research Solutions for Coronavirus – Sino Biological
SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Detection Kits, Antibodies and Proteins
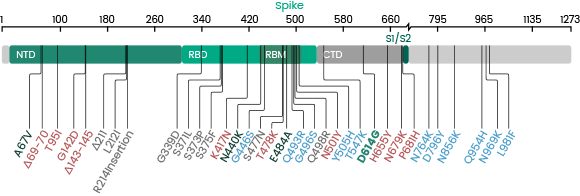
200+ SARS-CoV-2 Variants
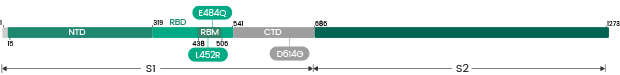
Several new variants of SARS-CoV-2 virus have emerged in recent months. The U.K. variant B.1.1.7, the Brazil variant P.1, the South Africa variant B.1.351, and the most recent Indian variant B.1.617 are particular concerning because of their high prevalence. A subset of the mutations identified in the RBD domain of the spike protein occurs in more than one strain. These convergent mutations are of high interest because they may be the cause of the increased transmissibility. Sino Biological has launched RBD and Spike proteins of these variants.
The mutations in these strains also occur in the nucleocapsid protein, which is commonly used as the biomarker in rapid antigen tests. It’s critical to assess whether the current commercial antigen tests can detect the mutated N proteins with the same sensitivity and specificity as their WT counterpart.
By monitoring the evolution of SARS-CoV-2, WHO has published these Variants of Concern (VOCs) to accelerate the globe to make quick response to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
Characteristics of VOCs can be:
• Increase in transmissibility or detrimental change in COVID-19 epidemiology
• Increase in virulence or change in clinical disease presentation
• Decrease in effectiveness of public health and social measures or available diagnostics, vaccines, therapeutics
Browse full list of variants
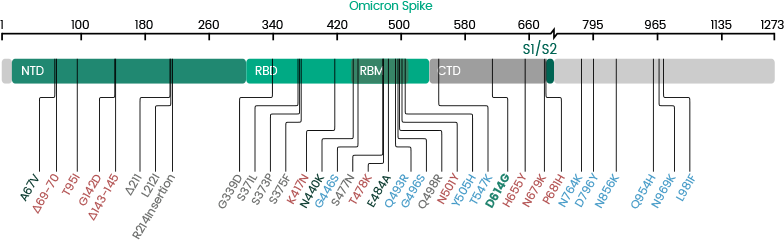
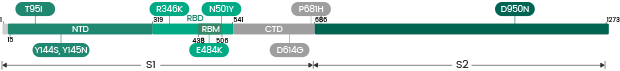
Mutations in the Spike Glycoprotein of Omicron
The Omicron variant is by far the most divergent variant characterized by a high number of mutations in the spike protein. Several mutations (e.g., N501Y, P681H) have been identified in previous variants and are associated with increased transmissibility, immune escape, or other properties.
- 30 amino acid changes: among which 15 are located in the RBD region
- Three deletions
- Three insertions in the spike protein NTD
Sino Biological has developed a panel of recombinant RBD/Spike and nucleocapsid protein variants which can be used to evaluate the efficacy of the antibodies and vaccination.
Recombinant Mutants from the Omicron Variant | B.1.1.529
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40589-V08H26 | S-ECD | A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40589-V08B33 | S-ECD | A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40592-V49H7 | RBD | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| 40589-V49H3-B | S-ECD | A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40592-V08H121 | RBD | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| 40592-V49H7-B | RBD | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| 40591-V08H41 | S1 | A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H |
| 40588-V07E34 | N | P13L, E31del, R32del, S33del, R203K, G204R |
Recombinant Mutants from the Indian Variant | B.1.617
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40588-V07E20 | N | R203M, D377Y |
| 40588-V07E29 | N | D63G, R203M, D377Y |
| 40592-V08H91 | RBD | T478K |
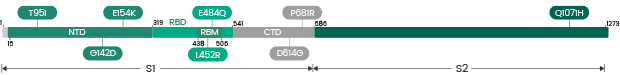
| 40589-V08B12 | S1+S2 | E154K, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, E1072K, K1073R |
| 40592-V02H3 | RBD | L452R, T478K |
| 40592-V08H88 | RBD | L452R,E484Q |
| 40592-V08H28 | RBD | L452R |
| 40591-V08H19 | S1 | D614G, E154K, E484Q, L452R, P681R |
| 40592-V08H81 | RBD | E484Q |
| 40588-V07E16 | N | D377Y |
other tags available His & AVI – please inquire
Recombinant Mutants from the U.K. Variant | B.1.1.7
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40592-V08H82 | RBD | N501Y |
| 40592-V08H82-B | RBD-Biotinylated | N501Y |
| 40591-V08H7 | S1 | HV69-70 deletion, N501Y, D614G |
| 40591-V08H12 | S1 | H69del, V70del, Y144del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H |
| 40588-V07E7 | N | D3L, R203K, G204R, S235F |
| 40588-V07E8 | N | D3L, S235F |
| 40589-V08B6 | S-ECD | H69del, V70del, Y144del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H |
Recombinant Mutants from the South Africa Variant | B.1.351
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40592-V08H82 | RBD | N501Y |
| 40592-V08H84 | RBD | E484K |
| 40592-V08H59 | RBD | K417N |
| 40592-V08H85 | RBD | K417N, E484K, N501Y |
| 40591-V08H10 | S1 | K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G |
Recombinant Mutants from the Brazil Variant | P.1
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40592-V08H82 | RBD | N501Y |
| 40592-V08H84 | RBD | E484K |
| 40592-V08H86 | RBD | K417T, E484K, N501Y |
Recombinant Mutants from the Denmark Mink Variant
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40592-V08H80 | RBD | Y453F |
| 40591-V08H8 | S1 | ΔH69/ΔV70, Y453F, D614G |
| 40592-V08H86 | RBD | K417T, E484K, N501Y |
High Frequency Mutation of Nucleocapsid
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40588-V07E1 | N | R203K, G204R |
| 40588-V07E2 | N | P13L |
| 40588-V07E3 | N | S194L |
| 40588-V07E4 | N | I292T |
Conserved Domain of Nucleocapsid from SARS-CoV-2
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40588-V07E5 | N-CTD | CTD |
| 40588-V07E10 | N-NTD | NTD |
SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Mutant |
||
| P13L 40588-V07E2 |
S194L 40588-V07E3 |
R203K, G204R 40588-V07E1 |
| I292T 40588-V07E4 |
D3L, R203K, G204R, S235F 40588-V07E7 |
D3L, S235F 40588-V07E8 |
SARS-CoV-2 S1+S2 ECD Mutant |
|
| HV69-70 deletion, D614G, D796H 40589-V08B5 |
HV69-70 deletion, Y144 deletion, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H 40589-V08B6 |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Mutant |
|||||
| P337S | F338L | V341I | F342L | A344S | A348S |
| A352S | N354D | S359N | V367F | (mFc Tag) V367F | N370S |
| A372S | A372T | F377L | K378N | K378R | P384L |
| T385A | T393P | V395I | D405V, Q414A | E406Q | |
| R408I | Q409E | Q414R | Q414E | K417N | A435S |
| W436R | N439K | N440K | K444R | V445F | G446V |
| G446S | L452R | Y453F | L455F | F456L | F456E |
| K458R | K458Q | E471Q | I472V | G476S | S477R |
| S477I | S477N | T478I | P479S | N481D | G482S |
| V483A | V483I | E484K | E484Q | G485S | F486S |
| N487R | F490L | F490S | S494P | P499R | N501Y |
| V503F | Y505C | Y508H | A520V | A520S | P521S |
| P521R | A522V | A522S | K417N, E484K, N501Y 40592-V08H85 |
K417T, E484K, N501Y 40592-V08H86 |
|
|
SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Mutant |
||
| HV69-70 deletion, Y144 deletion, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H 40591-V08H12 |
||
| HV69-70 deletion, Y453F, D614G 40591-V08H8 |
HV69-70 deletion, N501Y, D614G 40591-V08H7 |
L18F, D614G 40591-V08H6 |
| T20N, D614G 40591-V08H5 |
A222V, D614G 40591-V08H4 |
N234Q 40591-V08H11 |
| K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G 40591-V08H10 |
D614G 40591-V08H3 |
D614G 40591-V02H3 |
| HV69-70 deletion, N439K, D614G 40591-V08H9 |
E780Q 40590-V02H1 |
|
|
SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1+S2 ECD Mutant |
||
| R683A, R685A, F817P, A892P, A899P, A942P, K986P, V987P 40589-V08H4 |
Resource for Studying the U.K. Variant
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutation |
| 40592-V08H82 | RBD | N501Y |
| 40591-V08H7 | S1 | HV69-70 deletion, N501Y, D614G |
| 40591-V08H12 | S1 | H69del, V70del, Y144del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H |
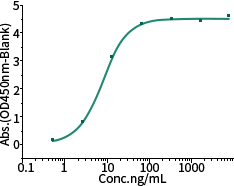
Recombinant Spike N501Y Mutant
Cat#: 40592-V08H82
Activity: Bind with ACE2
The spike protein of the Omicron Variant carries more than 30 mutations. It’s critically important to understand whether these mutations allow the Omicron variant to escape from neutralizing antibodies.
Mutations in the spike glycoprotein of Omicron
Source: Stanford University Coronavirus Database
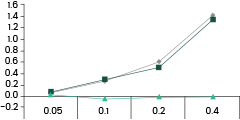
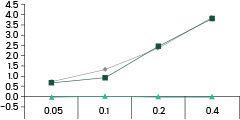
After screening a panel of previously established spike antibodies, we identified one mAb, clone 40592-MM117, strongly reactive with the Omicron Spike protein. There is another antibody that demonstrates moderate reactivity against the Omicron variant. All other tested clones, including several broad-spectrum ACE2-competing neutralizing antibodies, don’t bind with the mutant at all.
It’s noteworthy that clone 40592-MM117 has non-ACE2 competing neutralizing activity against both the original strain and the Delta variant. Interestingly, the other mAb tested reactive to Omicron also has non-ace2 binding neutralizing activity against previous strains. Whether the same clones can also neutralize the Omicron variant is currently being tested.
Sino Biological has developed recombinant Omicron Spike RBD Protein and Antibody reacting with Omicron to support the study of Omicron variant. More Omicron antigens, including B.1.1.529 S-ECD, S1, and Nucleocapsid, are coming soon.
| Omicron Spike Antibody is Available |
| SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody, Omicron Reactive, Mouse MAb | Cat: 40592-MM117 |
Data illustration of Antibodies and Omicron Mutants
Omicron Spike Antibody
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody, Omicron Reactive, Mouse MAb
Cat: 40592-MM117
• Ability to Recognize Omicron Spike Protein
40592-MM117 showed strong reactivity with Omicron spike protein.
| Cat# | ACE2 Competing | Neutralizing Activity | WT | Delta | Omicron |
| 40592-MM117 | |||||
| 40592-R505 | |||||
| 40150-D001 | |||||
| 40591-MM43 | |||||
| Broad-spectrum neutralization ab 1 | |||||
| Broad-spectrum neutralization ab 2 | |||||
| Broad-spectrum neutralization ab 3 | |||||
| Broad-spectrum neutralization ab 4 |
• Binding Activity by ELISA Assay against SARS-CoV-2 Variants
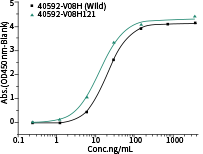
40592-MM117 shows binding activity against spike proteins of the Omicron variant. It also detects the wild type and Delta variants. In comparison, the other two broad-spectrum ACE2-competing neutralizing antibodies, 40591-MM43 and 40150-D001, do not bind with the Omicron variant.
Recombinant Omicron Mutants
SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) Spike RBD Protein (His Tag)
Cat: 40592-V08H121
• Mutations in RBD Region:
G339D、S371L、S373P、S375F、K417N、N440K、G446S、S477N、T478K、E484A、Q493R、G496S、Q498R、N501Y、Y505H
• More Omicron Variants is Developing by Sino Biological.
Please Contact Us for More Detailed Information.
| Cat# | Antigen | Tag | Expressed Host | Mutants |
| 40589-V08H26 NEW |
S-ECD Trimer | C-His | HEK293 | A67V, H69del, V70del, T95I, G142D, V143del, Y144del, Y145del, N211del, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40591-V08H41 NEW |
S1 | C-His | HEK293 | A67V, H69del, V70del, T95I, G142D, V143del, Y144del, Y145del, N211del, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H |
| 40592-V49H7-B Biotinylated NEW |
RBD | C-His-AVI | HEK293 | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| 40589-V08B33 (pre-order) |
S-ECD | C-His | Insect | A67V, H69del, V70del, T95I, G142D, V143del, Y144del, Y145del, N211del, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40589-V49H3-B Biotinylated (pre-order) |
S-ECD Trimer | C-His-AVI | HEK293 | A67V, H69del, V70del, T95I, G142D, V143del, Y144del, Y145del, N211del, L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40592-V49H7 (pre-order) |
RBD | C-His-AVI | HEK293 | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| 40588-V07E34 (pre-order) |
N | N-His | E.coli | P13L, E31del, R32del, S33del, R203K, G204R |
Since the COVID-19 outbreak, Sino Biological has been actively tracking the status of the virus to make products “up to date”. We have established the largest bank of recombinant mutant proteins of spike protein, its segments (e.g., S1, RBD, S2), and nucleocapsid. We are also continuously developing specific antibodies to these mutants, neutralizing antibodies, and monoclonal antibody pairs for antigen detection.
Antibodies for the Detection of Nucleocapsid Mutants
Sino Biological has newly developed a series of antibodies that can detect nucleocapsid mutants found in Variants of Interest (VOIs) and Variants of Concern (VOCs).
Binding Activity by ELISA Assay (Partial List)
 |
40588-MM123 | 40143-MM08 | 40588-MM137 | 40143-R004 | 40588-R001 | Antigen Mutation Description |
| 40588-V07E | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | Wild Type |
| 40588-V07E1 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | N (R203K, G204R), discovered in many lineages |
| 40588-V07E2 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | N (P13L), discovered in many lineages |
| 40588-V07E3 | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | N (S194L), discovered in many lineages |
| 40588-V07E4 | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | N (I292T), discovered in many lineages |
| 40588-V07E7 | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | N (D3L, R203K, G204R, S235F), found in B.1.1.7 |
| 40588-V07E8 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | +++ | N (D3L, S235F), found in B.1.1.7 |
| 40588-V07E9 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | N (T205I), found in B.1.351 |
| 40588-V07E11 | +++ | +++ | ++ | ++++ | +++ | N (P80R), found in P.1 |
| 40588-V07E19 | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | +++ | N (A12G, T205I), found in the B.1.429 & B.1.351 |
| 40588-V07E16 | +++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | N (D377Y), found in B.1.617 |
| 40588-V07E20 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | N (R203M, D377Y), found in B.1.617, B.1.617.1 |
| 40588-V07E29 | ++++ | ++++ | +++ | ++++ | ++++ | N (D63G, R203M, D377Y), found in B.1.617.2 |
| 40588-V07E30 | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | ++++ | N (P67S, R203M, D377Y), found in B.1.617.3 |
+: Binding Capacity
Please kindly contact us for more antibodies.
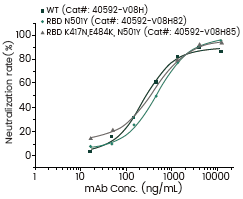
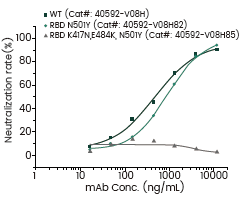
Neutralization Efficacy Assay aganist SARS-CoV-2 Variants
Some of the above mutations may have allowed the virus to escape from neutralizing antibodies. To characterize these variants, a new panel of monoclonal antibodies have been launched this month. These antibodies demonstrate differential neutralizing activities against different variants validated by Competitive ELISA Assay. Notably, the B.1.351 and P.1 variants seem to be immune to a subset of the antibodies.
| Neutralizing Antibodies | WT RBD | Recombinant RBD |
Recombinant S1 |
||||
| B.1.1.7 | B.1.351 | P.1 | B.1.617 | B.1.617 | B.1.429 | ||
| 40150-D001 | ++ | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| 40150-D002 | ++ | + | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| 40591-MM43 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| 40592-MM57 | + | + | – | – | + | + | + |
| 40592-R001 | +++ | +++ | – | – | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| 40592-R118 | +++ | +++ | – | – | + | + | + |
| 40592-R117 | +++ | +++ | – | – | +++ | +++ | +++ |
+: Neutralizing Capacity
The Aforementioned Recombinant RBD :
WT: 40592-V08B
B.1.1.7 | U.K. Variant: 40592-V08H82 (N501Y)
B.1.351 | South Africa Variant: 40592-V08H85 (K417N, E484K, N501Y)
P.1 | Brazil Variant: 40592-V08H86 (K417T, E484K, N501Y)
B.1.617 | India Variant: 40592-V08H88 (L452R, E484Q)
The Aforementioned Recombinant S1 :
B.1.617 | India Variant: 40591-V08H19 (E154K, E484Q, L452R, D614G, P681R)
B.1.429 | California Variant: 40591-V08H17 (W152C, L452R, D614G)
SARS-CoV-2 Antigens
All coronaviruses share very similar structures.
The viral genome encodes several proteins of unique functions, S protein
N protein
HE protein
papain-like proteases
M protein.
The two antigens of main pharmaceutical interest are the S (spike) protein and the N protein.
- The N (nucleocapsid) protein is often conserved, which can be used as a diagnostic marker.
- The Spike protein is mainly responsible for receptor binding, and is a common target for vaccines and antibodies. The size of the abundantly N-glycosylated S protein varies greatly between CoV species
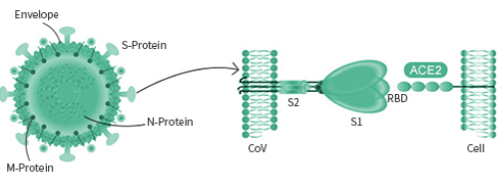
The spike protein is particularly important as its interaction with the host cell receptor is the pivotal step during the infection. Different viruses may utilize different surface receptor for binding. The HCOV- NL63, SARS-COV, and the new SARS-COV-2 viruses all use the ACE2 receptor, while the MERS-COV virus selectively binds with the DPP4 receptor. The HCOV-229E virus targets APN receptor. The rest two common coronavirus, HKU1 and OC43 bind with O-ac Sia.
Spike Protein
The spike protein is a large type I transmembrane protein containing two subunits, S1 and S2. S1 mainly contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which is responsible for recognizing the cell surface receptor. S2 contains basic elements needed for the membrane fusion. The S protein plays a key role in the induction of neutralizing-antibody and T-cell responses, as well as protective immunity.
The spike (S) glycoprotein of coronaviruses contains protrusions that will only bind to certain receptors on the host cell
Nucleocapsid Protein
The N protein constitutes the only protein present in the nucleocapsid. It is composed of two separate domains, an N-terminal and a C-terminal domains both capable of binding viral RNA in vitro
N protein is also heavily phosphorylated and binds to the viral genome
N protein also binds nsp3, a key component of replicase-transcriptase complex , and the M protein and subsequently packages the encapsidated genome into viral particles.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a membrane receptor expressed on the surface of airway epithelial cells.
The interaction between the viral spike protein and the ACE2 receptor is mediated by the RBD domain of the spike protein, and is believed to be the pivotal event in the membrane fusion process.
It’s been shown that SARS-COV-2 also uses ACE2 as the receptor for host cell entry. This finding suggests that blocking the interaction between the S protein and ACE2 is a valid approach to prevent or treat coronavirus infection.
Expression Systems – SARS-CoV-2
Mammalian cells CHO, HEK293
- Protein folding
- Post-translational modification
- Flexible and rapid production of proteins.
- Lower production yield than bacterial systems
- Higher cost than bacterial systems
- Complex culture media
Insect cells expression systems
- Robust
- Simple culture media
- High expression levels
- Able to perform a variety of post-translational modifications similar to mammalian cells
Bacterial Systems
- High protein expression yield
- Most economical
- No disulfite bonds
- Additional modifications are required post production
Tags
IgG-Fc-tag (mFc = mouse IgG – rFc = rabbit IgG)
- allows for rapid and simple detection of protein expression by ELISA
- allows for simple affinity purification of the Fc-tagged protein by protein A, protein G, and protein L affinity purification resins.
- increases protein expression yield.
His Tag
- 6xHis-tag is one of the simplest and most widely used purification tags
- The his-tag has a high affinity for metal ions Ni2+or Co2+immobilized on beads or a resin for such as IMAC columns
| N | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Nucleocapsid-His Protein | 40588-V08B | Expressed in Insect cell |
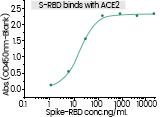
| S1 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S1-His Protein | 40591-V08B | Expressed in HEK293 cell, bind with ACE2 |
| S1 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S1-His Protein | 40591-V08B1 | Expressed in Insect cell, bind with ACE2 |
| RBD | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD-mFc Protein | 40592-V05H | Expressed in HEK293 cell, bind with ACE2 |
| RBD | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD-Fc Protein | 40592-V02H | Expressed in HEK293 cell, bind with ACE2 |
| RBD | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD-rFc Protein | 40592-V31H | Expressed in HEK293 cell, bind with ACE2 |
| RBD | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD-His Protein, Biotinylated | 40592-V08B-B | Expressed in Insect cell |
| S2 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S2-mFc Protein | 40592-V05H | Expressed in HEK293 cell |
| S1+S2 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S1+S2 ECD-His Protein | 40589-V08B1 | Expressed in Insect cell, bind with ACE2 |
| S1 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S1-mFc Protein | 40591-V05H1 | Expressed in HEK293 cell, bind with ACE2 |
| S1 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S1-Fc Protein | 40591-V02H | Expressed in HEK293 cell, bind with ACE2 |
| RBD | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD-His Protein | 40592-V08B | Expressed in Insect cell, bind with ACE2 |
| RBD | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD-His Protein | 40592-V08H | Expressed in HEK293 cell, bind with ACE2 |
| RBD | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD-His Protein,Biotinylated | 40592-V08H-B | Expressed in HEK293 cell |
| S2 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S2 ECD-His Protein | 40590-V08B | Expressed in Insect cell |
| Plpro | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Plpro-His protein | 40593-V07E | Expressed in E.coli cell |
An unprecedented mink cull has been ordered in Denmark amid the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 in these farmed animals. The plan was announced after scientists discovered a widespread Y453F mutation in the spike protein, that has been passed from animal to humans.
This mutation is of particular concern, because it occurs at a conservative domain of the receptor binding domain (RBD) directly involved in ACE2 binding. Results from some preliminary studies suggest the Y453F mutation affects the ability of the Spike protein to bind with ACE2, while others demonstrate that the mutated spike can escape from detection from a commercial anti-S antibody.
Although there is still no clear evidence indicating this mutation, or any other mutation like the popular D614G, has any clinical significance, the characteristics of the mutations need to be thoroughly investigated in the context of vaccine and antibody therapy.
Sino Biological has launched the recombinant Y453F RBD protein. This product is the newest addition to a large library of recombinant spike variants (full list here). These proteins can be used to evaluate the efficacy of the antibodies and vaccination.
SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
| Cat# | Antigen | Description | Type |
| 40588-T62 | Nucleocapsid | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Nucleocapsid Antibody | Rabbit PAb |
| 40143-R001 | Nucleocapsid | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibody | Rabbit MAb |
| 40143-MM05 | Nucleocapsid | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibody | Mouse MAb |
| 40143-R019 | Nucleocapsid | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Nucleocapsid Antibody | Rabbit MAb |
| 40143-MM08 | Nucleocapsid | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibody | Mouse MAb |
| 40143-R040 | Nucleocapsid | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibody | Rabbit MAb |
| 40143-R004 | Nucleocapsid | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibody | Rabbit MAb |
| 40150-R007 | Spike | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S1 Antibody | Rabbit MAb |
| 40150-D006 | Spike | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody | Chimeric MAb |
| 40150-D004 | Spike | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Spike antibody | Chimeric MAb |
| 40150-D003 | Spike | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Spike antibody | Chimeric MAb |
| 40150-D005 | Spike | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Spike antibody | Chimeric MAb |
| 40150-D002 | Spike | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Spike antibody | Chimeric MAb |
| 40150-D001 | Spike | SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2 Spike antibody | Chimeric MAb |
| 40590-D001 | Spike S2 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S2 Antibody, Chimeric Mab | Chimeric Mab |
| 40592-T62 | Spike | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike RBD Antibody | Rabbit PAb |
| 40590-T62 | Spike | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Spike S2 Antibody | Rabbit PAb |
Validated Applications
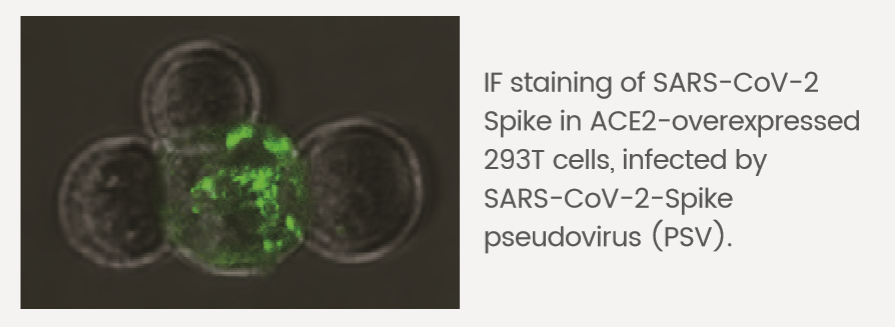
IF (40150-R007) – Pseudovirus Validated
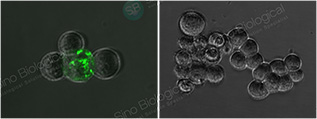
SARS-CoV-2 Spike in ACE2-overexpressed 293T cells, infected (left) or noninfected (right) by 2019-nCOV pseudovirus
IHC (40143-R019)
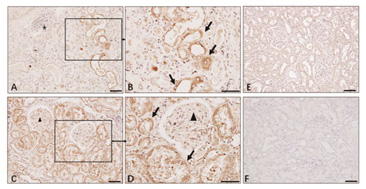
Renal tissue from COVID-19 Patient. N antigens in kidney tubules is validated by IHC
|
Catalogue
|
Species
|
Antigen
|
Type
|
Description
|
|
SARS-CoV-2
|
S RBD
|
Rabbit PAb
|
WB, ELISA, IHC-PF CM, ICC/IF, IP
|
|
|
SARS-CoV-2
|
Nucleocapsid
|
Rabbit PAb
|
WB, ELISA, IHC-PF CM, ICC/IF, IP
|
|
|
SARS-CoV-2
|
S2 subunit
|
Rabbit PAb
|
WB, ELISA, IHC-PF CM, ICC/IF, IP
|
|
|
SARS-CoV
|
Nucleocapsid
|
Rabbit PAb
|
Has cross-reactivity in ELISA with SARS-CoV-2 N Protein (Cat# 40588-V08B).
|
|
|
SARS-CoV
|
Spike
|
Rabbit PAb
|
Has cross-reactivity in ELISA and WB with SARS-CoV-2 S1 (Cat# 40591-V08H) and S-RBD (Cat# 40592-V05H)
|
Sars-CoV-2 Neutralising antibodies
| Cat # | 40591-MM43 | 40592-MM57 | 40592-R001 |
| Description | Anti-Spike S1 | Anti-Spike RBD | Anti-Spike RBD |
| Type | Mouse MAb | Mouse MAb | Rabbit MAb |
| Ig Type | Mouse IgG1 | Mouse IgG2b | Rabbit IgG |
| Application | Neutralization, ELISA | Neutralization, ELISA | Neutralization, ELISA |
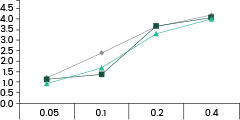
Neutralization Activity Assay
Neutralizing antibodies can effectively inhibit the infection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike pseudovirus on ACE2 overexpression 293T cells.
S1 Neutralizing Antibody
| Conc. (µg/mL) | Inhibition% |
| 100 | 96.39% |
| 10 | 94.57% |
| 1 | 42.24% |
| 0.1 | -5.53% |
RBD Neutralizing Antibody
| Conc. (µg/mL) | Inhibition% |
| 100 | 95.51% |
| 10 | 93.32% |
| 1 | 75.69% |
| 0.1 | 10.11% |
RBD Neutralizing Antibody Rabbit MAb
| Conc. (µg/mL) | Inhibition% |
| 100 | 99.56% |
| 4 | 99.9% |
| 0.16 | 59.29% |
| 0.032 | 5.59% |
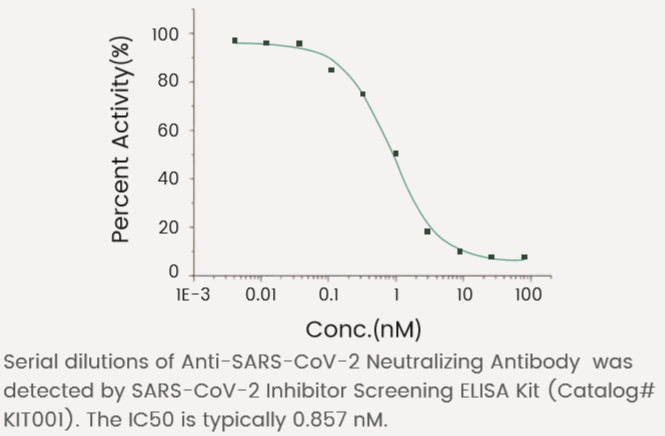
Competitive-ELISA Assay
Neutralizing ability was detected by SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitor Screening ELISA Kit (Catalog# KIT001) using competitive ELISA.
S1 Neutralizing Antibody
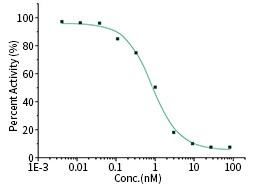
The IC50 is typically 0.857 nM
RBD Neutralizing Antibody
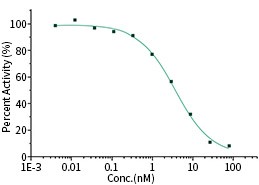
The IC50 is typically 3.694 nM
RBD Neutralizing Antibody Rabbit MAb
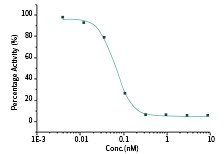
The IC50 is typically 0.066 nM
Specificity Assay
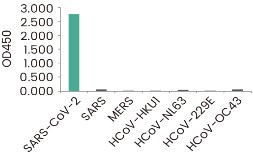
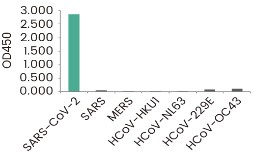
SARS-CoV-2 shares 80% sequence identity to the 2003 SARS-CoV. Hence, antibodies raised against SARS-CoV-2 antigens often shows various degree of cross-reactivity with the corresponding antigens of 2003 SARS-CoV. On the other hand, the similarities between SARS-CoV-2 and other members of human coronavirus are very limited. The following two clones of anti-spike antibodies have been tested against all seven coronavirus, and are shown to be specific to SARS-CoV-2 spike.
The reactivity of the antibodies against the known coronavirus is assessed in ELISA. The reactivity (OD450) is illustrated in the figure below.
S1 Neutralizing Antibody
RBD Neutralizing Antibody
Inihibitor Screening ELISA kits
| Cat # | Product Name | |
| KIT001 | SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) Inhibitor Screening ELISA Kit | Competitive ELISA |
Antibody Titer Assay Kits
The S and N detection kits employ a standard sandwich ELISA, allowing rapid quantification of the N and S antigens.
- All antibodies used in the kits are in-house developed monoclonal antibodies, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency.
- These assays may be used to quantify antigens on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 and/or pseudovirus, as well as antigens expressed recombinantly.
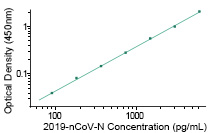
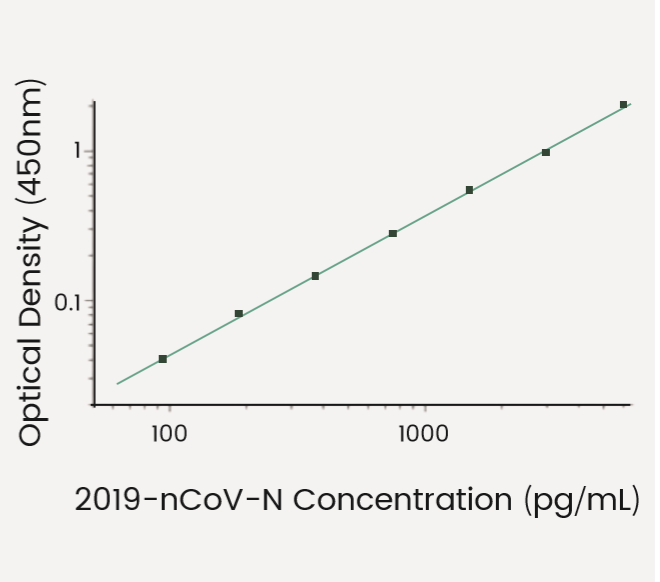
2019-nCoV N Detection Kit
(KIT40588)
Sino Biological and Nanommune (Irvine, California) jointly developed the coronavirus antigen array. These arrays are constructed by printing recombinant antigens on a nitrocellulose-coated membrane. It can analyze serum antibodies against 65 antigens from 23 types of viruses known to cause respiratory tract infections, including SARS-COV-2 and the other six coronaviruses. The array is specifically designed for high throughput serological surveillance studies.
|
Catalogue |
Description | Species | Tag | Vector |
| VG40588-UT | CoV Nucleocapsid 2019-nCoV | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40589-UT | CoV spike 2019-nCoV | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40592-UT | CoV spike 2019-nCoV | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40590-UT | CoV spike 2019-nCoV | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40591-UT | CoV spike 2019-nCoV | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40596-UT | CoV Hemagglutinin esterase | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40598-UT | CoV Membrane | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40599-UT | CoV NSP10 | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40594-UT | CoV 3CLpro / 3C-like protease | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40597-UT | CoV Envelope | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
| VG40593-UT | CoV NSP3 | 2019-nCoV | No Tag | Expression |
cDNA ORF clones expression plasmids
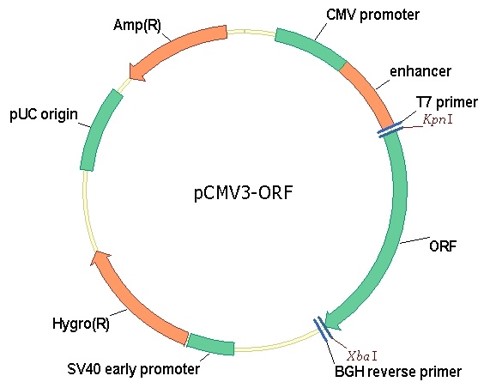
- Sino Biological provides ready-to-use expression ORF clones without subcloning. The expression ORF clones can be use for transfecting immediately.
- Codon Optimized clones for high expression, no tag
- Datasheet contains complete information on on plasmid, gene and quality control
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO SELECTING THE PROPER ANTIBODIES FOR YOUR COVID-19 STUDY
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemics has sickened 3.6 million people around the world, claiming over 250,000 lives. To address this global public health crisis, unprecedented efforts are being made to study the culprit virus, SARS-CoV-2. The biomedical community are working to develop rapid diagnostic reagents, vaccines, and therapies against this virus.
To support these studies, Sino Biological has developed a large collection of antibodies against different antigens of SARS-CoV-2. These antibodies can be used to detect and/or neutralize the virus in a variety of assays including ELISA, western blot, Immunofluorescent staining, Immunohistochemistry, SPR (Biacore and Octet), pseudovirus infection, and potentially in vivo animal studies.
This guide covers all available SARS-CoV-2 antibodies offered by Sino Biological. The readers can find technical information about their specificity and sensitivity, cross-reactivity, neutralizing potential, and their validated applications. The overarching goal for this guide is to help the readers to choose appropriate antibodies for their own experiments.
Same as all other coronaviruses, the genome of SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) encodes the spike protein, the envelope protein, the non-structure proteins including the proteases and methyltransferases, the membrane protein, and the nucleocapsid protein.

The spike protein (S-protein) is the common target for neutralizing antibodies and vaccines. Spike protein contains two subunits, S1 and S2. S1 contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which is responsible for recognizing and binding with the cell surface receptor ACE2. S2 subunit contains other basic elements needed for the membrane fusion.
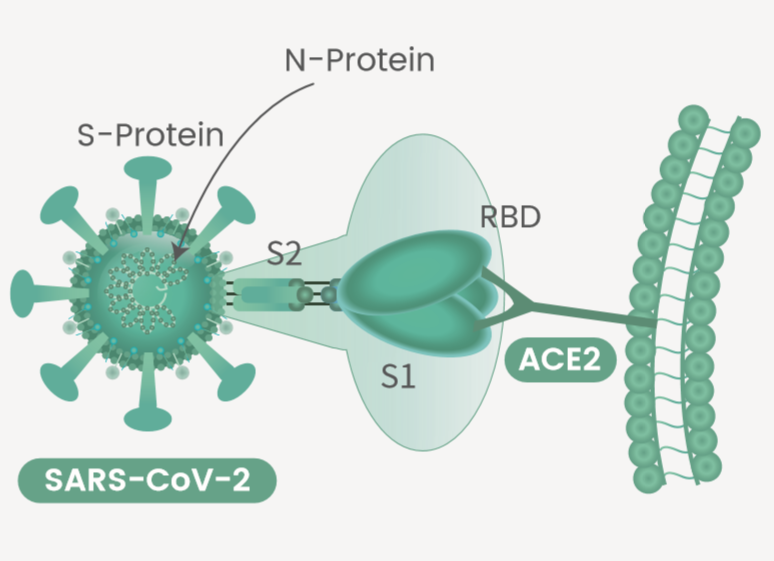

The Nucleocapsid Protein (N-protein) is a highly immunogenic phosphoprotein, and it is normally very conserved. The SARS-CoV-2 N protein is often used as a marker in diagnostic assays.

The papain-like protease (PlPro) is a protease. It mediates the post-translational processing of other non-structural proteins like replicase polyprotein. PlPro, and 3CLPro. PlPro is a target for antiviral drug development.

The methyltransferase is a non-structural protein. Methyltransferase mediates the methylation of the viral RNA, which may help the virus evade the host immune system. Methyltransferase inhibitor may work as an anti-viral treatment.

Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) binds with the Spike protein of coronaviruses SARS-CoV and HCoV-NL63. This interaction is mediated by the RBD domain of the spike protein, and is believed to be the pivotal event in the membrane fusion process.
ELSIA Antibody Pairs
Pairs Ⅰ
| Cat # | 40143-R004 (Capture) |
| Description | Anti-Nucleocapsid |
| Type | Rabbit MAb |
| Ig Type | Rabbit IgG |
| Cat # | 40143-R040 (Detection) |
| Description | Anti-Nucleocapsid |
| Type | Rabbit MAb |
| Ig Type | Rabbit IgG |
Pairs ⅠⅠ
| Cat # | 40143-MM05 (Capture) |
| Description | Anti-Nucleocapsid |
| Type | Mouse MAb |
| Ig Type | Mouse IgG |
| Cat # | 40143-R001 (Detection) |
| Description | Anti-Nucleocapsid |
| Type | Rabbit MAb |
| Ig Type | Rabbit IgG |
Western Blot Antibodies
| Cat # | 40143-R019 |
| Description | Anti-Nucleocapsid |
| Type | Rabbit MAb |
| Ig Type | Rabbit IgG |
FULL LIST OF ANTI-NUCLEOCAPSID ANTIBODIES
| Cat # | Description | Type | Ig Type |
| 40143-R001 | Anti-Nucleocapsid | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| 40143-R040 | Anti-Nucleocapsid | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| 40143-R004 | Anti-Nucleocapsid | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| 40588-R0004 | Anti-Nucleocapsid | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| 40143-R019 | Anti-Nucleocapsid | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| 40143-MM05 | Anti-Nucleocapsid | Mouse MAb | Mouse IgG1 |
| 40143-MM08 | Anti-Nucleocapsid | Mouse MAb | Mouse IgG1 |
| 40588-T62 | Anti-Nucleocapsid | Rabbit PAb | Rabbit IgG |
ELSIA Antibody Pairs
Pairs Ⅰ
| Cat # | 40150-D001 (Capture) |
| Description | Anti-Spike RBD |
| Type | Chimeric MAb |
| Ig Type | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| Cat # | 40150-D003 (Detection) |
| Description | Anti-Spike RBD |
| Type | Chimeric MAb |
| Ig Type | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
Pairs ⅠⅠ
| Cat # | 40150-D004 (Detection) |
| Description | Anti-Spike RBD |
| Type | Chimeric MAb |
| Ig Type | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| Cat # | 40150-D002 (Capture) |
| Description | Anti-Spike RBD |
| Type | Chimeric MAb |
| Ig Type | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
Neutralization Antibodies
| Cat # | 40591-MM43 |
| Description | Anti-Spike S1 |
| Type | Mouse MAb |
| Ig Type | Mouse IgG1 |
| Cat # | 40591-MM57 |
| Description | Anti-Spike RBD |
| Type | Chimeric MAb |
| Ig Type | Mouse IgG2b |
IF Antibodies
| Cat # | 40150-R007 |
| Description | Anti-Spike S1 |
| Type | Rabbit MAb |
| Ig Type | Rabbit IgG |
High Affinity Antibodies
| Cat # | 40150-D005 |
| Description | Anti-Spike RBD |
| Type | Chimeric MAb |
| Ig Type | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
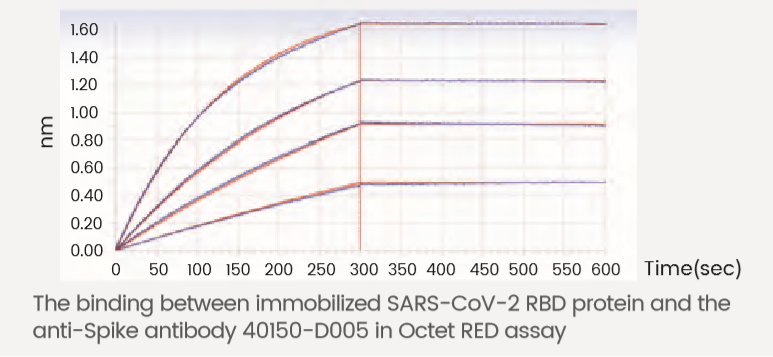
Antibodies against the S2 Protein
| Cat # | 40590-D001 |
| Description | Anti-Spike S2 |
| Type | Chimeric MAb |
| Ig Type | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
This is a chimeric antibody specifically recognizing the S2 domain of SARS-CoV-2. The specificity assay is assessed in ELISA which shows no cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV-2 S1, RBD or MERS-CoV S2.
FULL LIST OF ANTI-SPIKE ANTIBODIES
| Cat # | Description | Type | Ig Type |
| 40591-MM43 | Anti-Spike S1 | Mouse Mab,Neutralizing Antibody | Mouse IgG1 |
| 40150-R007 | Anti-Spike S1 | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| 40150-D001 | Anti-Spike S1 | Chimeric MAb | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| 40150-D002 | Anti-Spike S1 | Chimeric MAb | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| 40150-D003 | Anti-Spike S1 | Chimeric MAb | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| 40150-D004 | Anti-Spike S1 | Chimeric MAb | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| 40150-D005 | Anti-Spike S1 | Chimeric MAb | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| 40150-D006 | Anti-Spike S1 | Chimeric MAb | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| 40592-MM57 | Anti-Spike RBD | Mouse Mab,Neutralizing Antibody | Mouse IgG2b |
| 40592-T62 | Anti-Spike RBD | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| 40590-D001 | Anti-Spike S2 | Chimeric MAb | mouse v domain / human IgG1 |
| 40590-T62 | Anti-Spike S2 | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| 40589-T62 | Anti-Spike | Rabbit MAb | Rabbit IgG |
| Cat # | 40592-MM57 |
| Description | Spike RBD Antibody |
| Type | Mouse MAb |
| Ig Type | Monoclonal Mouse IgG2b |
| Application | ELISA, Neutralization |
| Cat # | 40591-MM43 |
| Description | Spike S1 Antibody |
| Type | Mouse MAb |
| Ig Type | Monoclonal Mouse IgG1 |
| Application | ELISA, Neutralization |
The reactivity of the antibodies against the known coronavirus is assessed in ELISA. The reactivity (OD450) is illustrated in the figure below.
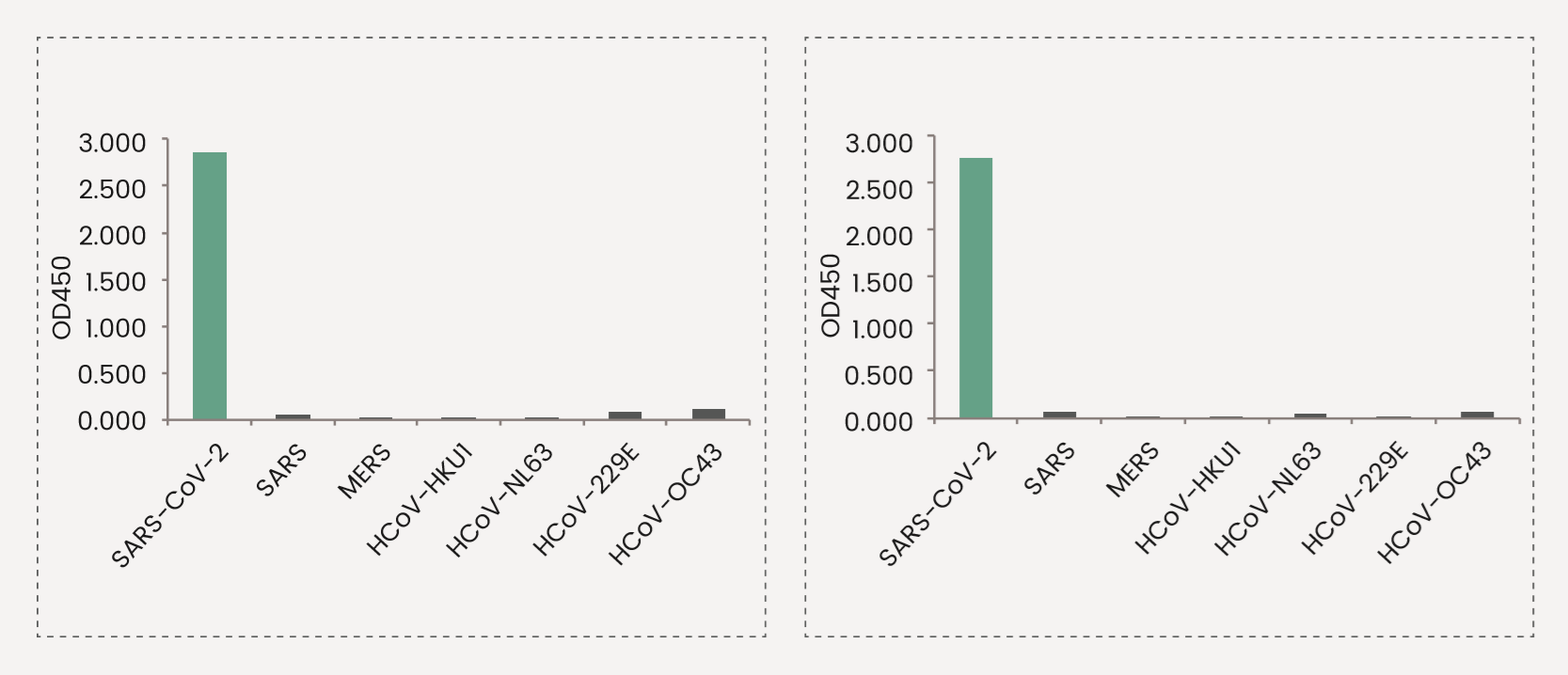
SARS-CoV-2 shares 80% sequence identity to the 2003 SARS-CoV. Hence, antibodies raised against SARS-CoV-2 antigens often shows various degree of cross-reactivity with the corresponding antigens of 2003 SARS-CoV. On the other hand, the similarities between SARS-CoV-2 and other members of human coronavirus are very limited. The following two clones of anti-spike antibodies have been tested against all seven coronavirus, and are shown to be specific to SARS-CoV-2 spike.
Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Variants
- Omicron (B.1.1.529)
- Mu (B.1.621)
- Lambda (C.37)
- Delta/Delta plus (AY.1, AY.2, AY.3)
- Delta (B.1.617.2)
- Alpha/Beta (B.1.1.7/ B.1.351/ A.2.2)
- Alpha/Beta/Gamma (B.1.1.7/ B.1.351/ P.1)
- Alpha (B.1.1.7)
- Beta (B.1.351)
- Gamma (P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2)
- Epsilon (B.1.427/429)
- Eta (B.1.525)
- Iota (B.1.526)
- Kappa (B.1.617.1)
- B.1.617
- B.1.617.3
- B.1.618
- B.1.620
- B.1.2
- A.23.1
- P.2
- P.3
- Mink Variant
- More
Omicron (B.1.1.529)
Mutations in the Spike Glycoprotein of Omicron
The Omicron variant is by far the most divergent variant characterized by a high number of mutations in the spike protein. Several mutations (e.g., N501Y, P681H) have been identified in previous variants and are associated with increased transmissibility, immune escape, or other properties.
- 30 amino acid changes: among which 15 are located in the RBD region
- Three deletions
- Three insertions in the spike protein NTD
| Cat# | Antigen | Tag | Expressed Host | Mutants |
| 40589-V08H26 | S-ECD | C-His | HEK293 | A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40589-V08B33 | S-ECD | C-His | Insect | A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40589-V49H3-B | S-ECD | C-His-AVI | HEK293 | A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, N856K, Q954H, N969K, L981F |
| 40592-V08H121 | RBD | C-His | HEK293 | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| 40592-V49H7 | RBD | HEK293 | C-His-AVI | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| 40592-V49H7-B | RBD | C-His-AVI | HEK293 | G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H |
| 40591-V08H41 | S1 | C-His | HEK293 | A67V, Δ69-70, T95I, G142D/Δ143-145, Δ211/L212I, ins214EPE, G339D, S371L, S373P, S375F, K417N, N440K, G446S, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, G496S, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, T547K, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H |
| 40588-V07E34 | N | N-His | E.coli | P13L, E31del, R32del, S33del, R203K, G204R |
Mu (B.1.621)
Variants in S Protein
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Mu | B.1.621 | 40588-V07E9 | N | T205I |
| Mu | B.1.621 | 40589-V08H20 (pre-order) | S1+S2 ECD | T95I, Y144S, Y145N, R346K, E484K, N501Y, D614G, P681H with prefusion trimer mutations construction |
| Mu | B.1.621 | 40591-V08H38 (pre-order) | S1 | T95I, Y144S, Y145N, R346K, E484K, N501Y, D614G, P681H |
| Mu | B.1.621 | 40592-V08H118 | RBD | R346K, E484K, N501Y |
| Mu | B.1.621 | 40592-V02H6 (pre-order) | RBD | R346K, E484K, N501Y |
Lambda (C.37)
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Lambda | C.37 | 40588-V07E31 | N | P13L, R203K, G204R, G214C |
| Lambda | C.37 | 40592-V08H113 | RBD | L452Q, F490S |
| Lambda | C.37 | 40589-V08B23 (pre-order) | S1+S2 ECD | G75V, T76I, R246N, Δ247, Δ253, L452Q, F490S, D614G, T859N |
| Lambda | C.37 | 40589-V08B24 (pre-order) | S1+S2 ECD | G75V, T76I, R246del, S247del, Y248del, L249del, T250del, P251del, G252del, D253N, L452Q, F490S, D614G, T859N |
| Lambda | C.37 | 40591-V08H31 | S1 | G75V, T76I, R246N, Δ247, Δ253, L452Q, F490S, D614G |
| Lambda | C.37 | 40591-V08H32 | S1 | G75V, T76I, (RSYLTPG246-252)deletion, D253N, L452Q, F490S, D614G |
| Lambda | C.37 | 40592-V49H6-B | RBD | L452Q, F490S |
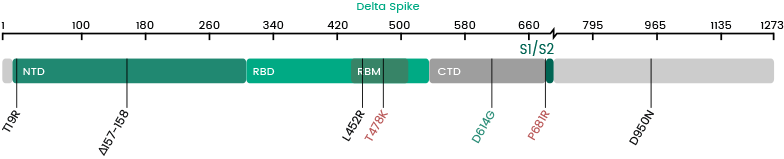
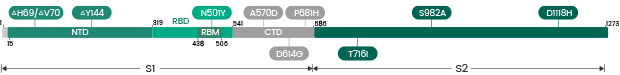
Delta/Delta plus (AY.1, AY.2, AY.3)
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Delta/Delta plus | AY.1/AY.3 | 40588-V07E32 | N | D63G, R203M, G215C, D377Y |
| Delta/Delta plus | AY.1/AY.2 | 40592-V08H115 | RBD | K417N, L452R, T478K |
| Delta/Delta plus | AY.1/AY.2 | 40592-V49H5-B | RBD | K417N, L452R, T478K |
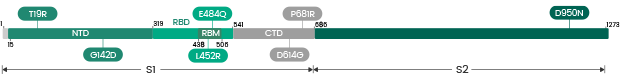
| Delta/Delta plus | AY.1 | 40589-V08B25 (pre-order) | S1+S2 ECD | T19R, G142D, W258L, K417N, L452R, T478KD614G, D950N, P681R |
| Delta/Delta plus | AY.2 | 40589-V08B26 (pre-order) | S1+S2 ECD | T19R, V70F, E156G, del157/158, A222V, K417N, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N |
| Delta/Delta plus | AY.3 | 40589-V08B27 (pre-order) | S1+S2 ECD | T19R, E156G, del157/158, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N |
Delta (B.1.617.2)
Variants in S Protein
Variants in N Protein
Recombinant Delta (B.1.617.2) Variants
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40588-V07E29 | N | D63G, R203M, D377Y |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40589-V49B4-B | S1+S2 ECD | 157-158deletion, T19R, G142D, E156G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40589-V08B16 | S1+S2 ECD | T19R, G142D, E156G, del157/158, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40591-V08H23 | S1 | T19R, G142D, E156G, del157/158, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40591-V49H2-B | S1 | (157-158)deletion, T19R, G142D, E156G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40592-V02H3 | RBD | L452R, T478K |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40592-V08H90 | RBD | L452R, T478K |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40592-V08H91 | RBD | T478K |
| Delta | B.1.617.2 | 40592-V49H1-B | RBD | L452R, T478K |
Alpha/Beta (B.1.1.7/ B.1.351/ A.2.2)
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Alpha/Beta | B.1.1.7/ B.1.351/ A.2.2 | 40588-V07E2 | N | P13L |
Alpha/Beta/Gamma (B.1.1.7/ B.1.351/ P.1)
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Alpha/Beta/Gamma | B.1.1.7/ B.1.351/ P.1 | 40592-V31H1 | RBD | N501Y |
Alpha (B.1.1.7)
Variants in S Protein
Variants in N Protein
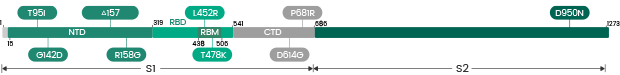
Recombinant Alpha (B.1.1.7) Variants
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40588-V07E1 | N | R203K, G204R |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40588-V07E17 | N | E378Q |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40588-V07E4 | N | I292T |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40588-V07E7 | N | D3L, R203K, G204R, S235F |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40588-V07E8 | N | D3L, S235F |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7/ B.1.237 | 40588-V07E3 | N | S194L |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40589-V08B6 | S1+S2 ECD | H69del, V70del, Y144del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40589-V49B-B | S1+S2 ECD | H69del, V70del, Y145del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40591-V08H12 | S1 | H69del, V70del, Y144del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40591-V08H12-B | S1-Biotinylated | H69del, V70del, Y144del, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40591-V08H7 | S1 | HV69-70deletion, N501Y, D614G |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40591-V49H4-B | S1 | (HV69-70, Y145)deletion, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40592-V02H1 | RBD | N501Y |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40592-V08H18 | RBD | S494P |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40592-V08H82 | RBD | N501Y |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40592-V08H82-B | RBD | N501Y |
| Alpha | B.1.1.7 | 40592-V49H2-B | RBD | N501Y |
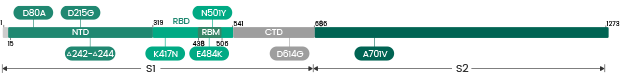
Beta (B.1.351)
Variants in S Protein
Variants in N Protein
Recombinant Beta (B.1.351) Variants
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/ B.1.351.3/B.1.427/B.1.429 | 40588-V07E9 | N | T205I |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40589-V08B11 | S1+S2 ECD | D80A, L242del, A243del, L244del, R246I, E484K, K417N, N501Y, D614G, A701V |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40589-V08B7 | S1+S2 ECD | L18F, D80A, D215G, LAL242-244deletion, R246I, K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G, A701V |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40589-V08B9 | S1+S2 ECD | D80A, K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G, A701V |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40589-V49B1-B | S1+S2 ECD | |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40589-V08B7-B | S1+S2-Biotinylated | L18F, D80A, D215G, LAL242-244deletion, R246I, K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G, A701V |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40591-V08H13 | S1 NTD | L18F, D80A, D215G, LAL242-244deletion, R246I |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40591-V08H10-B | S1 | K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40591-V08H10 | S1 | K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40591-V08H15 | S1 | L18F, D80A, D215G, LAL242-244deletion, R246I, K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40591-V49H5-B | S1 | (LAL242-244)deletion, L18F, D80A, D215G, R246I, K417N, E484K, N501Y, D614G |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40592-V08H59 | RBD | K417N |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40592-V08H59-B | RBD | K417N |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40592-V08H84 | RBD | E484K |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40592-V08H84-B | RBD | E484K |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40592-V08H85-B | RBD | K417N, E484K, N501Y |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40592-V31H2 | RBD | E484K |
| Beta | B.1.351 | 40592-V31H6 | RBD | K417N |
| Beta | B.1.351/ B.1.351.3 | 40592-V31H4 | RBD | K417N, E484K, N501Y |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40592-V02H4 | RBD | K417N, E484K, N501Y |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40592-V08H85 | RBD | K417N, E484K, N501Y |
| Beta | B.1.351/B.1.351.2/B.1.351.3 | 40592-V49H3-B | RBD | K417N, E484K, N501Y |
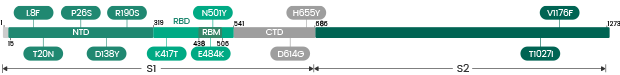
Gamma (P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2)
Variants in S Protein
Variants in N Protein
Recombinant Gamma (P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2) Variants
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40588-V07E11 | N | P80R |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40589-V08B10 | S1+S2 ECD | L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, D614G, H655Y, T1027I, V1176F |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40589-V08B8 | S1+S2 ECD | L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, D614G, H655Y, T1027I |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40591-V08H14 | S1 | L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, D614G, H655Y |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40591-V08H5 | S1 | T20N, D614G |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40591-V49H6-B | S1 | L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, R190S, K417T, E484K, N501Y, D614G, H655Y |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40592-V02H5 | RBD | K417T, E484K, N501Y |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40592-V08H86 | RBD | K417T, E484K, N501Y |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40592-V31H5 | RBD | K417T, E484K, N501Y |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40592-V31H7 | RBD | K417T |
| Gamma | P.1/ P.1.1/ P.1.2 | 40592-V49H4-B | RBD | E484K, K417T, N501Y |
Epsilon (B.1.427/429)
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Epsilon | B.1.427 | 40591-V08H27 | S1 | L452R, D614G |
| Epsilon | B.1.429/B.1.427 | 40591-V08H17 | S1 | W152C, L452R, D614G |
Eta (B.1.525)
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Eta | B.1.525 | 40588-V07E19 | N | A12G, T205I |
| Eta | B.1.525 | S1+S2 ECD | Q52R, A67V, 69/70del, 144del, E484K, D614G, Q677H, F888L | |
| Eta | B.1.525 | 40591-V08H29 | S1 | Q52R, A67V, 69/70del, 144del, E484K, D614G, Q677H |
| Eta | B.1.525 | 40591-V08H16 | S1 | Q677H |
Iota (B.1.526)
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Iota | B.1.526 | 40588-V07E18 | N | P199L, M234I |
| Iota | B.1.526 | 40592-V08H112 | RBD | S477N, E484K |
| Iota | B.1.526 | 40589-V08B21 | S1+S2 ECD | L5F, T95I, D253G, S477N, E484K, D614G, A701V |
| Iota | B.1.526 | 40591-V08H28 | S1 | L5F, T95I, D253G, S477N, E484K, D614G |
Kappa (B.1.617.1)
Variants in S Protein
Variants in N Protein
Recombinant Kappa (B.1.617.1) Variants
| Label | Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Kappa | B.1.617.1 | 40589-V49B3-B | S1+S2 ECD | T95I, G142D, E154K, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, Q1071H |
| Kappa | B.1.617.1 | 40589-V08B15 | S1+S2 ECD | T95I, G142D, E154K, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, Q1071H |
| Kappa | B.1.617.1 | 40591-V49H1-B | S1 | T95I, G142D, E154K, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R |
| Kappa | B.1.617.1 | 40591-V08H22 | S1 | T95I, G142D, E154K, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R |
| Kappa | B.1.617/B.1.617.1/B.1.617.3 | 40592-V02H2 | RBD | L452R, E484Q |
| Kappa | B.1.617/B.1.617.1/B.1.617.3 | 40592-V08H88 | RBD | L452R, E484Q |
| Kappa | B.1.617/B.1.617.1/B.1.617.3 | 40592-V08H88-B | RBD | L452R, E484Q |
| Kappa | B.1.617/B.1.617.1/B.1.617.3 | 40592-V49H-B | RBD | L452R, E484Q |
B.1.617
Variants in S Protein
Variants in N Protein
Recombinant B.1.617 Variants
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| B.1.617 | 40588-V07E16 | N | D377Y |
| B.1.617 | 40588-V07E20 | N | R203M, D377Y |
| B.1.617 | 40589-V08B12 | S1+S2 ECD | D614G, E154K, E484Q, E1072K, K1073R, L452R, P681R |
| B.1.617 | 40589-V08B13 | S1+S2 ECD | D614G, E154K, E484Q, G142D, H1101D, L452R, P681R, Q1071H |
| B.1.617 | 40589-V49B2-B | S1+S2 ECD | |
| B.1.617 | 40591-V08H19 | S1 | D614G, E154K, E484Q, L452R, P681R |
| B.1.617 | 40592-V08H28 | RBD | L452R |
| B.1.617 | 40592-V08H81 | RBD | E484Q |
B.1.617.3
Variants in S Protein
Variants in N Protein
Recombinant B.1.617.3 Variants
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| B.1.617.3 | 40588-V07E30 | N | P67S, R203M, D377Y |
| B.1.617.3 | 40589-V49B5-B | S1+S2 ECD | T19R, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, D950N, G142D |
| B.1.617.3 | 40589-V49B5-B | S1+S2 ECD | T19R, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, D950N, G142D |
| B.1.617.3 | 40589-V08B17 | S1+S2 ECD | T19R, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, D950N, G142D |
| B.1.617.3 | 40591-V08H24 | S1 | T19R, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R, G142D |
| B.1.617.3 | 40591-V49H3-B | S1 | T19R, G142D, L452R, E484Q, D614G, P681R |
B.1.618
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| B.1.618 | 40588-V07E28 | N | G18S, A119S, A217S, M234I, E367Q |
| B.1.618 | 40589-V08B14 | S1+S2 ECD | Y145del, H146del, E484K, D614G |
| B.1.618 | 40591-V08H21 | S1 | H49Y, Y145del, H146del, E484K, D614G |
B.1.620
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| B.1.620 | 40589-V08B18 (pre-order) | S1+S2 ECD | P26S, HV69-70del, V126A, Y144del, LLA241-243del, H245Y, S477N, E484K, D614G, P681H, T1027I, D1118H |
B.1.2
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| B.1.2 | 40588-V07E22 | N | P67S, P199L |
A.23.1
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| A.23.1 | 40588-V07E23 | N | S202N |
P.2
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| P.2 | 40588-V07E21 | N | A119S, R203K, G204R, M234I |
| P.2 | 40589-V08B19 | S1+S2 ECD | E484K, F565L, D614G, V1176F |
| P.2 | 40591-V08H26 | S1 | E484K, F565L, D614G, V1176F |
P.3
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| P.3 | 40592-V08H111 | RBD | E484K, N501Y |
Mink Variant
| Lineage | Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations |
| Mink Variant | 40591-V08H8 | S1 | ΔH69/ΔV70, Y453F, D614G |
| Mink Variant | 40592-V08H80 | RBD | Y453F |
| Mink Variant | 40592-V31H3 | RBD | Y453F |
More
| Catalogue | Antigen | Mutations | Tag |
| 40588-V07E12 | N | P199L | His |
| 40588-V07E13 | N | A220V | His |
| 40588-V07E14 | N | p67S | His |
| 40588-V07E15 | N | M234L | His |
| 40589-V08B4 | S1+S2 ECD | D614G | His |
| 40589-V08B5 | S1+S2 ECD | HV69-70deletion, D614G, D796H | His |
| 40591-V08H20 | S1 | N343Q | His |
| 40591-V02H3 | S1 | D614G | Fc |
| 40591-V08H11 | S1 | N234Q | His |
| 40591-V08H3 | S1 | D614G | His |
| 40591-V08H4 | S1 | A222V, D614G | His |
| 40591-V08H6 | S1 | L18F, D614G | His |
| 40591-V08H9 | S1 | HV69-70deletion, N439K, D614G | His |
| 40591-V08H25(pre-order) | S1 | P26S, HV69-70del, V126A, Y144del, LLA241-243del, H245Y, S477N, E484K, D614G, P681H | His |
| 40592-V08H100 | RBD | P479L | His |
| 40592-V08H101 | RBD | P479H | His |
| 40592-V08H102 | RBD | N481K | His |
| 40592-V08H103 | RBD | E484A | His |
| 40592-V08H104 | RBD | E484D | His |
| 40592-V08H105 | RBD | N487D | His |
| 40592-V08H106 | RBD | Y449H | His |
| 40592-V08H107 | RBD | G502V | His |
| 40592-V08H89 | RBD | F486A | His |
| 40592-V08H92 | RBD | N440D | His |
| 40592-V08H93 | RBD | F456Y | His |
| 40592-V08H94 | RBD | E471A | His |
| 40592-V08H95 | RBD | E471D | His |
| 40592-V08H96 | RBD | Y473F | His |
| 40592-V08H97 | RBD | A475T | His |
| 40592-V08H98 | RBD | G476A | His |
| 40592-V08H99 | RBD | S477G | His |
| 40592-V05H1 | RBD | V367F | mFc |
| 40592-V08H1 | RBD | V367F | His |
| 40592-V08H10 | RBD | R408I | His |
| 40592-V08H11 | RBD | V341I | His |
| 40592-V08H12 | RBD | Y508H | His |
| 40592-V08H14 | RBD | N439K | His |
| 40592-V08H15 | RBD | V503F | His |
| 40592-V08H16 | RBD | A522V | His |
| 40592-V08H19 | RBD | A372S | His |
| 40592-V08H2 | RBD | N354D | His |
| 40592-V08H20 | RBD | A520S | His |
| 40592-V08H21 | RBD | A522S | His |
| 40592-V08H22 | RBD | D405V, Q414A | His |
| 40592-V08H23 | RBD | Q414E | His |
| 40592-V08H24 | RBD | P384L | His |
| 40592-V08H25 | RBD | A348S | His |
| 40592-V08H26 | RBD | F338L | His |
| 40592-V08H27 | RBD | F377L | His |
| 40592-V08H29 | RBD | P521S | His |
| 40592-V08H2-B | RBD | N354D | His |
| 40592-V08H30 | RBD | T478I | His |
| 40592-V08H31 | RBD | V483I | His |
| 40592-V08H32 | RBD | S359N | His |
| 40592-V08H33 | RBD | K378R | His |
| 40592-V08H34 | RBD | Q409E | His |
| 40592-V08H35 | RBD | I472V | His |
| 40592-V08H36 | RBD | A372T | His |
| 40592-V08H37 | RBD | A344S | His |
| 40592-V08H39 | RBD | A520V | His |
| 40592-V08H4 | RBD | A435S | His |
| 40592-V08H40 | RBD | E406Q | His |
| 40592-V08H41 | RBD | F490S | His |
| 40592-V08H42 | RBD | K378N | His |
| 40592-V08H43 | RBD | N370S | His |
| 40592-V08H44 | RBD | Q414R | His |
| 40592-V08H45 | RBD | S477I | His |
| 40592-V08H46 | RBD | S477N | His |
| 40592-V08H47 | RBD | T385A | His |
| 40592-V08H48 | RBD | T393P | His |
| 40592-V08H49 | RBD | V395I | His |
| 40592-V08H5 | RBD | V483A | His |
| 40592-V08H50 | RBD | A475V | His |
| 40592-V08H51 | RBD | G446V | His |
| 40592-V08H52 | RBD | G485S | His |
| 40592-V08H53 | RBD | G482S | His |
| 40592-V08H54 | RBD | K444R | His |
| 40592-V08H55 | RBD | N440K | His |
| 40592-V08H56 | RBD | E471Q | His |
| 40592-V08H57 | RBD | P479S | His |
| 40592-V08H58 | RBD | A352S | His |
| 40592-V08H6 | RBD | F342L | His |
| 40592-V08H62 | RBD | P337S | His |
| 40592-V08H63 | RBD | P521R | His |
| 40592-V08H64 | RBD | S477R | His |
| 40592-V08H68 | RBD | L455F | His |
| 40592-V08H69 | RBD | K458Q | His |
| 40592-V08H7 | RBD | K458R | His |
| 40592-V08H70 | RBD | N481D | His |
| 40592-V08H71 | RBD | F456L | His |
| 40592-V08H72 | RBD | Y505C | His |
| 40592-V08H73 | RBD | F456E | His |
| 40592-V08H74 | RBD | F486S | His |
| 40592-V08H75 | RBD | N487R | His |
| 40592-V08H76 | RBD | G446S | His |
| 40592-V08H78 | RBD | P499R | His |
| 40592-V08H79 | RBD | V445F | His |
| 40592-V08H8 | RBD | G476S | His |
| 40592-V08H83 | RBD | F490L | His |
| 40592-V08H9 | RBD | W436R | His |